Unraveling the Ocean’s Giants: A Deep Dive into Great White Shark Migration Patterns
Related Articles: Unraveling the Ocean’s Giants: A Deep Dive into Great White Shark Migration Patterns
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Ocean’s Giants: A Deep Dive into Great White Shark Migration Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Ocean’s Giants: A Deep Dive into Great White Shark Migration Patterns
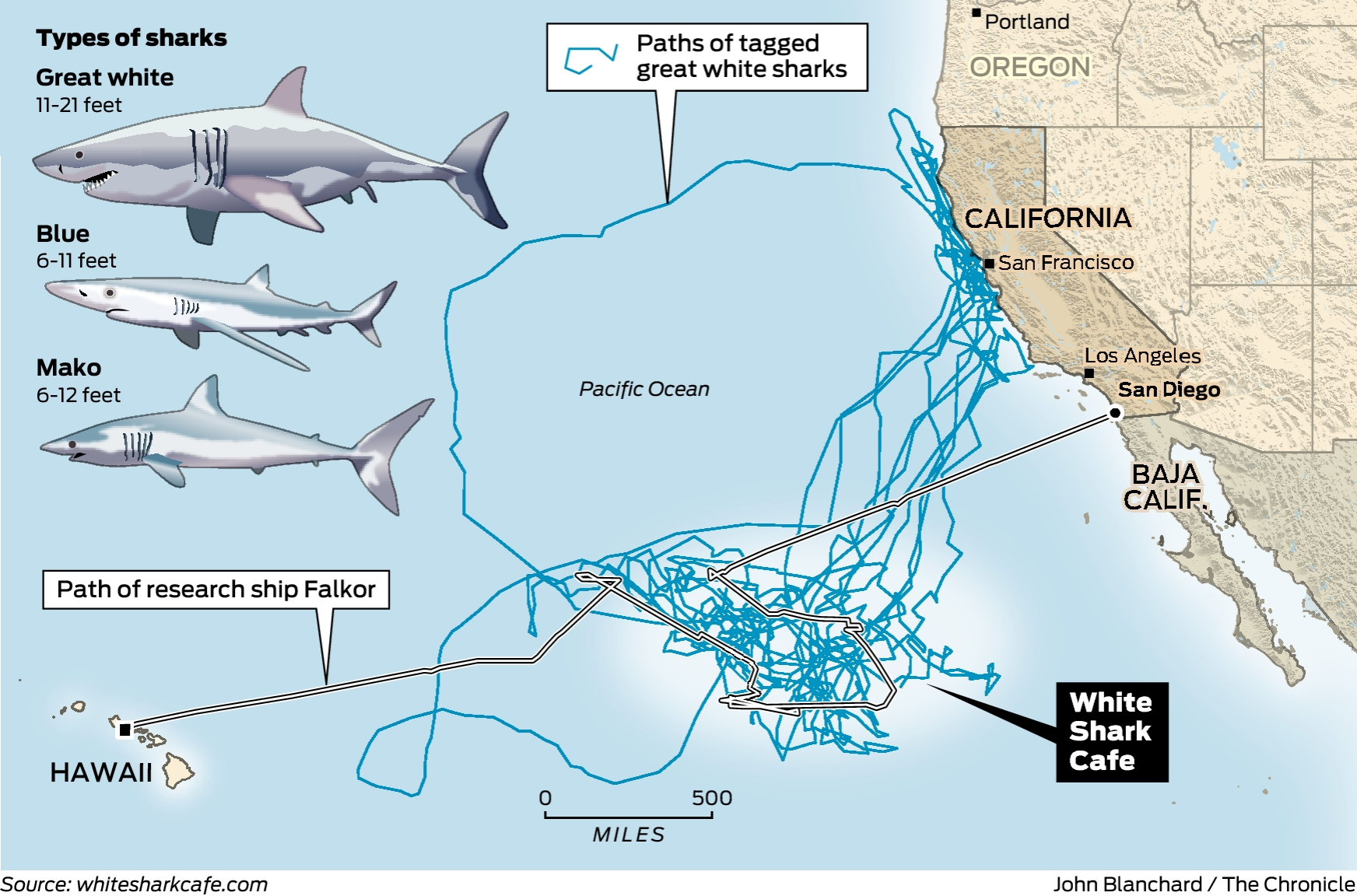
The vast expanse of the ocean harbors countless mysteries, and among its most captivating inhabitants are great white sharks. These apex predators, revered for their size and power, undertake remarkable journeys across the globe, their movements governed by an intricate interplay of environmental factors and biological imperatives. Understanding these migrations is crucial for conservation efforts, informing strategies to protect both sharks and humans.
Charting the Course: Unveiling the Great White’s Travel Routes
Great white sharks, like many other marine species, exhibit distinct migratory patterns, driven by a complex interplay of factors such as:
- Temperature: Great whites are ectothermic, meaning their body temperature is regulated by their environment. They prefer water temperatures between 12°C and 24°C, often migrating to warmer waters during the winter and cooler waters during the summer.
- Food Availability: As apex predators, great whites follow prey populations, moving to areas where seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals are abundant.
- Reproduction: Females may migrate to specific breeding grounds, potentially influenced by the availability of suitable nursery areas for their pups.
- Oceanographic Conditions: Currents and water circulation patterns play a significant role in guiding their movements, influencing their routes and timing.
Mapping the Migratory Routes: A Global Perspective
While specific migration patterns vary across different populations, researchers have identified several key areas and routes:
- California Coast: One of the most well-studied populations resides off the coast of California, where they exhibit seasonal movements between the northern and southern regions. During the summer months, they are often found near the Farallon Islands, a renowned breeding ground and feeding area. In the winter, they migrate south towards Baja California, potentially seeking warmer waters.
- South Africa: The waters off South Africa are another hotspot for great white sharks, with distinct populations inhabiting both the east and west coasts. Along the east coast, they are known to migrate between the Durban area and the Cape Peninsula, while on the west coast, they are frequently observed near Seal Island, a key feeding ground.
- Australia: Australia’s coastline is home to several great white shark populations, each with its unique migration patterns. The eastern population, found off the coast of New South Wales, is known to migrate between the northern and southern regions, potentially influenced by the availability of prey.
- North Atlantic: Great white sharks are also found in the North Atlantic, with populations inhabiting the waters off the coasts of the United States, Canada, and Europe. Their migration patterns in this region are less well-understood, but they are known to travel long distances, crossing vast stretches of ocean.
Advanced Tracking Technologies: Unlocking the Secrets of Migration
The study of great white shark migration has been revolutionized by the advent of advanced tracking technologies. These tools provide researchers with unprecedented insights into their movements, allowing them to:
- Satellite Tagging: Satellite tags are attached to the sharks, transmitting their location data via satellite. This technology allows researchers to track their movements over vast distances, providing valuable information about their migratory routes and timing.
- Acoustic Tagging: Acoustic tags emit signals that are detected by underwater receivers deployed in specific locations. This technology allows researchers to monitor the sharks’ movements within a specific area, providing valuable data on their habitat use and behavior.
- Archival Tagging: Archival tags record data such as temperature, depth, and light levels, which can be downloaded later. This technology provides insights into the sharks’ behavior and physiology over time, including information about their diving patterns and thermal preferences.
The Significance of Understanding Migration Patterns
The study of great white shark migration holds profound implications for both conservation and human safety:
- Conservation: Understanding their migratory patterns is crucial for identifying critical habitats, establishing marine protected areas, and mitigating threats such as fishing gear entanglement and habitat destruction.
- Human Safety: Mapping their movements helps identify areas where encounters with humans are more likely, allowing for better risk assessment and the development of strategies to minimize potential conflicts.
- Scientific Research: Studying their migration patterns provides valuable information about their behavior, ecology, and physiology, contributing to a deeper understanding of these magnificent creatures.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Great White Shark Migration
1. Why do great white sharks migrate?
Great white sharks migrate for a variety of reasons, including seeking warmer waters, following prey populations, breeding, and potentially seeking suitable nursery areas for their pups.
2. How far do great white sharks migrate?
Great white sharks are known to travel vast distances, with some individuals migrating thousands of kilometers across the globe.
3. How long does it take for great white sharks to complete a migration?
The duration of a migration varies depending on the distance traveled, the individual shark, and environmental factors. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
4. How do researchers track great white sharks?
Researchers use advanced tracking technologies, such as satellite tags, acoustic tags, and archival tags, to monitor the movements of great white sharks.
5. Are great white shark migration patterns changing?
Climate change and other environmental factors may be influencing the migration patterns of great white sharks, leading to potential shifts in their distribution and behavior.
6. What are the conservation implications of understanding great white shark migration?
Understanding their migration patterns is crucial for identifying critical habitats, establishing marine protected areas, and mitigating threats to their populations.
7. How can we ensure the safety of humans and great white sharks?
By understanding their migration patterns, we can identify areas where encounters are more likely and develop strategies to minimize potential conflicts, such as shark deterrent devices and responsible fishing practices.
Tips: Contributing to Great White Shark Conservation
- Support organizations dedicated to marine conservation: Contribute to organizations that conduct research on great white sharks and advocate for their protection.
- Promote sustainable fishing practices: Choose seafood from sustainable sources and support policies that limit bycatch and protect marine habitats.
- Reduce your plastic footprint: Plastic pollution poses a significant threat to marine life, including great white sharks. Reduce your plastic consumption and support initiatives that address this issue.
- Educate yourself and others: Learn about great white sharks and share your knowledge with friends and family, promoting understanding and respect for these magnificent creatures.
Conclusion: A Call for Continued Research and Conservation
The study of great white shark migration continues to unveil the intricate workings of these apex predators, revealing their remarkable journeys across the vast ocean. Understanding their movements is crucial for conservation efforts, ensuring the survival of these iconic creatures and safeguarding the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. By supporting research, promoting responsible practices, and raising awareness, we can contribute to the long-term health of great white shark populations and the oceans they call home.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Ocean’s Giants: A Deep Dive into Great White Shark Migration Patterns. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!