Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
- 3.1 Deciphering the Elevation Map: A Visual Guide to Australia’s Landforms
- 3.2 Beyond the Visual: Unveiling the Significance of the Elevation Map
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Elevation Map of Australia
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding and Using the Elevation Map of Australia
- 3.5 Conclusion: The Elevation Map as a Window into Australia’s Diverse Landscape
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
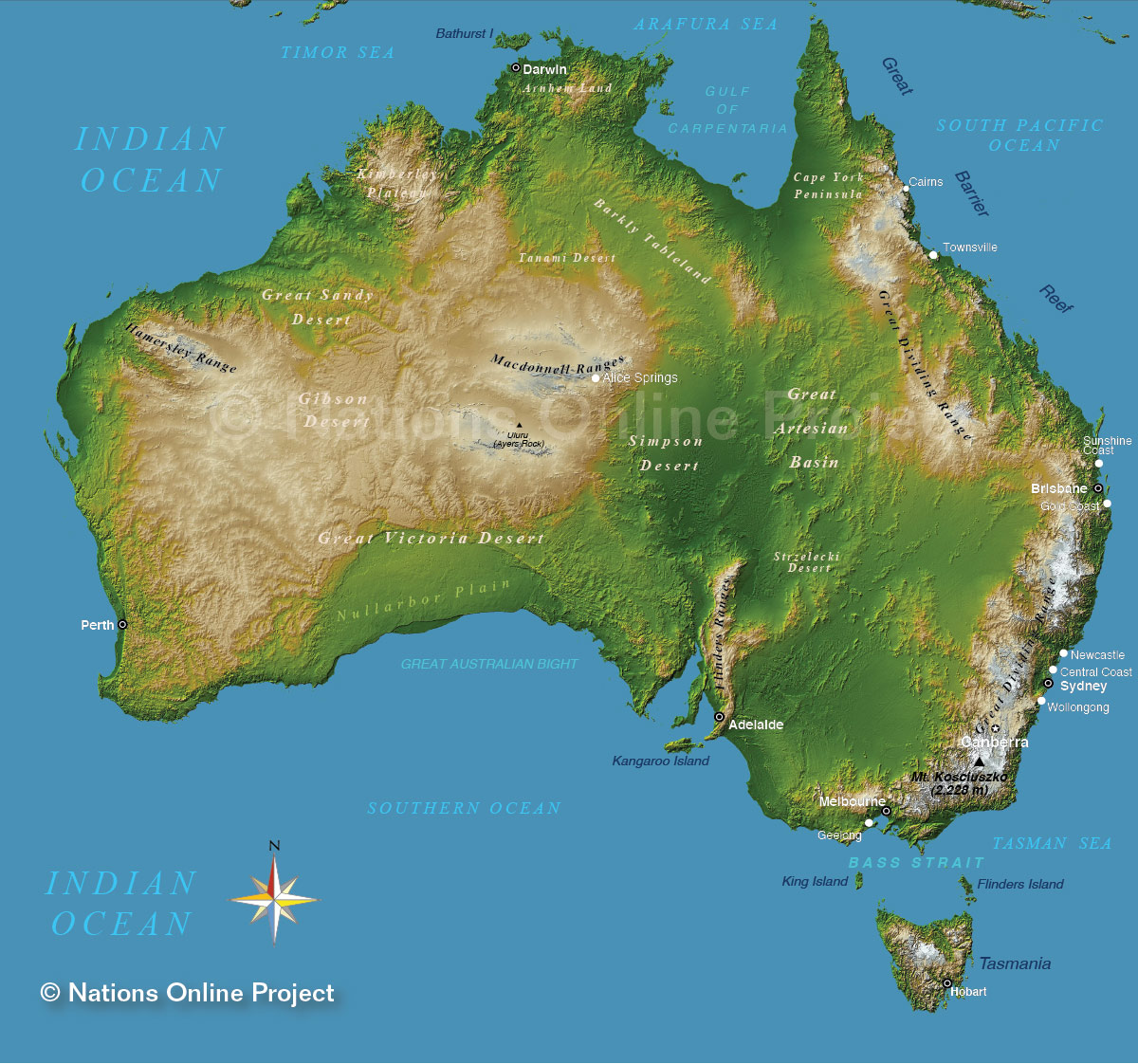
Australia, the world’s smallest continent and largest island, boasts a diverse landscape shaped by ancient geological forces and weathering over millennia. Understanding this topography is crucial for various disciplines, from environmental management and infrastructure development to tourism and scientific research. The elevation map of Australia provides a visual representation of this intricate terrain, offering invaluable insights into the country’s physical characteristics.
Deciphering the Elevation Map: A Visual Guide to Australia’s Landforms
The elevation map of Australia depicts the height of every point on the continent above sea level, using color gradients to represent different elevations. This color scheme, often ranging from deep greens for low-lying areas to white or brown for high peaks, allows for a quick and intuitive understanding of the country’s topography.
Key Features Revealed:
- The Great Dividing Range: This vast mountain range, stretching over 3,500 kilometers along the eastern coast, is clearly visible on the elevation map as a prominent ridge of high elevations. The range’s highest peak, Mount Kosciuszko, stands at 2,228 meters, marking the highest point in mainland Australia.
- The Western Plateau: Occupying over two-thirds of the continent, the Western Plateau is characterized by its relatively flat and low-lying terrain. The map reveals its vast expanse and gradual slopes, punctuated by isolated ranges and mesas.
- The Nullarbor Plain: This vast, arid plain, stretching over 1,000 kilometers across the southern part of Western Australia, is depicted as a remarkably flat area on the elevation map. Its near-uniform elevation underscores its unique geological history.
- The Coastal Plains: The elevation map highlights the narrow coastal plains that fringe the eastern and southern coasts, showcasing the transition from the high elevations of the Great Dividing Range to the lower-lying areas along the coastline.
- The River Systems: Major river systems like the Murray-Darling Basin are easily identifiable on the elevation map, with their courses tracing the landscape and revealing their origins in the highlands and their journey towards the coast.
Beyond the Visual: Unveiling the Significance of the Elevation Map
The elevation map of Australia transcends its visual appeal, serving as a vital tool for various applications:
1. Environmental Management:
- Water Resource Management: The map helps identify water catchment areas and potential sources of water supply, crucial for managing water resources in a continent facing drought challenges.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Understanding the elevation map’s data helps assess the impact of climate change on different regions, enabling informed strategies for mitigating its effects.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The map aids in identifying areas with unique topographic features, supporting the conservation of diverse ecosystems and threatened species.
2. Infrastructure Development:
- Transportation Networks: The elevation map guides the planning and construction of roads, railways, and pipelines, ensuring efficient connectivity across varied terrains.
- Urban Planning: The map informs urban development decisions, considering factors like slope stability, flood risk, and access to resources for sustainable growth.
- Energy Infrastructure: The map helps identify suitable locations for renewable energy projects like wind farms and solar power plants, taking into account factors like wind patterns and solar irradiance.
3. Tourism and Recreation:
- Outdoor Activities: The elevation map highlights areas suitable for hiking, mountain biking, rock climbing, and other outdoor activities, attracting adventure enthusiasts.
- Scenic Routes: The map assists in planning scenic drives and tours, offering breathtaking views and insights into the diverse landscape.
- Tourism Development: The map helps identify potential tourist destinations, guiding investment and development in areas with unique topographic features.
4. Scientific Research:
- Geological Studies: The elevation map provides valuable data for geological research, helping understand the formation of the continent’s landforms and the distribution of minerals.
- Climate Modeling: The map contributes to climate modeling studies, aiding in predicting future climate patterns and their impact on different regions.
- Ecological Research: The map helps researchers understand the distribution of flora and fauna across different elevations, shedding light on biodiversity patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Elevation Map of Australia
1. What is the highest point in Australia?
The highest point in mainland Australia is Mount Kosciuszko, located in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, with an elevation of 2,228 meters. However, if considering all Australian territories, the highest point is Mount Wilhelm in Papua New Guinea, with an elevation of 4,509 meters.
2. What is the lowest point in Australia?
The lowest point in Australia is Lake Eyre, a large, shallow salt lake in South Australia. Its elevation fluctuates, but it can drop to -15 meters below sea level during dry periods.
3. How is the elevation map of Australia created?
The elevation map is created using various data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground-based surveys. Advanced technology like lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) is used to precisely measure the height of the terrain.
4. What are the different types of elevation maps available?
There are different types of elevation maps, each with its own level of detail and purpose. These include:
- Contour maps: Show elevation changes using lines that connect points of equal elevation.
- Digital elevation models (DEMs): Provide a digital representation of the terrain, enabling detailed analysis and modeling.
- 3D elevation maps: Offer a realistic three-dimensional view of the landscape, enhancing visualization and understanding.
5. Where can I access the elevation map of Australia?
Various sources provide access to the elevation map of Australia, including:
- Government agencies: The Australian Bureau of Meteorology and Geoscience Australia offer free and publicly accessible datasets.
- Online mapping services: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap provide interactive elevation maps with detailed information.
- Specialized mapping software: Software like ArcGIS and QGIS offer advanced tools for analyzing and visualizing elevation data.
Tips for Understanding and Using the Elevation Map of Australia
- Start with a general overview: Begin by exploring the map at a broad scale, identifying major landforms and their relative elevations.
- Focus on specific areas of interest: Zoom in on regions relevant to your needs, whether for environmental management, infrastructure development, or tourism planning.
- Use different map types: Explore different map types, like contour maps and 3D models, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
- Combine the elevation map with other data: Integrate the elevation map with other datasets, such as rainfall patterns, soil types, and vegetation cover, for a more holistic analysis.
- Consult experts: Seek guidance from experts in relevant fields, like geographers, geologists, and environmental scientists, for interpreting and applying the elevation map effectively.
Conclusion: The Elevation Map as a Window into Australia’s Diverse Landscape
The elevation map of Australia serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s unique topography and its implications for various aspects of human activity. By visualizing the intricate interplay of mountains, plains, and coastlines, the map provides a comprehensive overview of the continent’s physical characteristics, guiding informed decision-making in diverse sectors. Whether for environmental management, infrastructure development, tourism planning, or scientific research, the elevation map of Australia remains an invaluable resource for exploring and appreciating the country’s diverse and dynamic landscape.
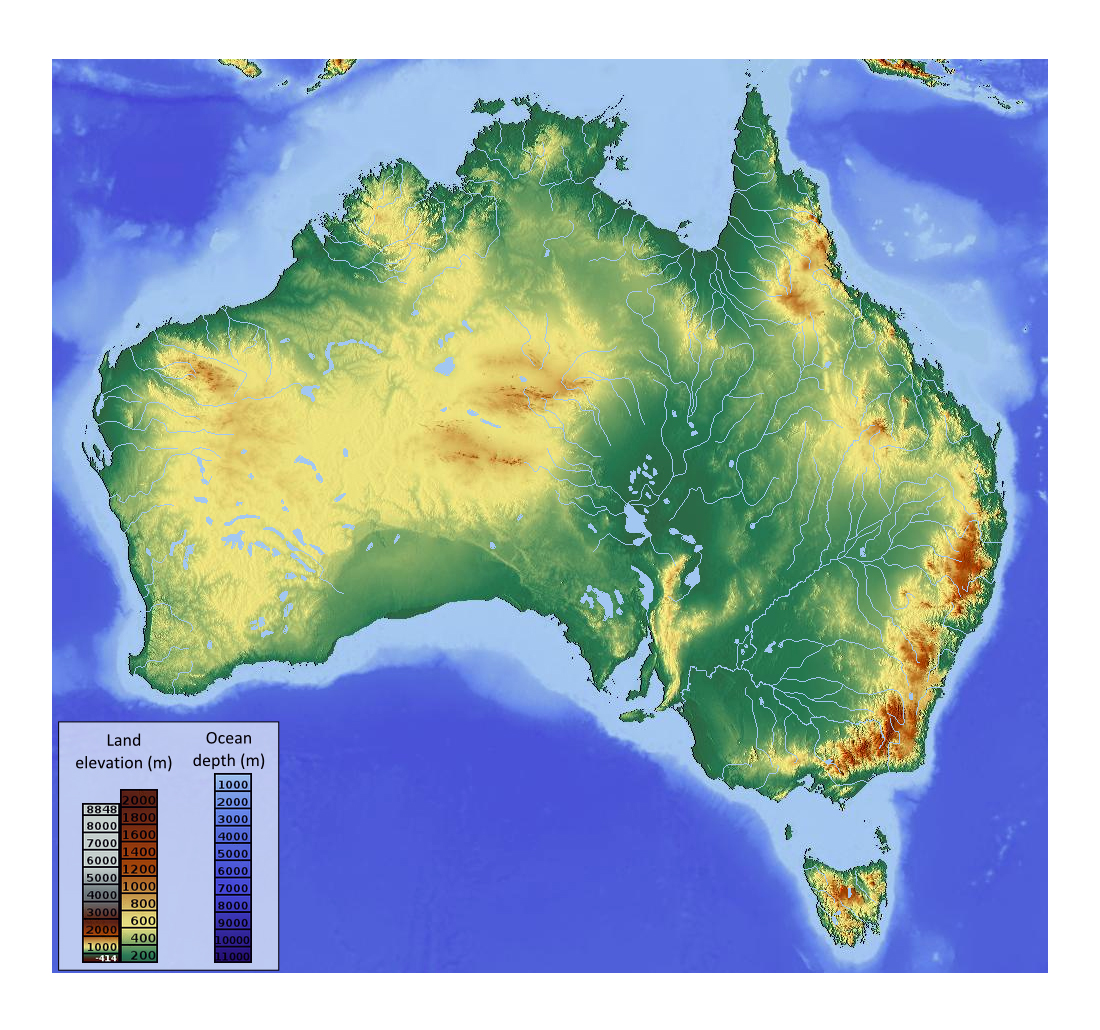


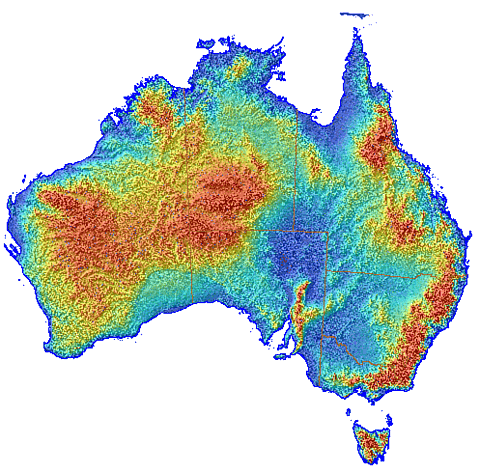

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Australia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!