Unveiling the Continent: A Comprehensive Exploration of Africa’s Geographic Landscape
Related Articles: Unveiling the Continent: A Comprehensive Exploration of Africa’s Geographic Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Continent: A Comprehensive Exploration of Africa’s Geographic Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Continent: A Comprehensive Exploration of Africa’s Geographic Landscape

Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, vibrant cultures, and rich history. Understanding its geography is crucial for appreciating its complexities and appreciating the intricate interplay between its environment and its people. This article delves into the continent’s geographic features, exploring its physical attributes, climatic variations, and the significance of its landscape in shaping its history, culture, and future.
A Journey Through the Continent’s Terrain:
Africa’s physical geography is characterized by vast and varied landscapes, encompassing:
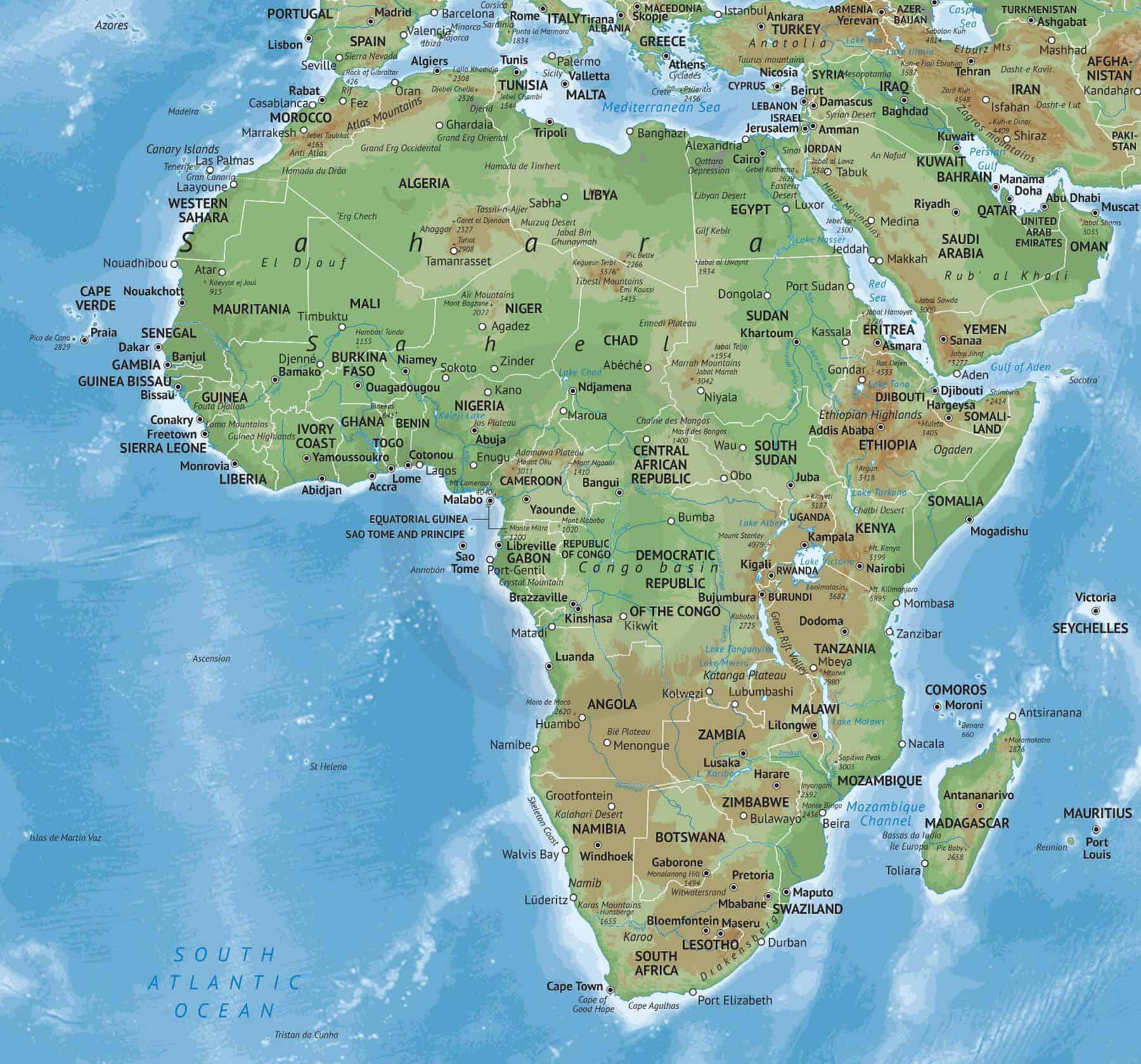
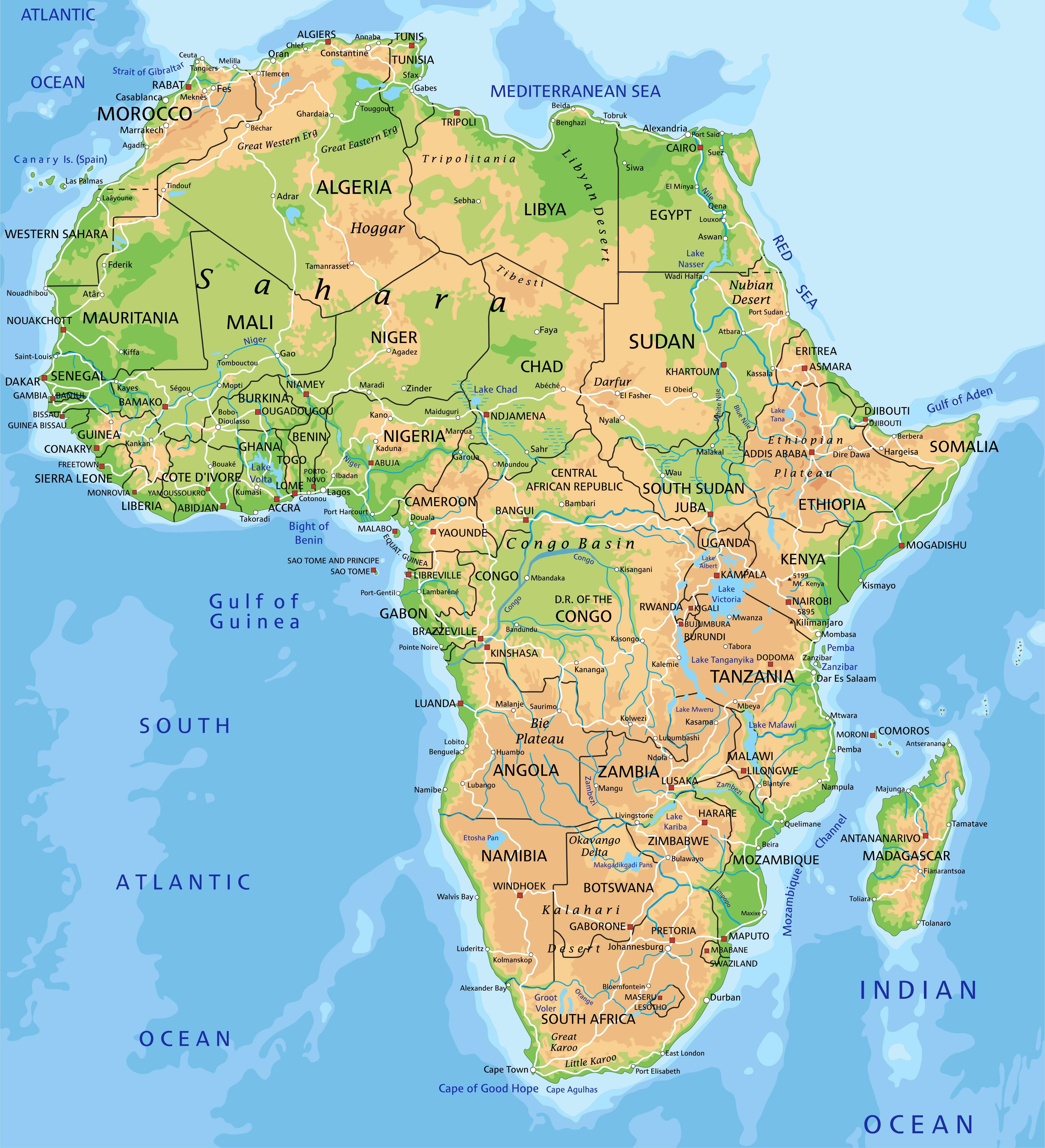
- Vast Plateaus: The continent’s interior is dominated by high plateaus, such as the Ethiopian Highlands and the East African Plateau, which rise to significant elevations and contribute to its diverse climate.
- Mountain Ranges: The Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Drakensberg in South Africa, and the Ruwenzori Mountains in East Africa are prominent mountain ranges that influence precipitation patterns and create unique ecosystems.
- Extensive Deserts: The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, dominates North Africa, while the Namib and Kalahari deserts stretch across the southern part of the continent. These arid regions present unique challenges and opportunities for life and human adaptation.
- River Systems: The Nile, the longest river in the world, flows through North and East Africa, providing vital water resources and fertile land for agriculture. Other major rivers, such as the Congo, Niger, and Zambezi, also play a crucial role in shaping the continent’s landscape and supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Coastal Regions: Africa boasts an extensive coastline, with diverse coastal environments ranging from sandy beaches to rocky cliffs and mangrove forests. These regions are vital for fishing, trade, and tourism.
Climate Variations: A Mosaic of Weather Patterns:
Africa’s vast size and varied topography result in a wide range of climates, from scorching deserts to lush rainforests.
- Tropical Climates: Equatorial regions experience hot and humid tropical climates with abundant rainfall, supporting dense rainforests and diverse wildlife.
- Arid Climates: The Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari deserts experience extremely hot and dry conditions, with limited vegetation and sparse populations.
- Mediterranean Climates: The northern and southern coastal regions enjoy mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, making them ideal for agriculture and tourism.
- Subtropical Climates: Areas further away from the equator experience distinct seasons, with warm summers and cooler winters, supporting a variety of ecosystems.
The Impact of Geography on History and Culture:
Africa’s geography has profoundly shaped its history and culture, influencing:
- Settlement Patterns: The availability of water, fertile land, and natural resources has influenced human settlement patterns throughout the continent.
- Trade Routes: Rivers and coastlines have served as vital trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures across the continent.
- Cultural Diversity: Different geographic regions have fostered unique cultures, languages, and traditions, reflecting the adaptation of people to their specific environments.
- Resource Management: The management of natural resources, such as water, land, and wildlife, has been a constant challenge and an integral part of African societies.
Understanding the Significance of Africa’s Geography:
Understanding Africa’s geography is crucial for several reasons:
- Sustainable Development: Effective resource management, environmental conservation, and sustainable development strategies require a deep understanding of the continent’s physical attributes and ecosystems.
- Conflict Resolution: Geographical factors, such as access to water, land, and resources, can contribute to conflicts. Understanding these factors is essential for conflict prevention and resolution.
- Economic Growth: The exploitation of natural resources, development of infrastructure, and promotion of sustainable tourism are all influenced by the continent’s geographic features.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Africa is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as droughts, floods, and rising sea levels. Understanding the continent’s geography is essential for developing effective adaptation strategies.
FAQs about Africa’s Geography:
Q: What are the major geographical features of Africa?
A: Africa is characterized by vast plateaus, mountain ranges, extensive deserts, major river systems, and diverse coastal regions.
Q: What are the different climate zones in Africa?
A: Africa experiences tropical, arid, Mediterranean, and subtropical climates, influenced by its vast size and varied topography.
Q: How has geography shaped African history and culture?
A: Africa’s geography has influenced settlement patterns, trade routes, cultural diversity, and resource management practices.
Q: What are the challenges and opportunities related to Africa’s geography?
A: Africa faces challenges related to resource management, conflict resolution, economic growth, and climate change adaptation, while also benefiting from its diverse resources and unique landscapes.
Tips for Exploring Africa’s Geography:
- Use maps and atlases: Visualizing Africa’s geography through maps and atlases can provide a comprehensive understanding of its features.
- Read about different regions: Explore books, articles, and documentaries about specific regions of Africa to gain insights into their unique landscapes and cultures.
- Travel and experience: Visiting different parts of Africa can provide firsthand experience of its diverse geography and the impact it has on people’s lives.
- Engage with experts: Consult with geographers, anthropologists, and environmental scientists to gain deeper knowledge about Africa’s geography and its complexities.
Conclusion:
Africa’s geography is a testament to the continent’s remarkable diversity and complexity. From its vast plateaus and mountain ranges to its extensive deserts and diverse coastal regions, Africa’s landscape is a rich tapestry of natural wonders. Understanding this geography is not only essential for appreciating the continent’s beauty and richness but also for addressing the challenges and opportunities it presents for its people and its future. By delving deeper into the continent’s physical attributes, climate variations, and the interplay between geography and culture, we can gain a more profound appreciation for the intricate and fascinating world of Africa.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Continent: A Comprehensive Exploration of Africa’s Geographic Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!