Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the North American Fault Lines
Related Articles: Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the North American Fault Lines
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the North American Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the North American Fault Lines
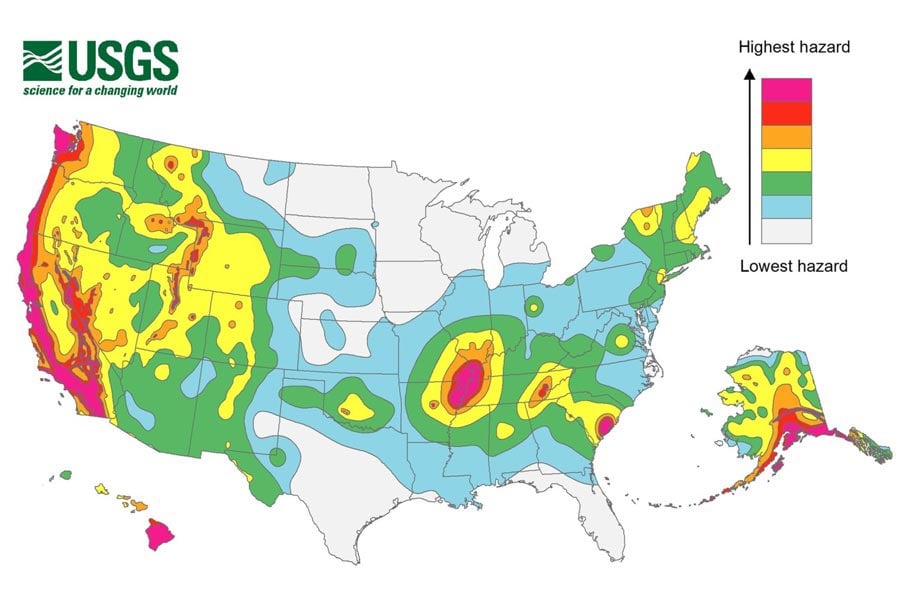
The Earth’s crust is not a monolithic entity, but rather a dynamic mosaic of plates constantly in motion. This tectonic dance manifests in various ways, including the formation of mountains, volcanic eruptions, and, most dramatically, earthquakes. Understanding the intricate network of fault lines crisscrossing the North American continent is crucial for comprehending the geological forces shaping our landscape and for mitigating the risks associated with seismic activity.
Understanding Fault Lines: The Threads of Tectonic Movement
Fault lines represent fractures in the Earth’s crust where tectonic plates interact. These interactions can be characterized as convergent, divergent, or transform. Convergent boundaries, where plates collide, give rise to mountain ranges and volcanic activity. Divergent boundaries, where plates pull apart, lead to the formation of rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges. Transform boundaries, where plates slide horizontally past each other, are responsible for generating powerful earthquakes.
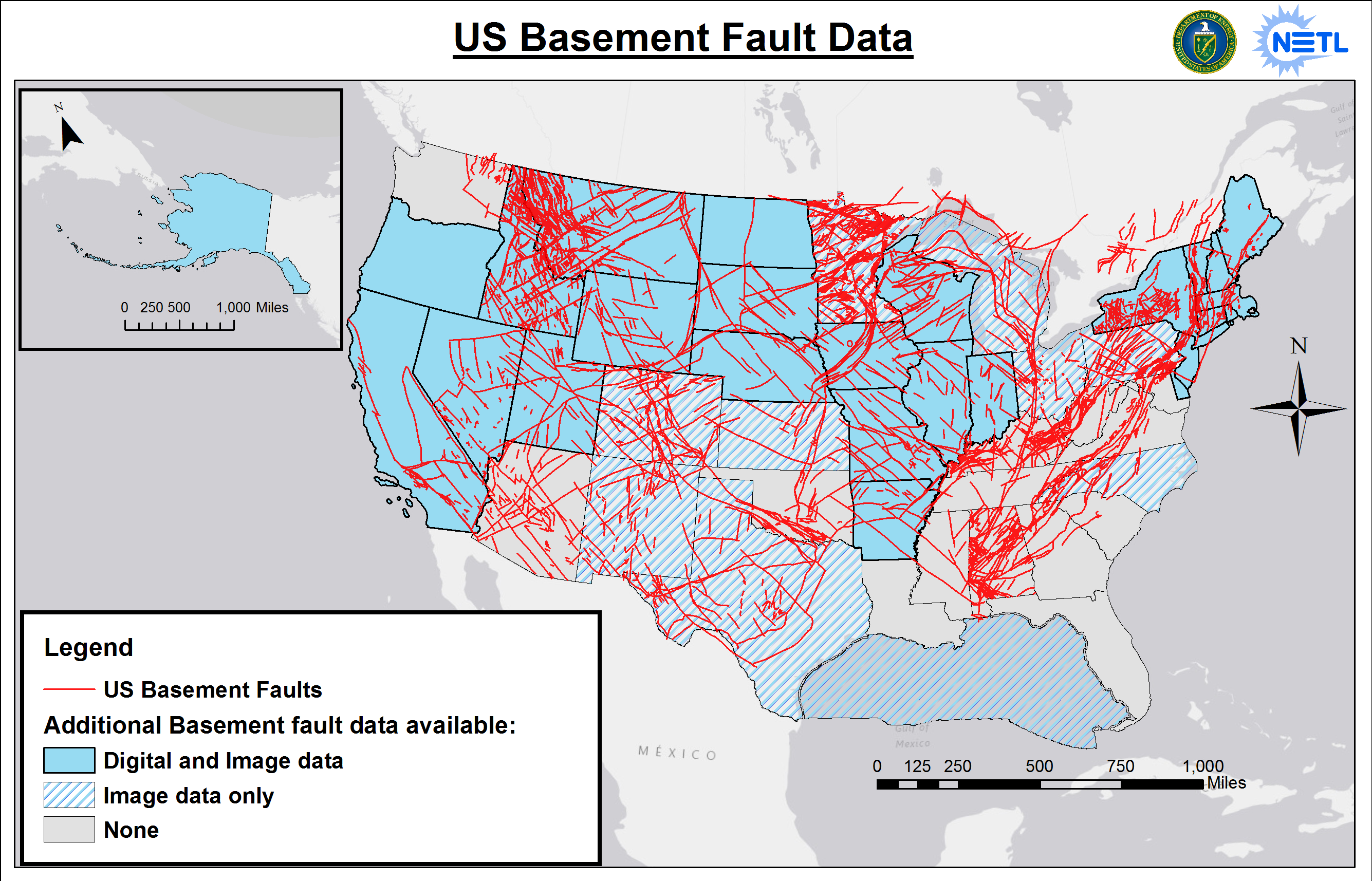
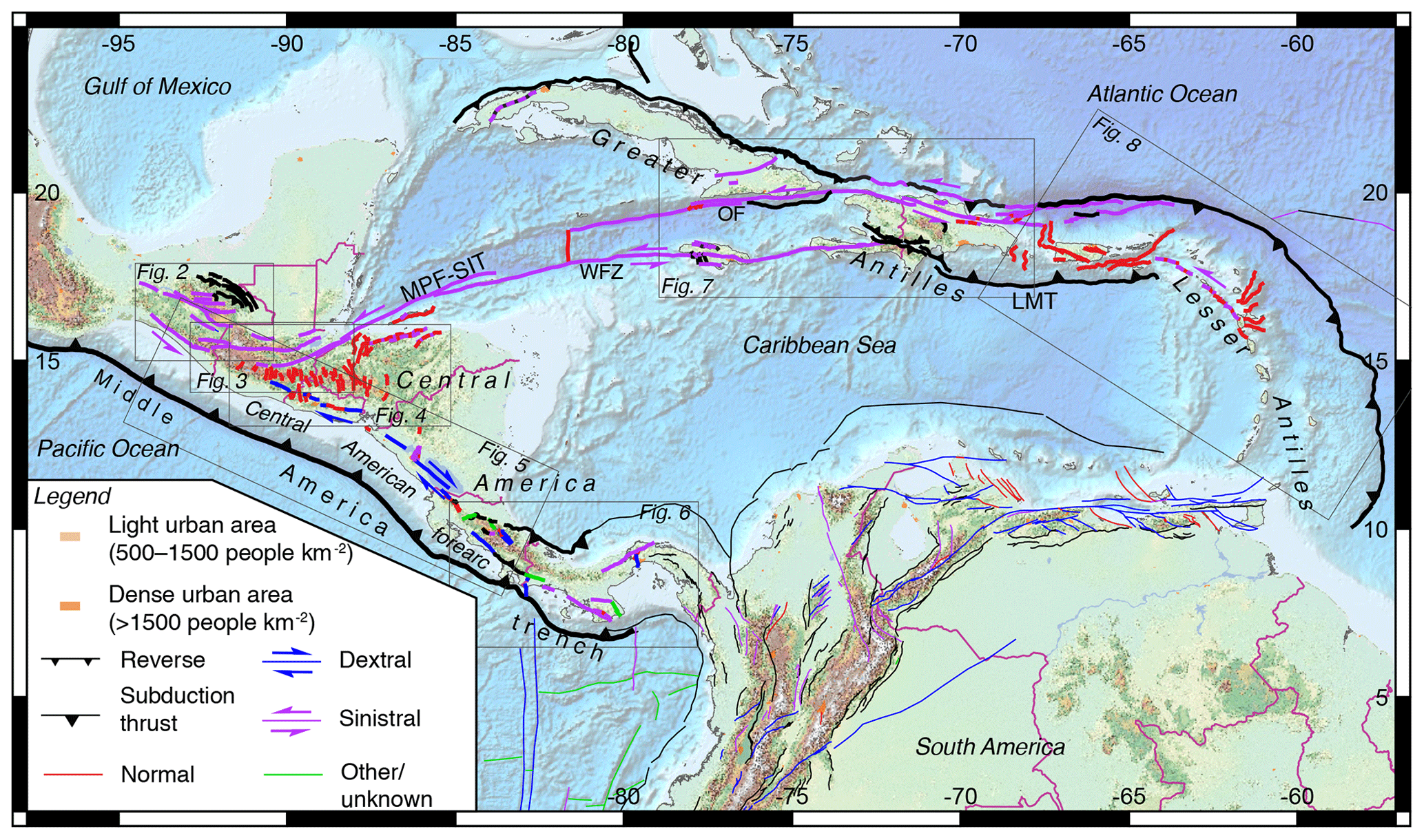
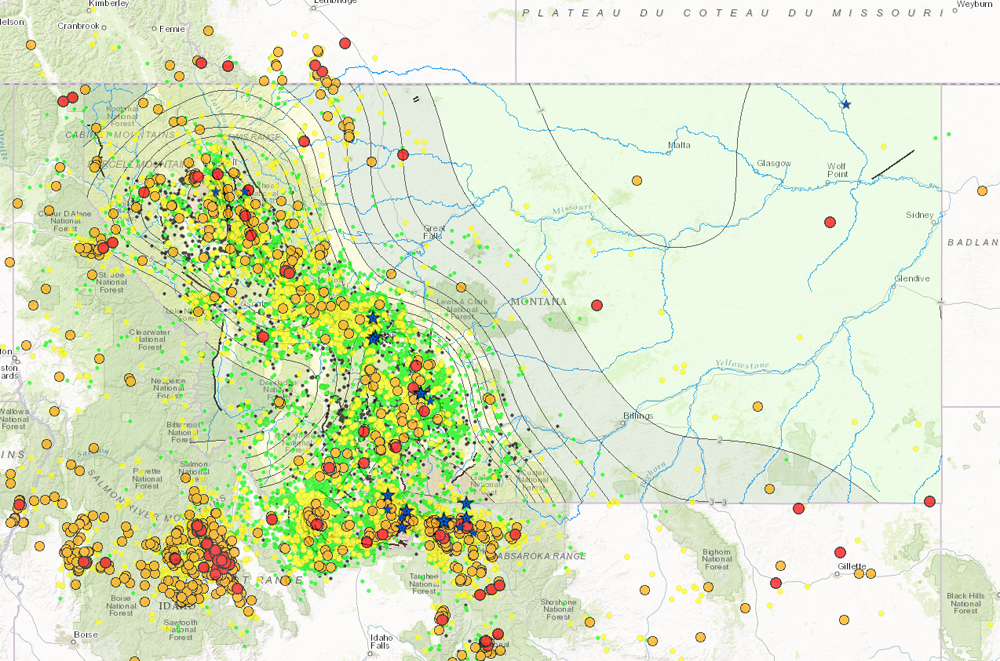
The North American Fault Line Network: A Complex and Dynamic System
North America sits atop several major tectonic plates, including the North American Plate, the Pacific Plate, and the Cocos Plate. These plates interact along numerous fault lines, creating a complex and dynamic seismic landscape. The most prominent fault lines in North America include:
-
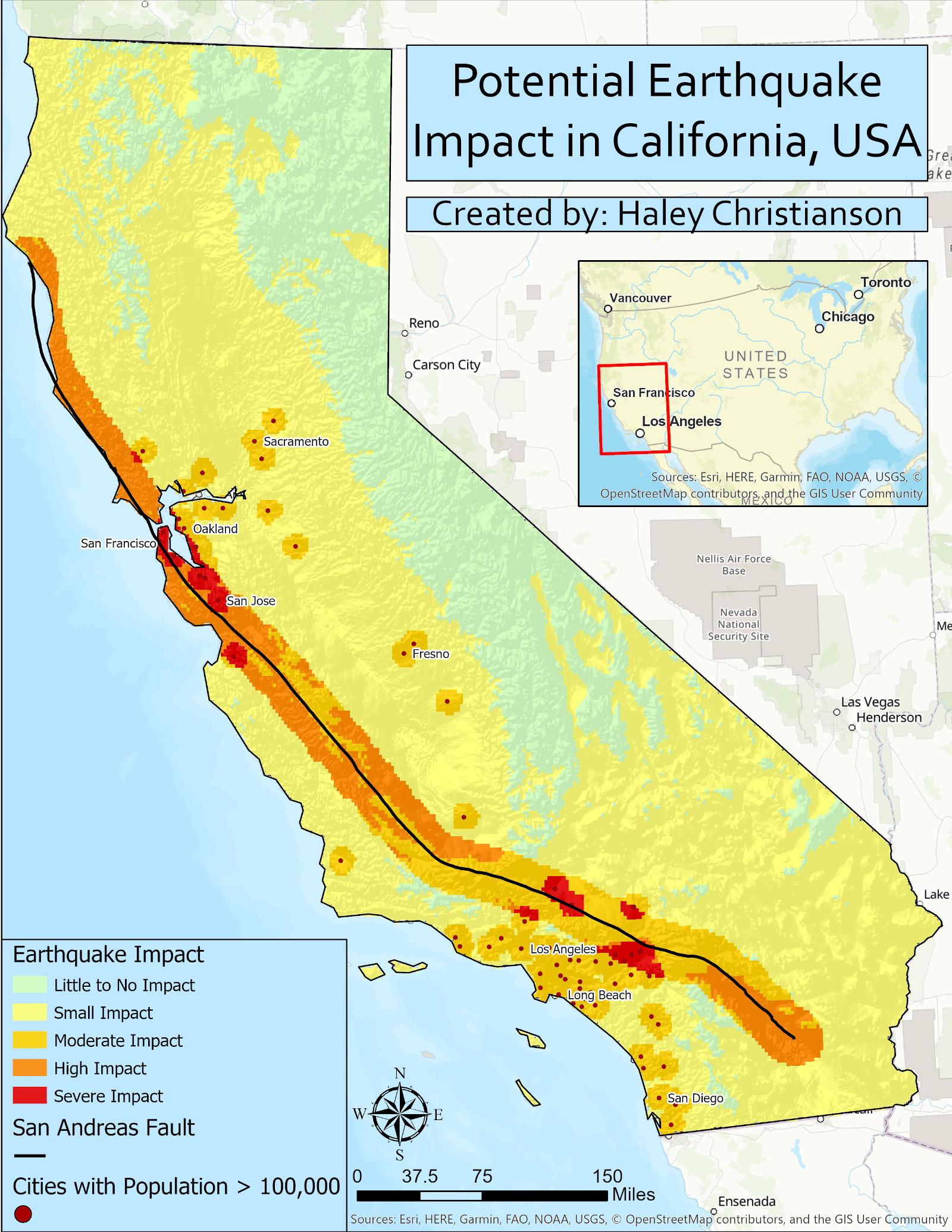
The San Andreas Fault: This transform boundary, stretching over 800 miles from the Salton Sea in California to Cape Mendocino, is arguably the most famous fault line in North America. It marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and is responsible for numerous significant earthquakes, including the devastating 1906 San Francisco earthquake.
-
The Queen Charlotte Fault: Located off the coast of British Columbia, this transform boundary marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. It is responsible for generating powerful earthquakes in the region.
-
The Denali Fault: Situated in Alaska, this transform boundary marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. It is known for generating large earthquakes, including the 2002 Denali earthquake, one of the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded in North America.
-
The Wasatch Fault: This normal fault, running along the eastern edge of the Wasatch Mountains in Utah, represents a zone of crustal extension. It is responsible for generating moderate earthquakes, posing a significant risk to the densely populated Wasatch Front.
-
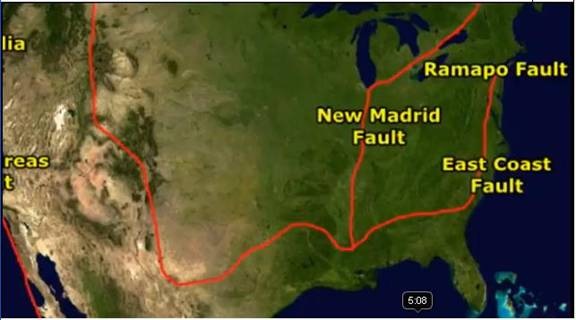
The New Madrid Seismic Zone: This intraplate seismic zone, located in the central United States, is characterized by a series of ancient faults. While the zone is not directly associated with plate boundaries, it is responsible for generating powerful earthquakes, including the New Madrid earthquakes of 1811-1812, which were some of the most powerful earthquakes ever recorded in North America.
The Importance of Understanding North American Fault Lines
Understanding the locations and characteristics of North American fault lines is paramount for several reasons:
-
Earthquake Prediction and Mitigation: By studying fault lines, scientists can better predict the likelihood and intensity of future earthquakes. This knowledge allows for the development of earthquake-resistant infrastructure, early warning systems, and emergency preparedness plans, mitigating the impact of seismic events.
-
Resource Exploration: Fault lines often act as conduits for the movement of fluids, including oil, gas, and geothermal energy. Understanding fault line dynamics can aid in the exploration and extraction of these valuable resources.
-
Land Use Planning: Knowledge of fault lines is crucial for responsible land use planning. By identifying areas prone to seismic activity, policymakers can avoid building critical infrastructure in high-risk zones, ensuring the safety of communities and minimizing potential economic damage.
-
Understanding Geological History: Fault lines provide a window into the Earth’s geological history, revealing the movements and interactions of tectonic plates over millions of years. Studying fault lines helps scientists unravel the complex processes that have shaped the continents and the Earth’s surface.
FAQs about North American Fault Lines
Q: How often do earthquakes occur along North American fault lines?
A: The frequency of earthquakes along North American fault lines varies significantly depending on the specific fault and its activity level. Some faults, like the San Andreas Fault, are known for their high frequency of earthquakes, while others, like the New Madrid Seismic Zone, experience periods of relative inactivity punctuated by rare but powerful events.
Q: Are there any areas in North America that are considered earthquake-proof?
A: While some areas of North America are less prone to earthquakes than others, no region can be considered truly earthquake-proof. Seismic activity is a natural phenomenon that can occur anywhere on Earth, and even areas with low historical earthquake activity can experience significant events.
Q: Can scientists predict earthquakes with certainty?
A: While scientists can predict the likelihood of earthquakes based on historical activity and fault line characteristics, predicting the exact time and magnitude of an earthquake remains a challenge. Continued research and advancements in seismology are essential for improving earthquake prediction capabilities.
Q: What can I do to prepare for an earthquake?
A: Preparing for an earthquake is essential for ensuring personal safety and minimizing potential damage. Actions include:
- Securing heavy objects: Secure heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Creating an emergency kit: Prepare an emergency kit with essential supplies like water, food, first-aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Developing an evacuation plan: Establish a plan for evacuating your home or workplace in the event of an earthquake.
- Learning earthquake safety procedures: Educate yourself and your family on earthquake safety procedures, including drop, cover, and hold.
Tips for Understanding North American Fault Lines
- Consult reputable sources: When researching fault lines, rely on information from reputable sources like government agencies, scientific organizations, and academic institutions.
- Use interactive maps: Interactive maps provide a visual representation of fault lines and their locations, enabling a deeper understanding of the seismic landscape.
- Stay informed about seismic activity: Keep up to date on earthquake activity in your region by subscribing to news alerts and following reputable organizations like the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
- Engage in community preparedness: Participate in community preparedness programs and exercises to enhance awareness and preparedness for earthquakes.
Conclusion
The network of fault lines crisscrossing North America serves as a constant reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet. Understanding these fault lines is not only crucial for comprehending the geological forces shaping our landscape but also for mitigating the risks associated with seismic activity. By recognizing the importance of fault lines and engaging in responsible land use planning, earthquake preparedness, and continuous research, we can better navigate the seismic landscape of North America and ensure the safety and well-being of our communities.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Seismic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the North American Fault Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!