Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Plots
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Plots
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Plots. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Plots
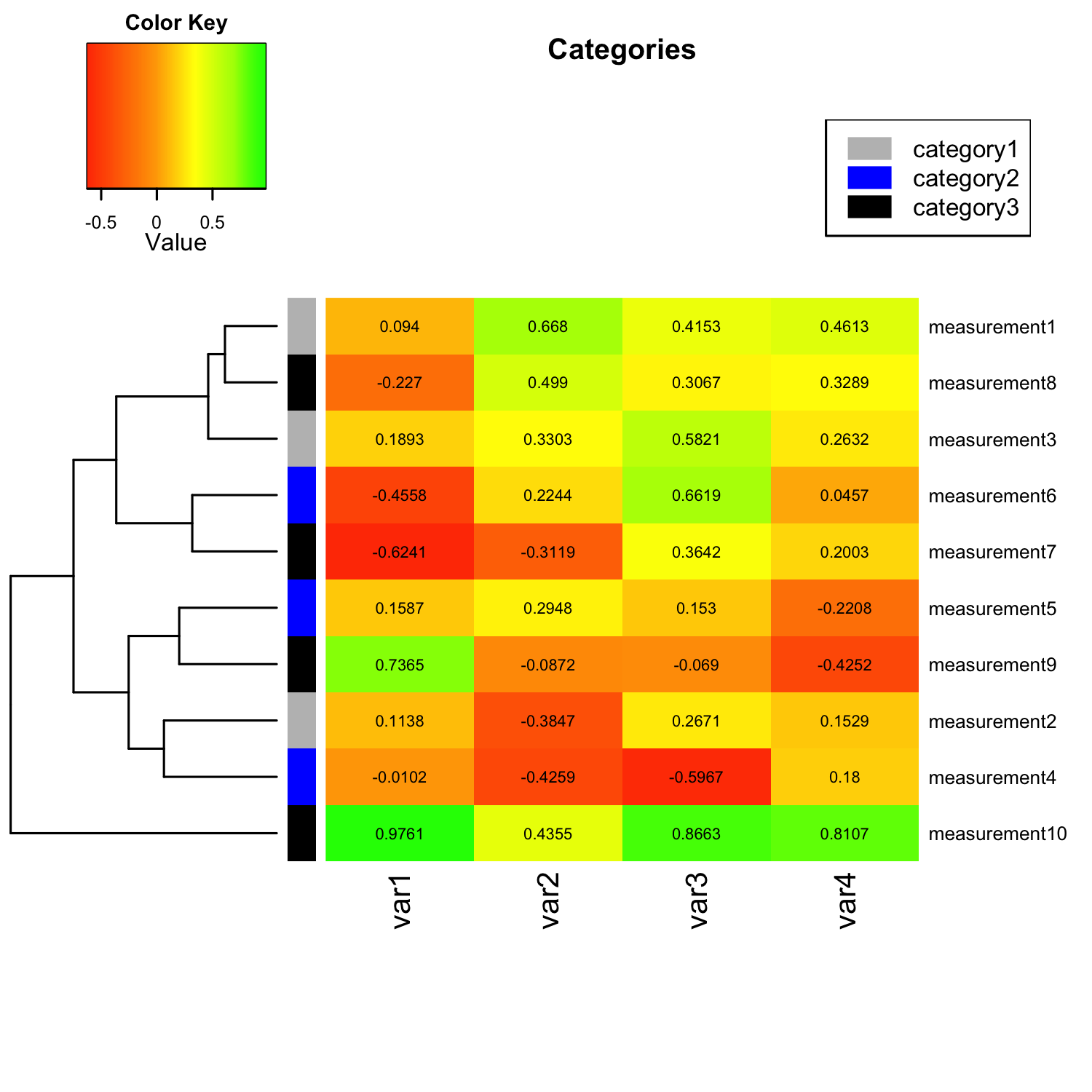
Heat maps, a powerful visualization tool, have become indispensable in diverse fields ranging from data analysis and market research to website optimization and scientific exploration. Their ability to represent complex data sets through color gradients allows for rapid identification of trends, anomalies, and areas of interest. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of heat map plots, exploring their construction, applications, and invaluable contributions to data interpretation.
Understanding the Essence of Heat Maps
At its core, a heat map is a graphical representation that uses color variations to depict data distribution across a defined area. Each cell within the map corresponds to a specific data point, with color intensity reflecting the magnitude of the corresponding value. The color scheme typically employs a gradient, where warmer colors (e.g., red, orange) represent higher values, and cooler colors (e.g., blue, green) represent lower values.
Construction and Interpretation
The construction of a heat map involves several key steps:
-
Data Preparation: The data to be visualized must be organized and formatted appropriately. This often involves grouping data points into categories or bins.
-
Grid Formation: A grid is created, with each cell representing a specific category or data point. The size and arrangement of the grid can vary depending on the nature of the data and the desired level of detail.
-
Color Assignment: A color scheme is chosen to represent the data values. The intensity of the color within each cell corresponds to the magnitude of the data point.
-
Visualization: The colored cells are displayed within the grid, creating a visual representation of the data distribution.
Interpreting a heat map requires careful consideration of the color scheme and the underlying data:
-
Areas of High Value: Cells with warmer colors indicate higher values, highlighting areas of interest or potential trends.
-
Areas of Low Value: Cells with cooler colors indicate lower values, potentially indicating areas requiring further investigation or improvement.
-
Patterns and Trends: The overall color distribution can reveal patterns, clusters, or trends within the data.
Applications of Heat Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Heat maps find widespread application across various domains, offering valuable insights and facilitating decision-making. Here are some notable examples:
1. Website Analysis: Heat maps are instrumental in understanding user behavior on websites. By tracking mouse movements, clicks, and scroll depth, they provide visual representations of user engagement, highlighting areas of interest and identifying potential usability issues.
2. Market Research: Heat maps can analyze customer demographics, preferences, and purchasing patterns. By mapping these factors geographically, businesses can gain insights into market segmentation, target specific customer groups, and optimize marketing strategies.
3. Data Exploration and Visualization: Heat maps are invaluable for exploring large datasets, identifying patterns, and revealing relationships between variables. They simplify complex data by visually representing its distribution, facilitating quicker identification of trends and outliers.
4. Scientific Research: Heat maps find applications in diverse scientific fields, including biology, chemistry, and physics. They can visualize gene expression patterns, analyze protein interactions, or depict temperature distribution in physical systems.
5. Finance and Investment: Heat maps are used to analyze stock market trends, identify investment opportunities, and assess risk. They can visualize correlations between different assets, helping investors make informed decisions.
6. Healthcare: Heat maps aid in medical diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. They can visualize tumor growth patterns, analyze medical imaging data, and track patient vital signs.
7. Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Heat maps are employed to optimize production processes, track inventory levels, and identify bottlenecks in supply chains. They can visualize machine performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize resource allocation.
8. Operations Management: Heat maps are used to analyze operational data, identify areas of inefficiency, and improve process flow. They can visualize workflow bottlenecks, identify resource constraints, and optimize resource allocation.
Benefits of Using Heat Maps:
-
Intuitive Visualization: Heat maps provide a clear and intuitive visual representation of data, making it easy to understand complex relationships and patterns.
-
Data Exploration and Discovery: They facilitate the identification of trends, anomalies, and areas of interest within large datasets, enabling deeper insights and data-driven decision-making.
-
Effective Communication: Heat maps effectively communicate data insights to a wider audience, regardless of their technical expertise, fostering collaboration and understanding.
-
Improved Decision-Making: By highlighting key areas and potential issues, heat maps empower data-driven decision-making, leading to better outcomes and optimized processes.
FAQs about Heat Maps:
1. What are the different types of heat maps?
There are several types of heat maps, each tailored to specific applications:
- Click Maps: Track mouse clicks on a webpage, revealing areas of user interaction.
- Scroll Maps: Track scroll depth on a webpage, indicating how far users scroll before leaving.
- Movement Maps: Track mouse movements on a webpage, revealing user navigation patterns.
- Eye-Tracking Maps: Track eye movements, providing insights into user attention and focus.
- Density Maps: Represent the concentration of data points within a specific area, revealing areas of high density or clustering.
2. How can I create a heat map?
There are numerous software tools available for creating heat maps. Popular options include:
- Google Analytics: Offers built-in heat map functionalities for website analysis.
- Hotjar: Provides a comprehensive suite of heat map tools, including click, scroll, and movement maps.
- Crazy Egg: Offers a user-friendly interface for creating and analyzing heat maps.
- Microsoft Excel: Can be used to create basic heat maps using conditional formatting.
- R and Python: Programming languages with libraries specifically designed for creating heat maps.
3. What are the limitations of heat maps?
While powerful, heat maps have limitations:
- Data Interpretation: The interpretation of heat maps can be subjective and may require domain expertise.
- Oversimplification: They can oversimplify complex data, potentially missing nuanced relationships.
- Visual Distortion: The color scheme and grid size can influence the visual perception of data.
- Limited Information: They may not provide the full context of the data, requiring additional analysis.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Maps:
- Choose the Right Data: Select data relevant to the specific question or problem being addressed.
- Define Clear Categories: Group data points into meaningful categories or bins.
- Select Appropriate Color Scheme: Use a color scheme that clearly differentiates high and low values and is visually appealing.
- Optimize Grid Size: Choose a grid size that provides sufficient detail without overwhelming the viewer.
- Consider Data Scaling: Normalize data values to ensure fair comparisons across different categories.
- Provide Context and Explanation: Clearly label axes, legend, and provide additional information to aid interpretation.
Conclusion:
Heat maps are versatile visualization tools that offer valuable insights into data distribution, trends, and patterns. Their ability to transform complex data into easily understandable visual representations makes them invaluable for data exploration, decision-making, and communication. By understanding the principles of heat map construction and interpretation, users can effectively leverage this powerful tool to gain a deeper understanding of data and make informed decisions across various fields.
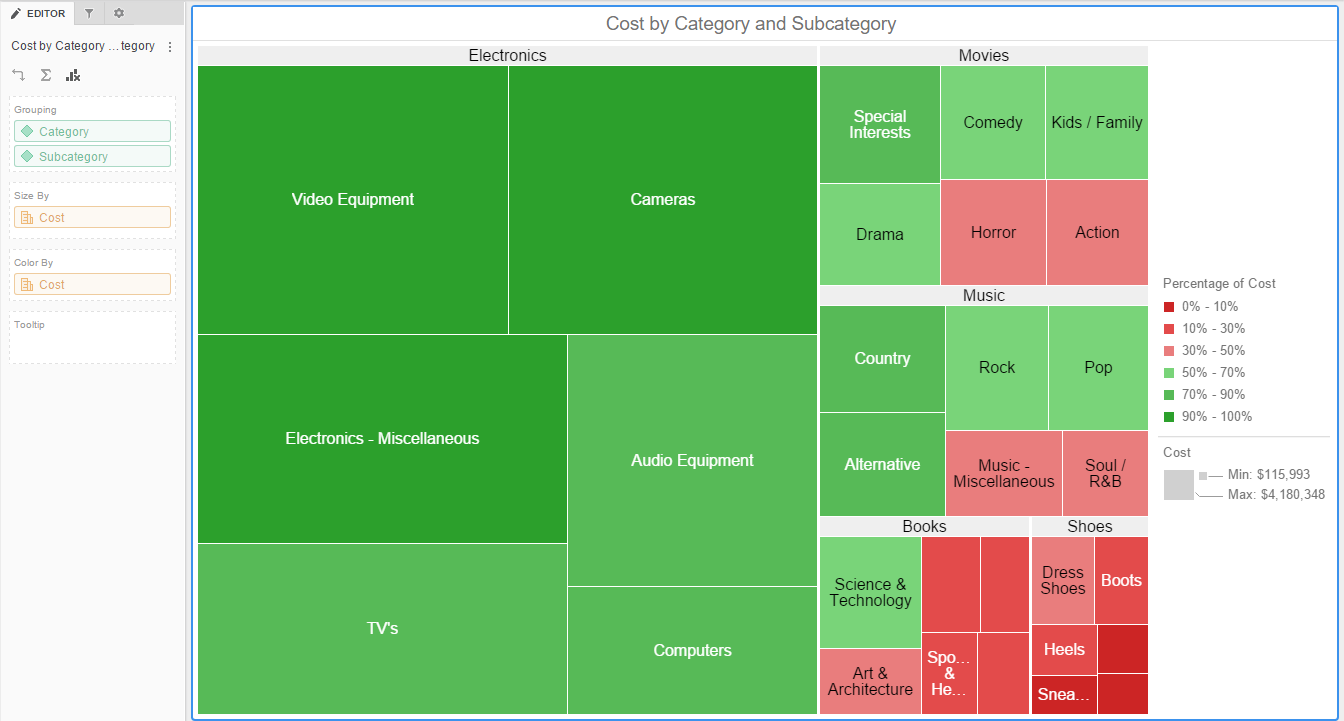
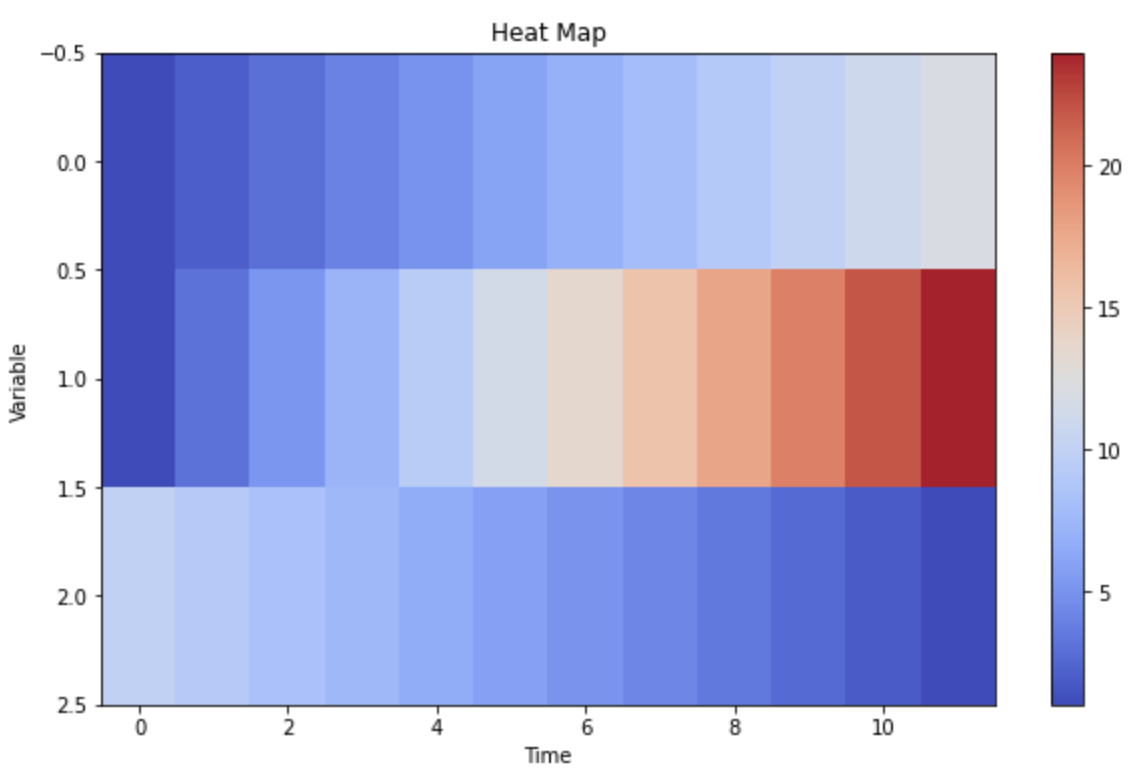
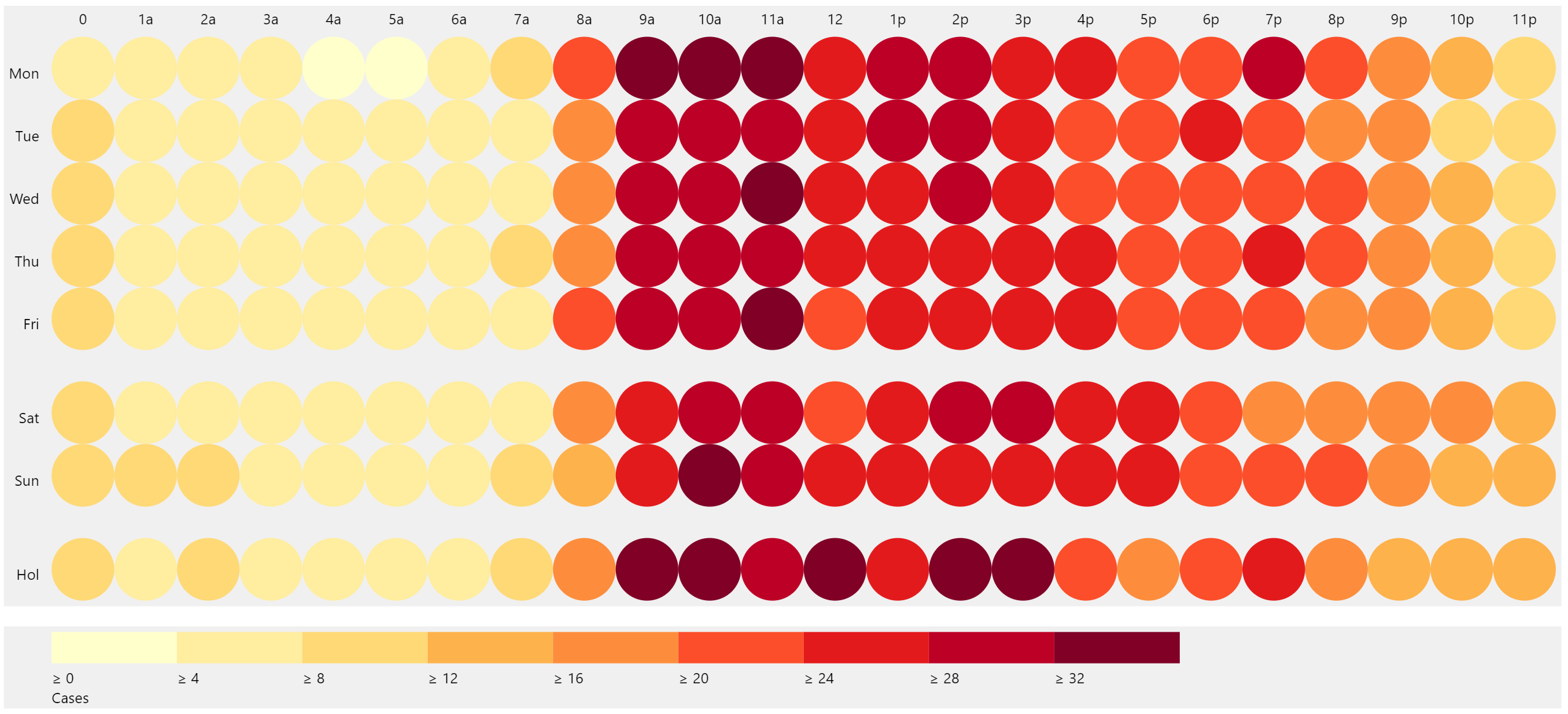

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Plots. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!