Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of Germany
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of Germany
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of Germany. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of Germany

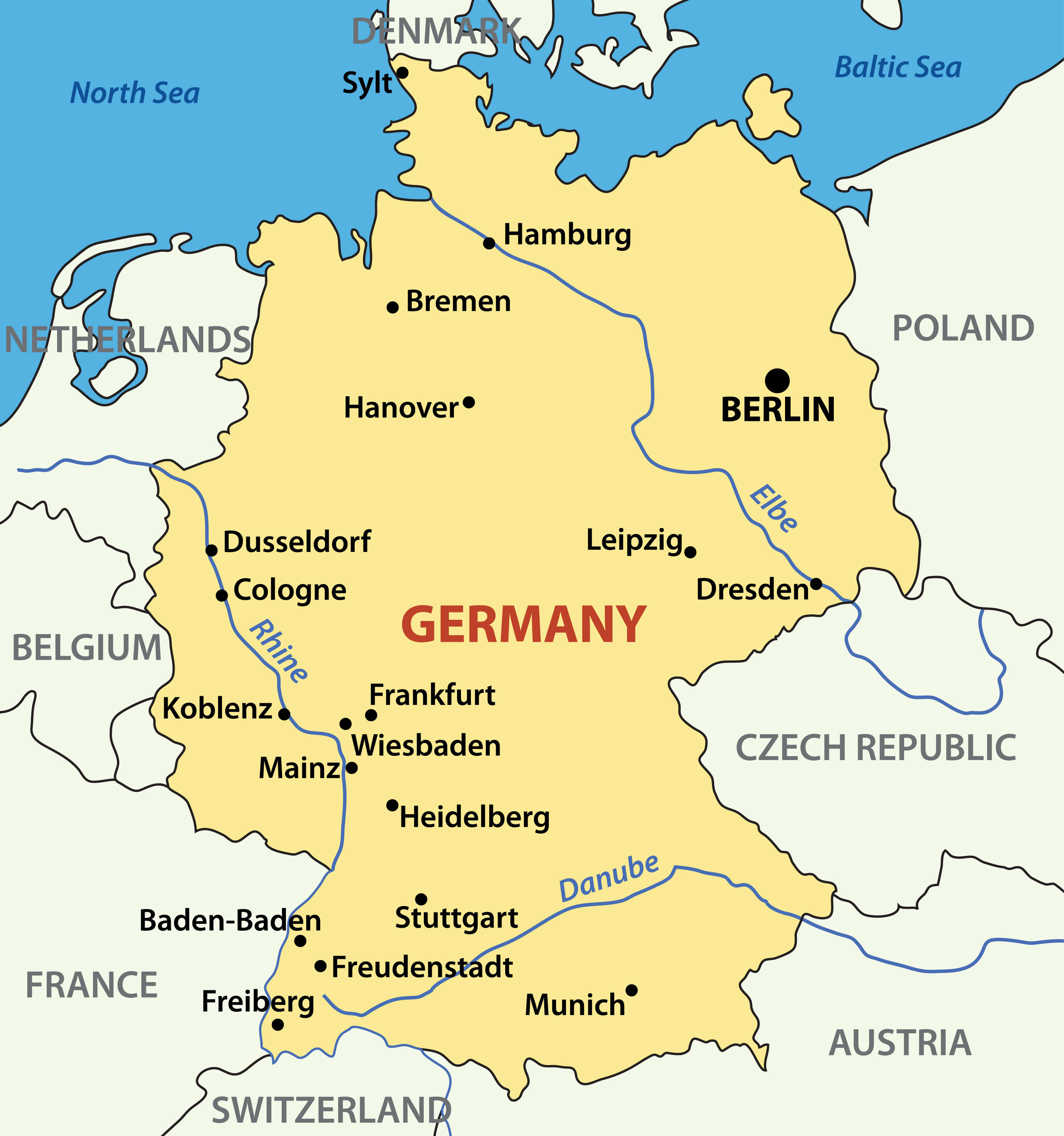
Germany, a nation steeped in history and culture, boasts a diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding the physical geography of this European powerhouse is crucial for comprehending its history, economy, and cultural identity. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Germany’s physical map, exploring its key features, geological formations, and the impact these have on the nation’s character.
A Tapestry of Landscapes: Unveiling Germany’s Physical Features
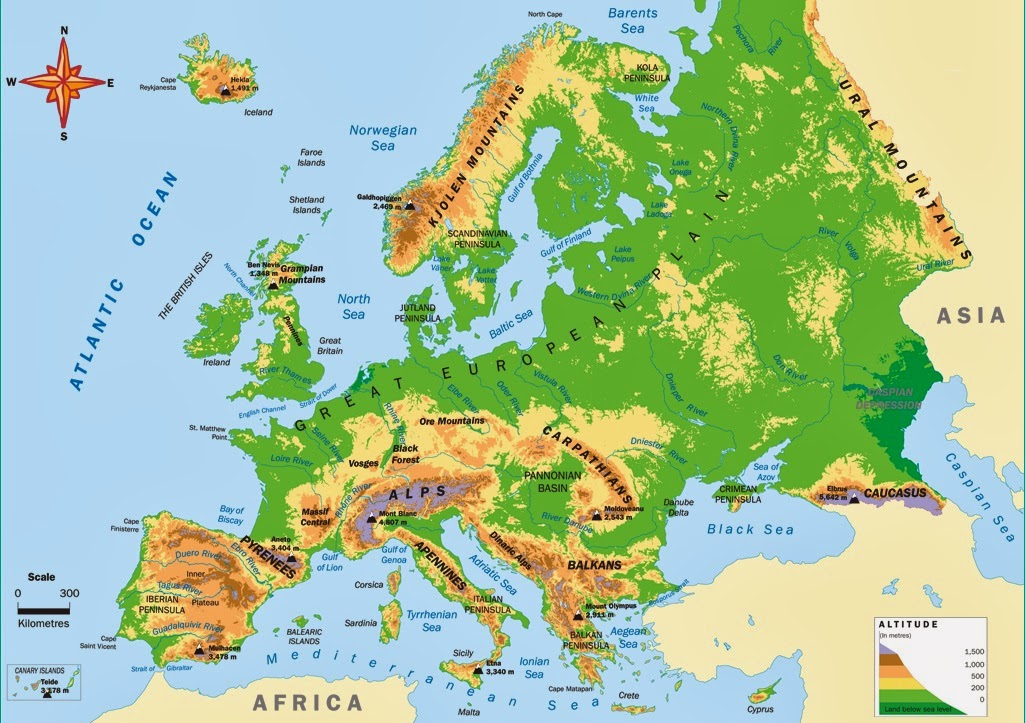
Germany’s physical map reveals a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, each contributing to the nation’s unique character. From the rugged peaks of the Alps to the fertile plains of the North German Plain, the country showcases a remarkable range of geographic features.
1. The North German Plain: A Land of Abundance
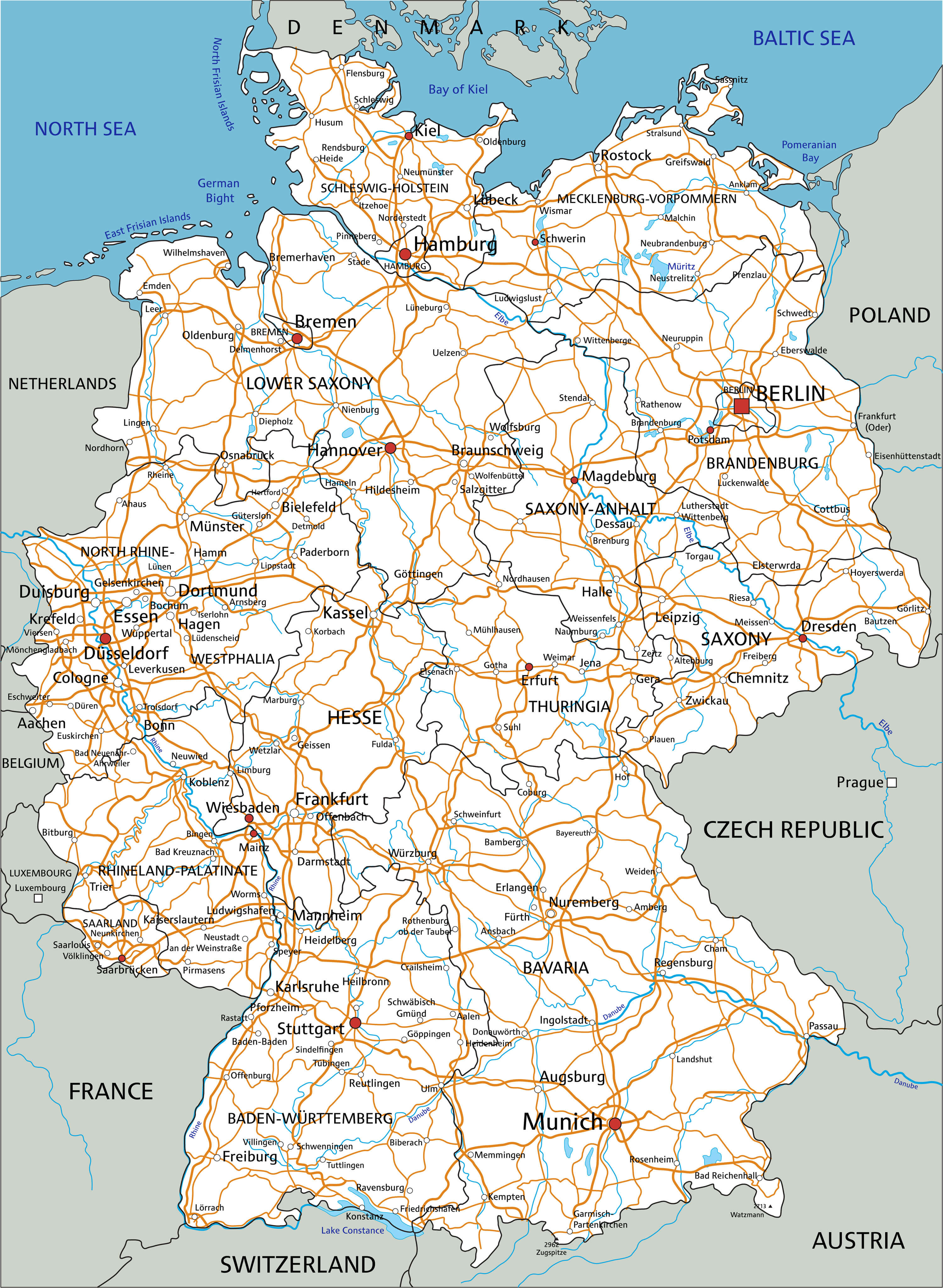
Stretching across the northern half of Germany, the North German Plain is a vast, low-lying expanse characterized by its fertile soils and gentle rolling hills. This region, historically known for its agriculture, is responsible for a significant portion of Germany’s agricultural output. The Elbe, Weser, and Oder rivers wind their way through the plain, providing vital transportation routes and contributing to the region’s agricultural prosperity.
2. The Central Uplands: A Land of Variety
The Central Uplands, a region situated between the North German Plain and the Alps, presents a diverse landscape of rolling hills, forested plateaus, and river valleys. This region is characterized by its rich history, vibrant culture, and a blend of agricultural and industrial activities. The Rhine River, a major waterway traversing the region, has played a crucial role in shaping the Central Uplands’ economic and cultural development.
3. The Alps: A Majestic Mountain Range
The majestic Alps, a towering mountain range that defines Germany’s southern border, are a testament to the country’s dramatic topography. The region’s dramatic peaks, glaciers, and alpine lakes offer breathtaking natural beauty and attract tourists from around the globe. The Alps also play a significant role in shaping Germany’s climate, influencing rainfall patterns and creating a unique microclimate in the southern regions.
4. The German Lowlands: A Coastal Region
The German Lowlands, a coastal region bordering the North Sea and Baltic Sea, are characterized by their flat terrain, sandy beaches, and coastal lagoons. This region is known for its maritime traditions, fishing industry, and picturesque coastal towns. The North Sea and Baltic Sea have played a vital role in shaping Germany’s history and culture, influencing its trade routes and maritime heritage.
Geological Foundations: Shaping Germany’s Landscape
The physical map of Germany is not merely a visual representation; it reflects the country’s complex geological history. The interplay of tectonic forces, volcanic activity, and glacial erosion has sculpted the landscape, creating the diverse features we observe today.
1. The Hercynian Orogeny: A Geological Legacy
The Hercynian Orogeny, a mountain-building event that occurred during the Paleozoic Era, played a crucial role in shaping Germany’s geological foundation. This process, involving the collision of tectonic plates, resulted in the formation of the Central Uplands, a region characterized by its ancient rocks and mineral deposits.
2. The Alpine Orogeny: A More Recent Influence
The Alpine Orogeny, a more recent mountain-building event, occurred during the Cenozoic Era and had a profound impact on Germany’s southern regions. This process, involving the collision of the African and Eurasian plates, resulted in the formation of the Alps, a majestic mountain range that dominates the southern landscape.
3. Glacial Erosion: Shaping the Northern Landscape
During the Quaternary Ice Age, glaciers advanced and retreated across Germany, leaving behind a distinctive mark on the landscape. Glacial erosion shaped the North German Plain, creating its characteristic flat terrain, glacial lakes, and fertile soils. The glaciers also deposited vast quantities of sediment, forming the coastal lowlands and contributing to the region’s fertile agricultural land.
The Importance of Understanding Germany’s Physical Map
Understanding the physical map of Germany offers a valuable lens through which to view the nation’s history, culture, and economy. This knowledge provides insights into:
- Historical Development: The physical landscape has influenced the course of German history, shaping settlement patterns, migration routes, and strategic considerations.
- Economic Activities: The diverse landscape has supported a variety of economic activities, from agriculture in the plains to mining in the mountains and tourism in the Alps.
- Cultural Diversity: Germany’s physical map has contributed to the country’s cultural diversity, influencing regional dialects, traditions, and architectural styles.
FAQs: Exploring the Physical Map of Germany
Q: What is the highest mountain in Germany?
A: The highest mountain in Germany is Zugspitze, located in the Bavarian Alps, with a summit elevation of 2,962 meters (9,718 feet).
Q: What is the largest river in Germany?
A: The largest river in Germany is the Rhine River, which flows for approximately 1,230 kilometers (764 miles) through the country.
Q: What are the major climate zones in Germany?
A: Germany experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The northern regions have a more maritime climate with mild winters and cool summers, while the southern regions experience a more continental climate with colder winters and warmer summers.
Q: What are some of the major geological formations in Germany?
A: Germany’s geological formations include the Hercynian Uplands, the Alpine Orogeny, and the North German Plain, each with its own unique geological history and characteristics.
Tips for Studying the Physical Map of Germany
- Utilize Online Resources: Interactive maps, satellite imagery, and digital elevation models provide valuable tools for exploring Germany’s physical map.
- Explore Physical Geography Textbooks: Textbooks on physical geography offer comprehensive information about Germany’s landscape, geological history, and climate.
- Visit Germany: Experiencing Germany’s diverse landscapes firsthand provides a deeper understanding of the country’s physical map and its impact on the nation’s character.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Physical Map of Germany
The physical map of Germany is more than just a visual representation; it is a testament to the country’s complex geological history, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural tapestry. By understanding the interplay of geological forces, climate patterns, and human activity, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique character of this European nation. From the rolling hills of the Central Uplands to the majestic peaks of the Alps, Germany’s physical map reveals a captivating story of nature, history, and human ingenuity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of Germany. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!