Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Relief
Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Relief
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Relief. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Relief

Topographic maps are essential tools for understanding the Earth’s surface. They are visual representations of the landscape, capturing not only the location of features like roads, rivers, and buildings but also the elevation of the terrain. This crucial element, known as topographic map relief, allows users to visualize the shape and form of the land, providing critical insights for various applications.
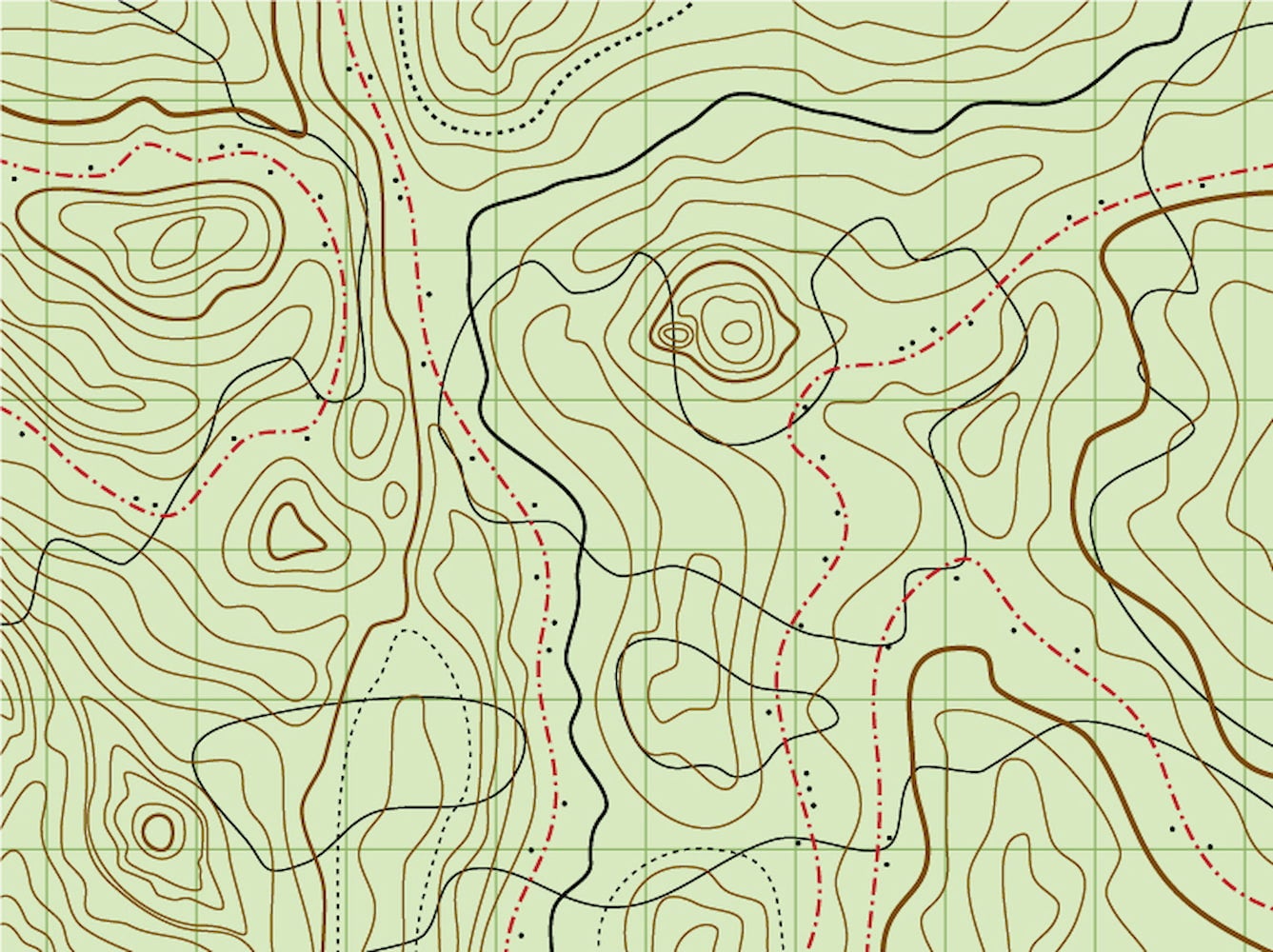
Understanding Topographic Map Relief
Topographic map relief is the representation of elevation changes on a map. It is depicted through a variety of methods, each offering a unique way to interpret the terrain:
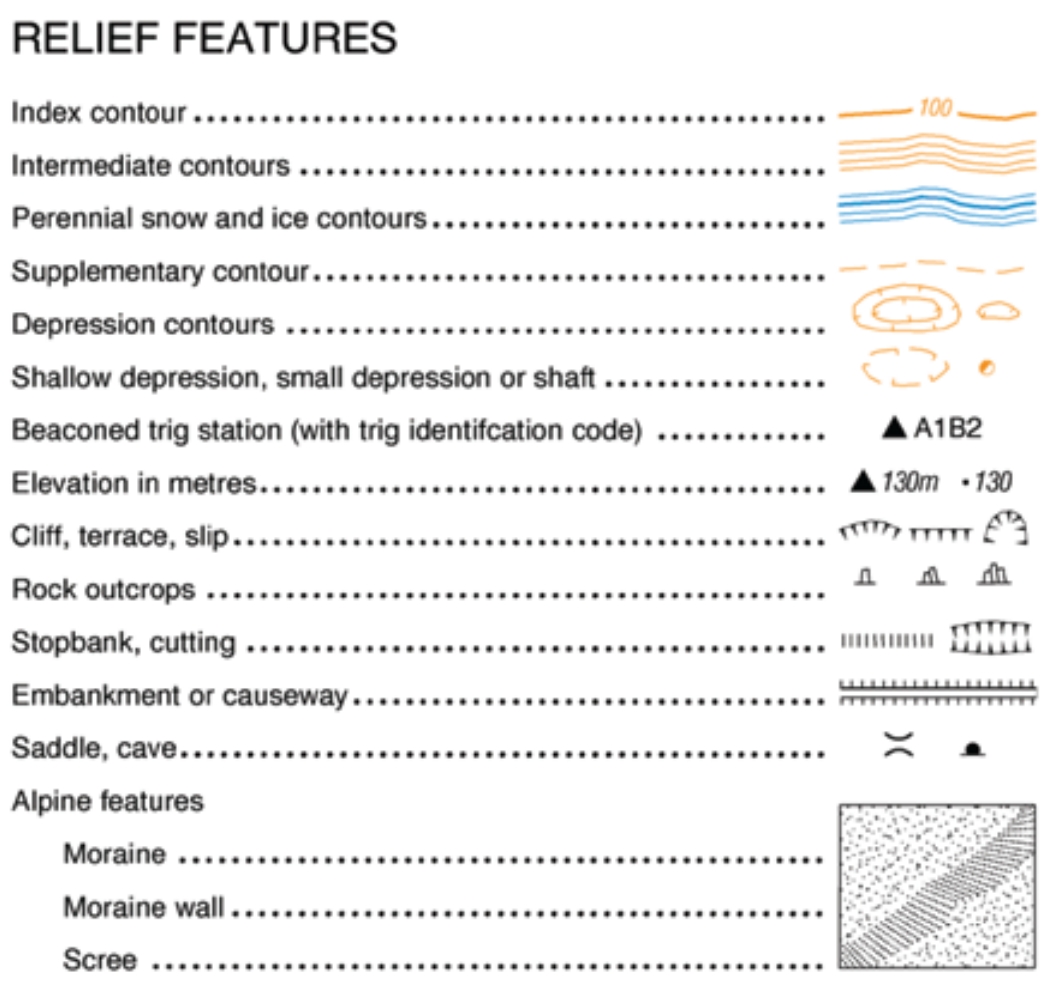
1. Contour Lines:
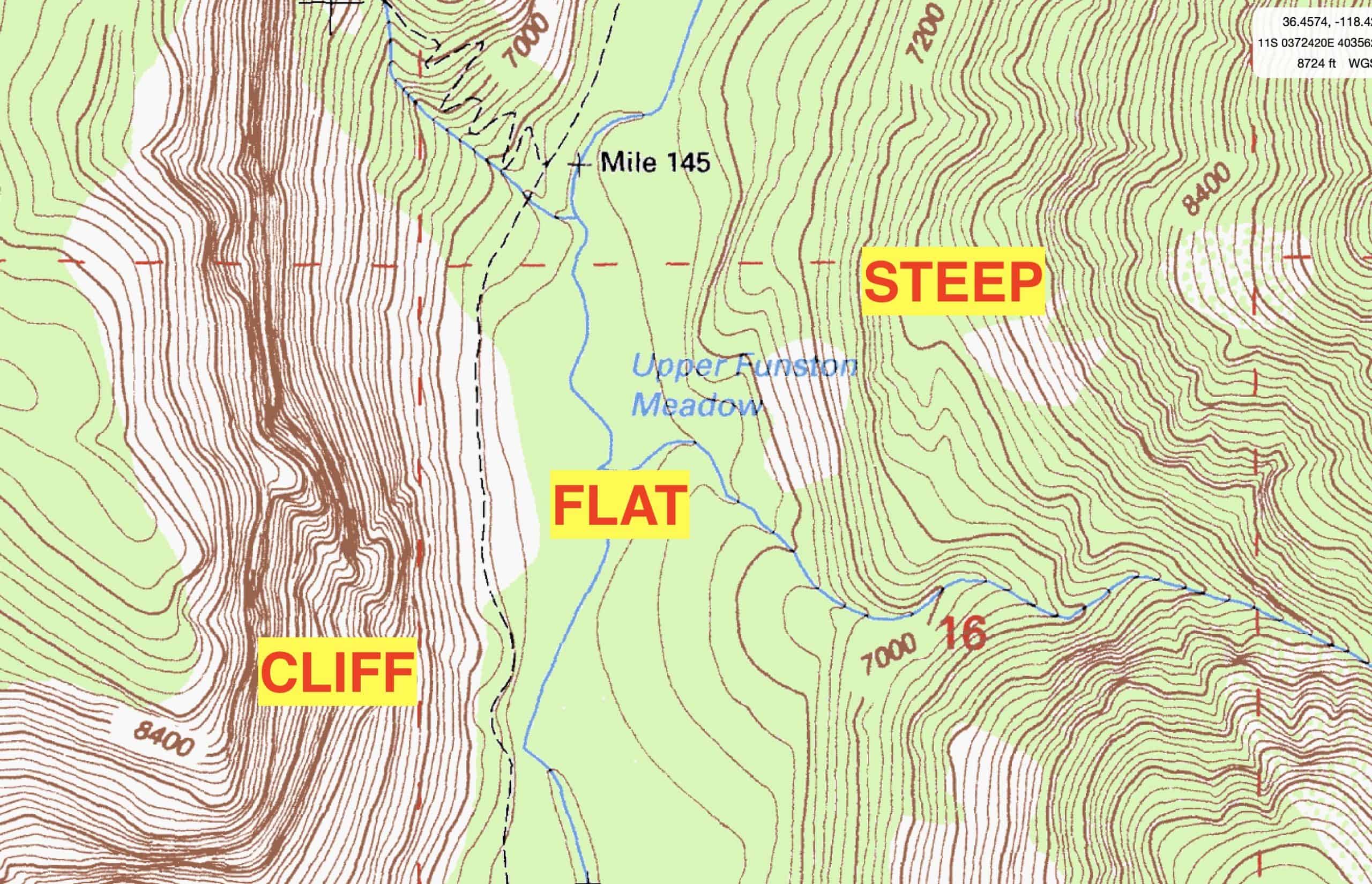
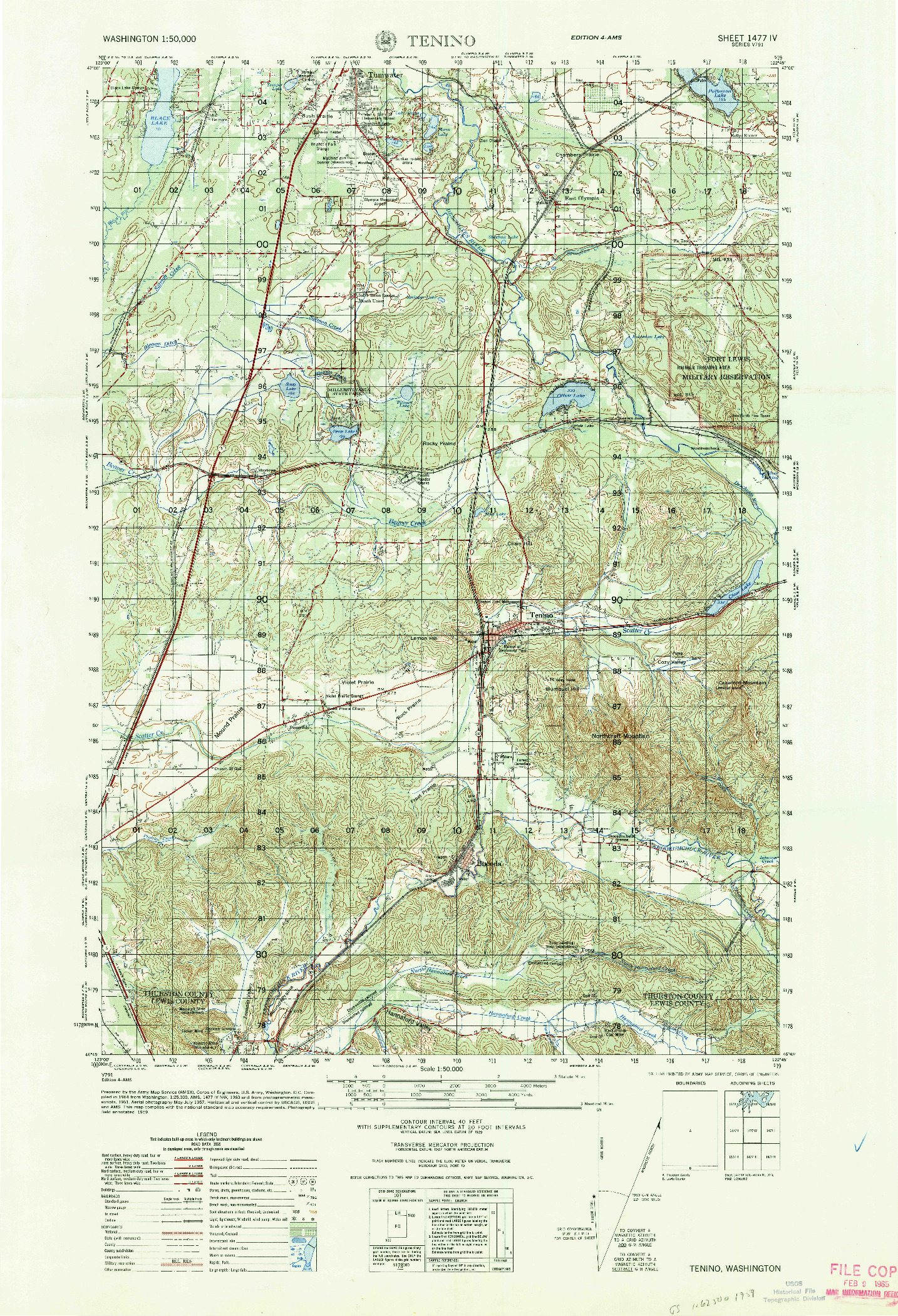
The most common and effective method for depicting relief is through contour lines. These lines connect points of equal elevation, creating a series of interconnected curves that trace the shape of the land. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; conversely, widely spaced lines indicate a gentle incline.
2. Hachures:
Hachures are short, parallel lines drawn perpendicular to the direction of the slope. They are typically used to represent steep slopes and are often combined with contour lines for a more detailed representation.
3. Shaded Relief:
Shaded relief uses light and shadow to create a three-dimensional effect, simulating the appearance of the terrain as if illuminated by the sun. This technique enhances the visual perception of the landform, making it easier to understand the overall topography.
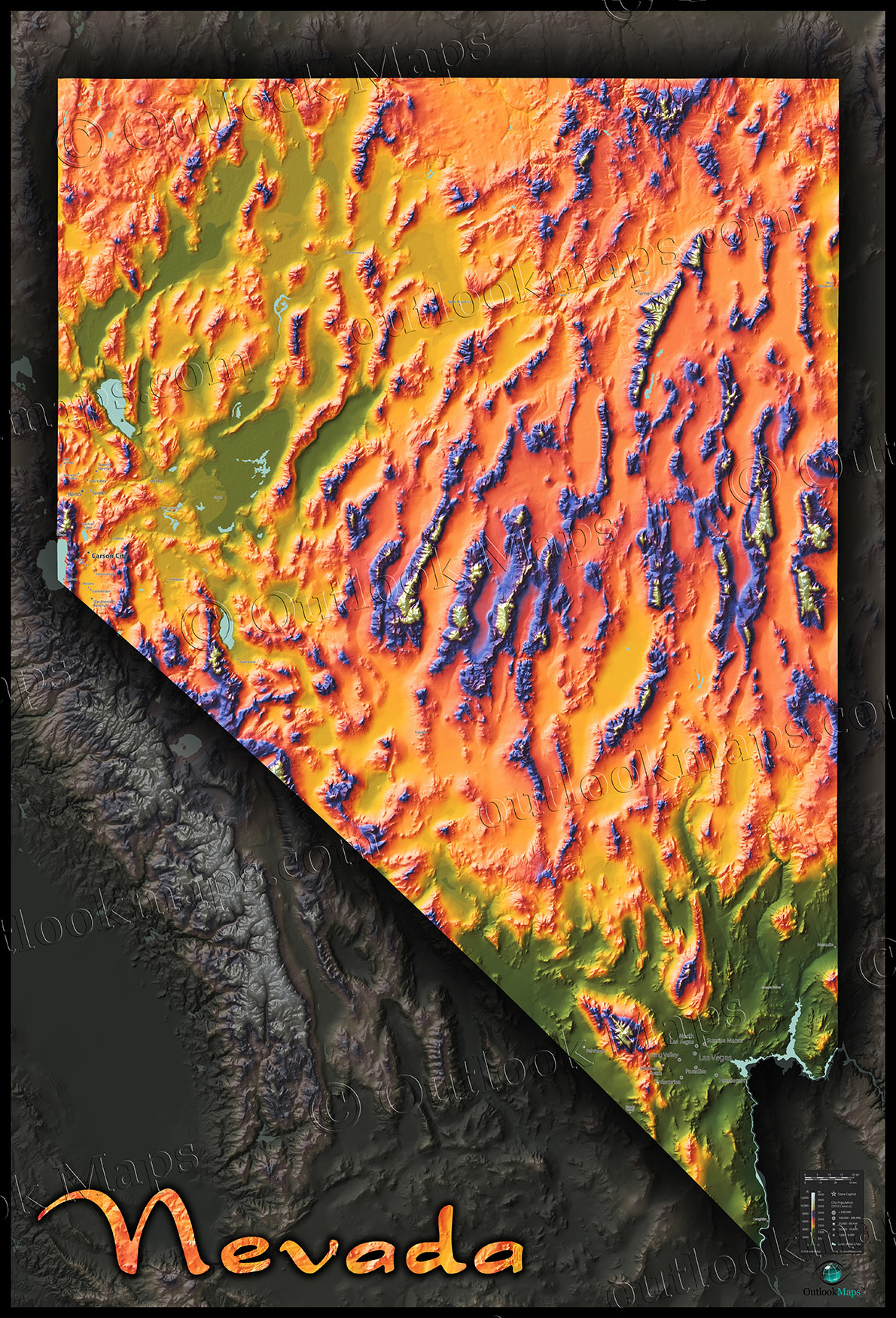
4. Hypsometric Tinting:
Hypsometric tinting employs different colors to represent various elevation ranges. This method provides a quick visual overview of the terrain, highlighting the highest and lowest points and the general distribution of elevation.
5. Digital Elevation Models (DEMs):
Digital elevation models are three-dimensional representations of the terrain, often generated from satellite imagery or LiDAR data. These models offer a highly detailed and accurate depiction of the landform, enabling precise analysis and visualization.
The Importance of Topographic Map Relief
Topographic map relief is crucial for a wide range of applications, including:
1. Navigation and Outdoor Recreation:
Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps to navigate challenging terrain, identify potential hazards, and plan their routes. The relief information helps them understand the steepness of slopes, the location of ridges and valleys, and the presence of natural obstacles.
2. Land Management and Development:
Topographic maps are essential tools for land planners, engineers, and developers. They provide critical information about the terrain, allowing them to assess the feasibility of construction projects, plan infrastructure development, and manage natural resources.
3. Environmental Studies and Disaster Management:
Topographic maps are invaluable for environmental scientists and disaster response teams. They provide insights into the distribution of vegetation, the flow of water, and the potential for landslides and floods. This information is vital for environmental monitoring, risk assessment, and disaster preparedness.
4. Military and Defense:
Military planners and intelligence agencies use topographic maps for strategic planning, terrain analysis, and target identification. The relief information provides critical insights into the battlefield environment, allowing for effective deployment of troops and resources.
5. Scientific Research and Analysis:
Topographic maps are used by researchers in various fields, including geology, geography, and ecology. They provide data for studying landform evolution, analyzing environmental change, and understanding the distribution of species.
FAQs about Topographic Map Relief
1. How are contour lines used to depict elevation?
Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, forming a series of interconnected curves that trace the shape of the land. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; conversely, widely spaced lines indicate a gentle incline.
2. What are the benefits of using shaded relief on topographic maps?
Shaded relief uses light and shadow to create a three-dimensional effect, enhancing the visual perception of the landform and making it easier to understand the overall topography.
3. How are digital elevation models (DEMs) used in topographic mapping?
DEMs are three-dimensional representations of the terrain, generated from satellite imagery or LiDAR data. They provide a highly detailed and accurate depiction of the landform, enabling precise analysis and visualization.
4. What are the limitations of using topographic maps for navigation?
Topographic maps can be outdated, and the terrain may have changed since the map was created. Additionally, the scale of the map may not be suitable for navigating complex terrain.
5. How can topographic maps be used to assess the risk of landslides?
Topographic maps can be used to identify areas with steep slopes, which are more prone to landslides. The distribution of vegetation and the presence of geological features can also be analyzed to assess the risk.
Tips for Using Topographic Map Relief
1. Understand the Map Scale: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and the accuracy of the relief representation.
2. Identify Key Features: Pay attention to contour lines, ridges, valleys, and other prominent landforms to understand the overall topography.
3. Use a Contour Interval Guide: The contour interval indicates the elevation difference between adjacent contour lines.
4. Consider the Purpose of the Map: The specific application of the map will influence the type of relief information required.
5. Utilize Digital Tools: Software programs and online resources can enhance the interpretation of topographic map relief.
Conclusion
Topographic map relief is a fundamental element of these maps, providing crucial insights into the shape and form of the Earth’s surface. By understanding the various methods of representing elevation, users can effectively interpret the terrain, navigate challenging landscapes, plan development projects, and conduct scientific research. The importance of topographic map relief extends across various disciplines, making it an indispensable tool for anyone seeking to understand and interact with the natural world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Relief. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!