Unveiling the Power of Spatial Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to XY Coordinate Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to XY Coordinate Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Spatial Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to XY Coordinate Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Spatial Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to XY Coordinate Maps
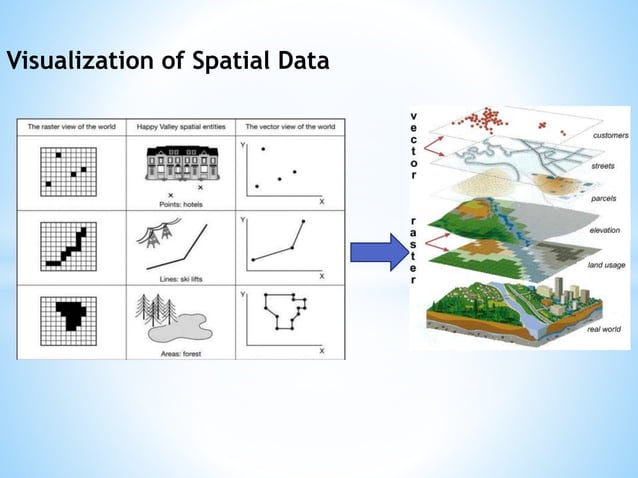
In the vast expanse of information, the ability to represent and navigate spatial relationships is paramount. Enter the world of XY coordinate maps, a fundamental tool that empowers us to understand and interact with the physical environment in a structured and quantifiable way. This comprehensive guide delves into the essence of XY coordinate maps, exploring their construction, applications, and significance in various fields.
The Foundation of Spatial Mapping: Understanding XY Coordinates
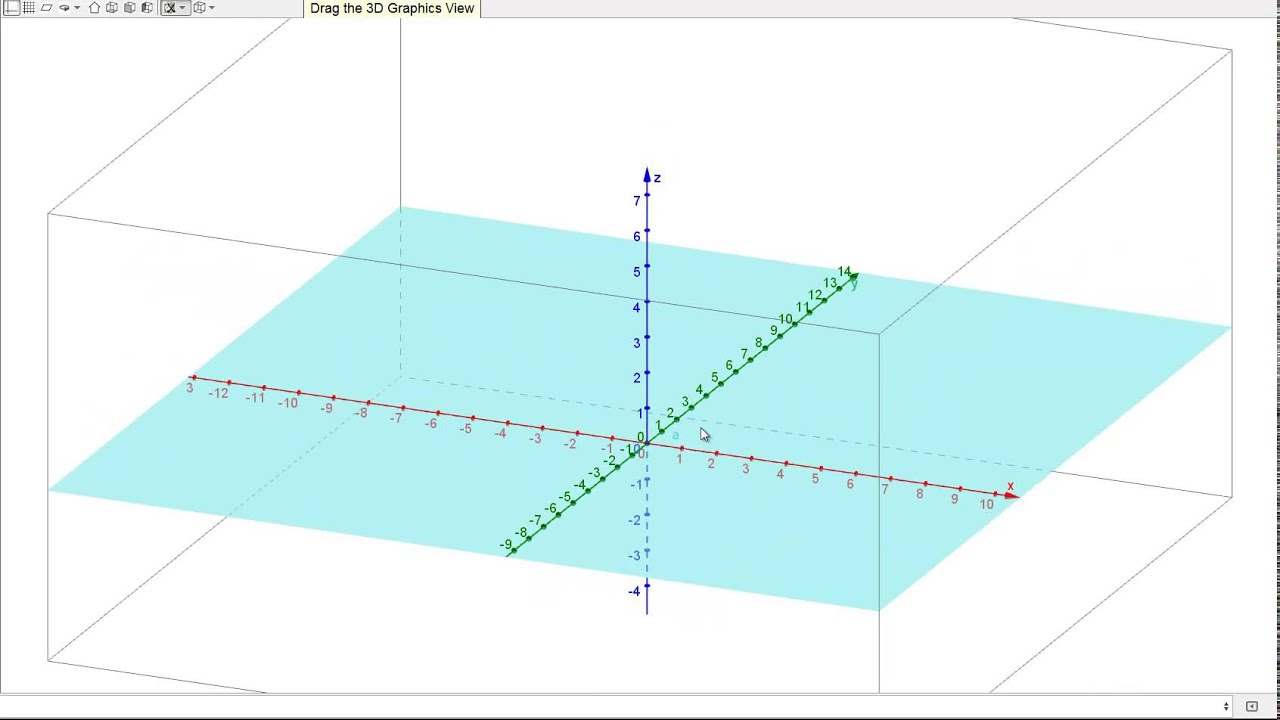
At the heart of XY coordinate maps lies a simple yet powerful concept: the Cartesian coordinate system. This system, named after the renowned mathematician René Descartes, utilizes two perpendicular axes, traditionally labeled X and Y, to define a unique location within a plane.
- The X-axis extends horizontally, representing the left-right orientation.
- The Y-axis extends vertically, representing the up-down orientation.
Every point on the plane is defined by an ordered pair (x, y), where:
- x represents the point’s horizontal distance from the origin (the intersection of the X and Y axes).
- y represents the point’s vertical distance from the origin.
This system provides a standardized framework for representing spatial information, enabling us to precisely locate and measure distances between any two points on the map.
The Construction of XY Coordinate Maps
The process of constructing an XY coordinate map involves several key steps:
-
Defining the Coordinate System: The first step is to establish a specific coordinate system, often based on a standard projection like the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) or the State Plane Coordinate System. This ensures compatibility and accuracy across different maps.
-
Establishing the Origin: The origin of the coordinate system serves as the reference point for all other locations on the map. It is typically chosen based on practical considerations, such as the center of a specific area or a prominent landmark.
-
Scaling and Units: The map’s scale determines the ratio between the distances on the map and the corresponding distances in the real world. Common units include meters, kilometers, feet, or miles.
-
Plotting Points: Once the coordinate system and scale are defined, individual points of interest are plotted on the map using their corresponding XY coordinates. These points can represent anything from buildings and roads to geographical features like rivers and mountains.
-
Adding Layers and Features: XY coordinate maps are often enhanced by adding various layers of information, such as elevation contours, land use classifications, or population density. These layers provide a richer and more comprehensive understanding of the mapped area.
Applications of XY Coordinate Maps: A Wide Range of Disciplines
The versatility of XY coordinate maps extends far beyond simple location identification. Their applications span a diverse range of disciplines, including:
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): XY coordinates form the foundation of GIS, enabling the creation and analysis of spatial data. GIS applications are used in urban planning, environmental management, disaster response, and many other areas.
-
Navigation and Mapping: GPS systems rely heavily on XY coordinates to determine a user’s location and provide accurate navigation instructions. Mapping services like Google Maps and Apple Maps utilize XY coordinates to render detailed representations of the world.
-
Engineering and Construction: XY coordinates are crucial for site planning, infrastructure development, and construction projects. They ensure precise alignment and accurate measurements for buildings, roads, and other structures.
-
Surveying and Land Management: Surveyors use XY coordinates to measure and map land boundaries, creating accurate property records and facilitating land transactions.
-
Scientific Research: Researchers across various fields, including ecology, archaeology, and astronomy, utilize XY coordinates to analyze spatial patterns, track movements, and conduct scientific investigations.
Benefits of Using XY Coordinate Maps
The widespread adoption of XY coordinate maps stems from their numerous benefits:
-
Precision and Accuracy: The use of numerical coordinates ensures a high degree of precision in representing spatial information. This allows for accurate measurements and analysis, leading to more informed decision-making.
-
Standardization and Compatibility: The Cartesian coordinate system provides a universal framework for representing spatial data, ensuring compatibility across different maps and systems. This facilitates data sharing and collaboration between different organizations and individuals.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: XY coordinate maps can be scaled to represent areas of varying sizes, from small-scale maps of a single room to large-scale maps of entire continents. This flexibility allows for tailored mapping solutions to meet specific needs.
-
Data Integration and Analysis: XY coordinate maps enable the integration of various types of spatial data, including geographical features, demographic information, and environmental data. This facilitates comprehensive analysis and the discovery of spatial relationships.
FAQs Regarding XY Coordinate Maps
Q: What are the different types of coordinate systems used in XY coordinate maps?
A: There are numerous coordinate systems used in XY coordinate maps, each with its specific advantages and applications. Some common systems include:
-
Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM): A global coordinate system divided into zones that minimize distortion and are widely used for mapping and navigation.
-
State Plane Coordinate System (SPCS): A system designed for specific states in the United States, providing high accuracy for local mapping and surveying.
-
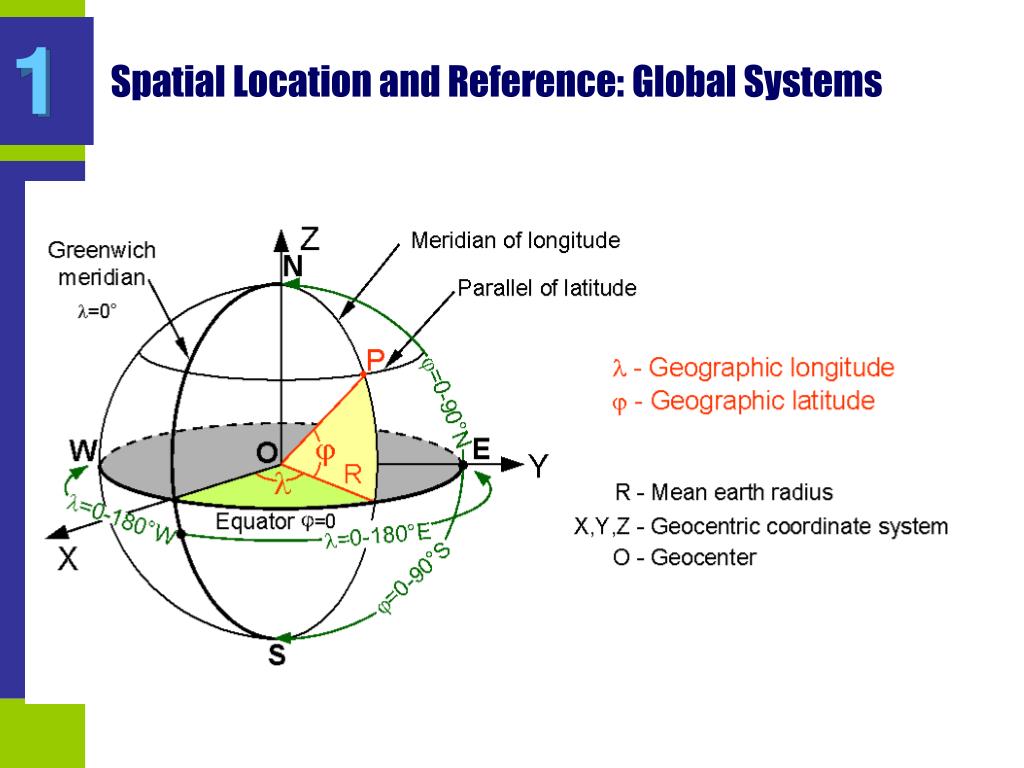
Geographic Coordinate System (GCS): Uses latitude and longitude to define locations on the Earth’s surface, commonly used for global applications.
Q: How do I convert between different coordinate systems?
A: Converting between different coordinate systems often requires specialized software or online tools that utilize mathematical formulas and transformations. These tools take into account the specific parameters of each coordinate system to ensure accurate conversions.
Q: How can I create my own XY coordinate map?
A: Creating an XY coordinate map requires specialized software like GIS applications or dedicated mapping tools. These programs allow you to define a coordinate system, import data, and plot points on the map.
Q: What are the limitations of XY coordinate maps?
A: While powerful, XY coordinate maps do have limitations:
-
Distortion: Representing the Earth’s curved surface on a flat map inevitably introduces some distortion, particularly at larger scales.
-
Data Accuracy: The accuracy of an XY coordinate map depends on the quality of the input data. Inaccurate measurements or data errors can lead to inaccuracies in the map.
-
Data Interpretation: Understanding the information presented on an XY coordinate map requires knowledge of the coordinate system, scale, and various map symbols.
Tips for Effective Use of XY Coordinate Maps
-
Choose the Appropriate Coordinate System: Select the coordinate system best suited for the scale and location of the map, ensuring accuracy and compatibility with other data.
-
Use Clear and Consistent Symbols: Employ clear and consistent symbols to represent different features on the map, ensuring easy understanding and interpretation.
-
Provide a Legend: Include a legend that explains the meaning of different symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map.
-
Consider Map Projections: Understand the effects of different map projections on the representation of spatial information, choosing the most appropriate projection for the intended use.
Conclusion
XY coordinate maps serve as a fundamental tool for understanding and interacting with the physical world. Their ability to represent spatial information with precision and accuracy makes them indispensable in various fields, from navigation and mapping to scientific research and urban planning. As technology advances, the applications of XY coordinate maps will continue to expand, further enhancing our ability to analyze, manage, and interact with the spatial environment. Understanding the principles and applications of XY coordinate maps empowers us to navigate the world around us with greater clarity and efficiency.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Spatial Representation: A Comprehensive Guide to XY Coordinate Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
