Unveiling the Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Levels
Related Articles: Unveiling the Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Levels
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Levels. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Levels

Maps, ubiquitous tools for navigating the physical and digital landscapes, often appear as simple representations of our world. However, beneath their seemingly straightforward surface lies a complex system of layers, each offering unique perspectives and insights. These layers, commonly referred to as "map levels," are the building blocks of comprehensive and informative mapping, enabling us to understand and interact with the world in increasingly nuanced ways.
Understanding Map Levels: A Foundation for Informed Exploration
Imagine a map as a multi-layered cake, each slice representing a different aspect of the world. The base layer might depict the fundamental terrain, showcasing mountains, valleys, and waterways. Above it, a layer of roads and highways might be added, revealing the network of human-made paths connecting various locations. Further layers could depict population density, political boundaries, or even the distribution of specific flora and fauna.
Each of these layers, or map levels, provides a distinct perspective, adding depth and complexity to our understanding of the mapped area. This layered approach allows us to filter and prioritize information, focusing on the aspects most relevant to our needs.
The Significance of Map Levels: Beyond Basic Navigation
The significance of map levels extends far beyond basic navigation. They enable us to:
- Visualize and analyze spatial relationships: Map levels allow us to understand how different elements interact within a given area. For instance, overlaying population density data on a map of healthcare facilities can reveal potential areas of underserved communities.
- Identify trends and patterns: By analyzing data across multiple map levels, we can identify spatial patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden. This is crucial for urban planning, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Communicate complex information effectively: Map levels allow us to convey complex information in a clear and concise manner. This is particularly important for conveying scientific data, environmental analysis, and social research findings.
- Support decision-making: By providing a comprehensive and customizable view of the world, map levels empower informed decision-making in various fields, including business, government, and research.
Exploring the Diverse World of Map Levels
The specific map levels used in a given application depend on the purpose and scope of the project. However, some common map levels include:
- Base Maps: These are the foundational layers that provide the geographic context for the map. They typically include terrain features, such as mountains, rivers, and lakes, along with political boundaries and major roads.
- Thematic Layers: These layers represent specific data sets, such as population density, crime rates, or vegetation cover. They are often used to highlight particular trends or patterns within a given area.
- Data Layers: These layers contain raw data points, such as locations of businesses, schools, or public facilities. They can be used to create custom maps or to analyze spatial relationships between different data points.
- Dynamic Layers: These layers are interactive and can be updated in real-time, such as traffic flow data or weather conditions. They provide a dynamic view of the world and allow for real-time decision-making.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Map Levels
1. What are the different types of map levels?
The types of map levels vary widely depending on the purpose of the map. Some common types include base maps, thematic layers, data layers, and dynamic layers.
2. How are map levels used in different industries?
Map levels are used across various industries, including:
- Urban Planning: To visualize population density, infrastructure development, and potential areas for growth.
- Environmental Management: To monitor deforestation, track wildlife populations, and assess environmental impact.
- Transportation: To optimize routes, analyze traffic flow, and plan infrastructure development.
- Business: To identify target markets, analyze customer demographics, and optimize logistics.
- Healthcare: To track disease outbreaks, analyze healthcare access, and plan medical facilities.
3. What are the benefits of using map levels?
The benefits of using map levels include:
- Enhanced Visualization: Map levels allow for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the mapped area.
- Improved Data Analysis: Map levels facilitate the analysis of spatial relationships and the identification of trends and patterns.
- Effective Communication: Map levels enable the clear and concise communication of complex information.
- Informed Decision-Making: Map levels empower informed decision-making in various fields.
4. How can I create my own map levels?
Creating custom map levels typically involves:
- Collecting data: Gathering relevant data points, such as location coordinates, attributes, and timestamps.
- Processing data: Cleaning, formatting, and organizing the data into a structured format.
- Visualizing data: Choosing appropriate symbols, colors, and map projections to effectively represent the data.
- Integrating data: Combining different data sets into a single map layer or multiple map layers.
Tips: Leveraging Map Levels for Success
- Define your objectives: Clearly define the purpose of your map and the information you want to convey.
- Choose appropriate data sources: Select reliable and relevant data sources that align with your objectives.
- Experiment with different map levels: Explore different map levels and combinations to find the most effective representation of your data.
- Use clear and concise labeling: Ensure that your map is easy to understand by using clear and concise labels for all features.
- Provide context: Include a legend or key to explain the meaning of different symbols and colors on your map.
- Consider accessibility: Design your map to be accessible to users with disabilities, using appropriate color schemes and font sizes.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Map Levels
Map levels are powerful tools that allow us to explore, analyze, and understand our world in increasingly sophisticated ways. By embracing the layered nature of mapping, we can gain deeper insights, make informed decisions, and communicate complex information effectively. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and powerful applications of map levels, further enhancing our ability to navigate and understand the world around us.


![]()
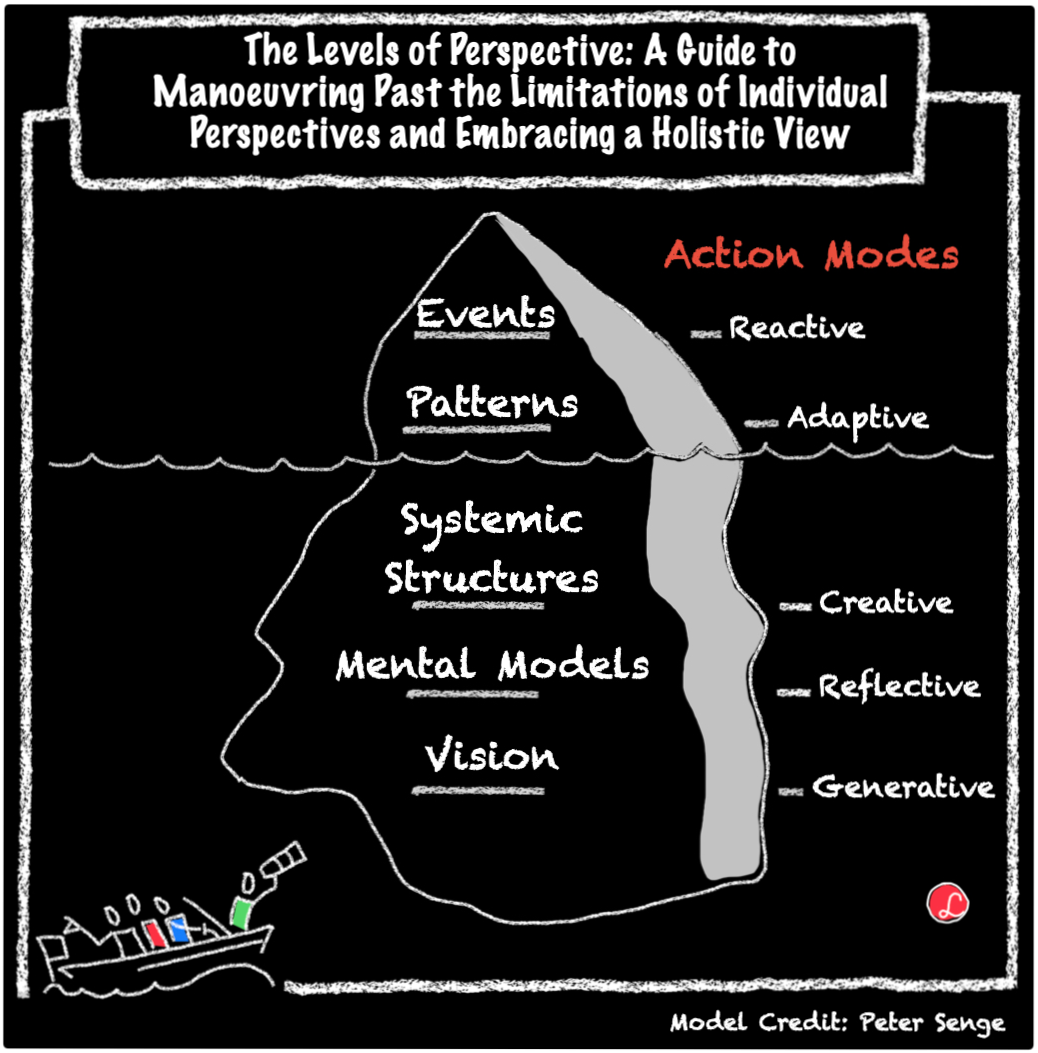


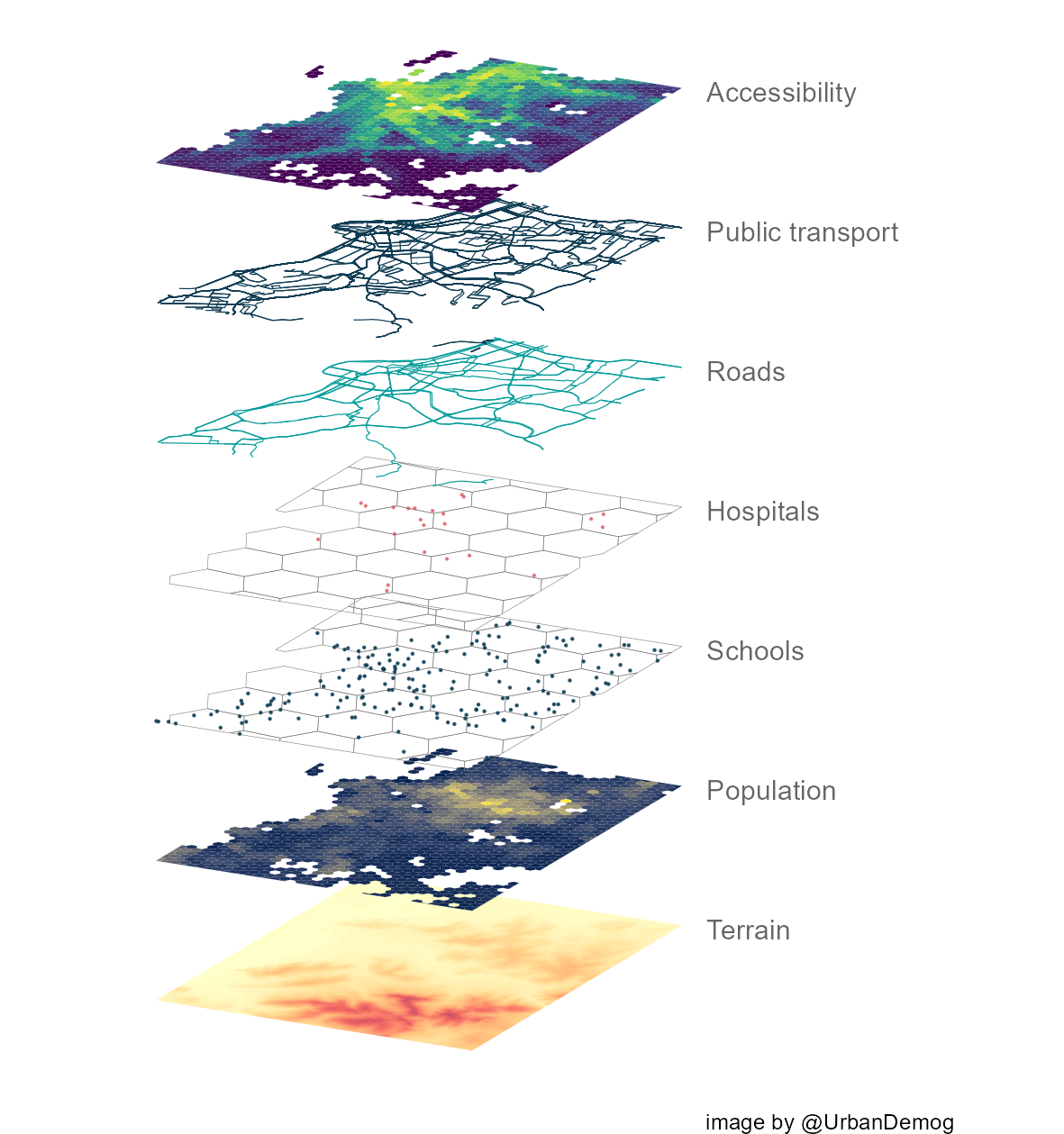
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Layers: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Levels. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!