Unmasking the Enemy: Understanding Malaria in Africa through Mapping
Related Articles: Unmasking the Enemy: Understanding Malaria in Africa through Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Enemy: Understanding Malaria in Africa through Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Enemy: Understanding Malaria in Africa through Mapping
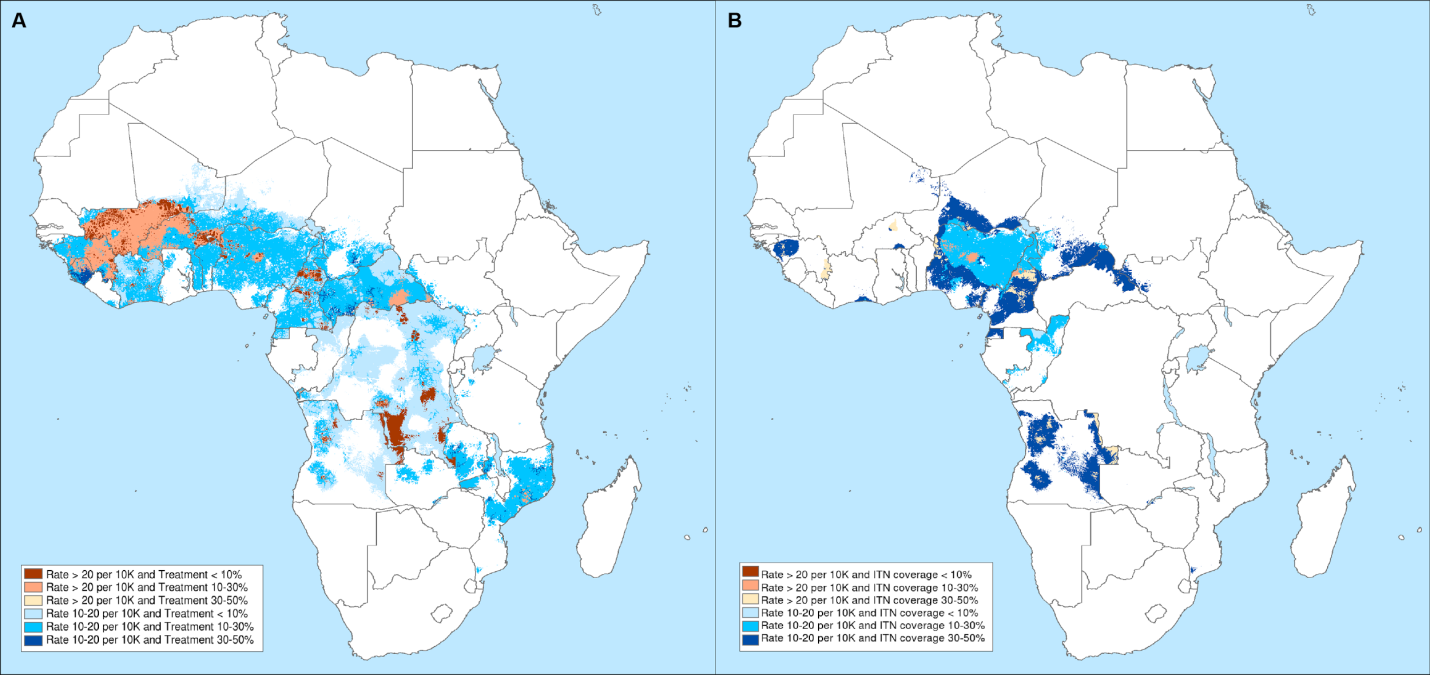
Malaria, a mosquito-borne disease, has plagued humanity for centuries, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Africa, with its vast expanse and diverse climates, bears the brunt of this parasitic burden. The continent accounts for over 90% of global malaria cases and deaths, with children under five years of age being the most vulnerable.
To effectively combat this public health crisis, understanding the geographical distribution of malaria is paramount. This is where malaria maps come into play. These visual representations, often incorporating data from diverse sources, provide invaluable insights into the prevalence and intensity of malaria transmission across the continent.
Mapping Malaria: A Multifaceted Approach
Malaria maps are not merely static representations of disease hotspots. They are dynamic tools that evolve with the changing landscape of malaria transmission. Several factors influence the accuracy and relevance of these maps:
-
Data Sources: Data for malaria maps is collected through various means, including:
- Surveillance Systems: National and regional surveillance programs collect data on reported malaria cases, contributing to the understanding of current trends.
- Surveys: Regular surveys, often conducted in collaboration with local communities, provide valuable information on parasite prevalence and mosquito densities.
- Climate and Environmental Data: Factors like rainfall patterns, temperature fluctuations, and vegetation cover play a significant role in mosquito breeding and malaria transmission. Satellite imagery and climate models contribute to this data pool.
-
Mapping Techniques: Various mapping techniques are employed, each with its strengths and limitations:
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use color gradients to depict variations in malaria prevalence across different geographic units, such as districts or provinces.
- Point Maps: These maps display individual malaria cases or outbreaks, providing a granular view of disease distribution.
- Risk Maps: These maps combine data from multiple sources to predict the likelihood of malaria transmission in specific areas, aiding in targeted interventions.
- Time Dimension: Malaria maps are not static snapshots. They can be dynamic, incorporating temporal data to illustrate trends over time. This allows for the identification of areas where malaria prevalence is increasing or decreasing, enabling a more informed response to the disease.
Benefits of Malaria Maps: Guiding Strategies for a Healthier Africa
Malaria maps provide a wealth of information that is instrumental in guiding effective malaria control and elimination strategies:
- Targeted Interventions: Maps help identify areas with high malaria transmission, allowing for the allocation of resources and interventions where they are most needed. This ensures that control efforts are efficient and reach those most at risk.
- Prioritizing Research: Understanding the geographical distribution of malaria helps prioritize research efforts. For example, mapping studies can identify areas where drug resistance is emerging, prompting the development of new treatment strategies.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Malaria maps are essential for monitoring the effectiveness of control programs. By comparing maps over time, program managers can assess the impact of interventions and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Early Warning Systems: Mapping can help predict outbreaks and identify areas at risk of resurgence. This allows for the timely implementation of preventive measures, reducing the spread of the disease.
- Public Health Education: Malaria maps can be used to educate communities about the risks of malaria and promote preventive measures. This empowers individuals to take ownership of their health and reduce their vulnerability to the disease.
Challenges and Future Directions
While malaria maps offer invaluable insights, challenges remain in their development and application:
- Data Availability and Quality: In many parts of Africa, data collection remains inconsistent or incomplete, limiting the accuracy of malaria maps. This emphasizes the need for robust surveillance systems and reliable data sources.
- Resource Constraints: Developing and maintaining effective malaria mapping systems requires significant resources, including technical expertise, data management infrastructure, and financial support.
- Integrating Diverse Data: Combining data from different sources, such as climate models, surveillance systems, and community surveys, requires sophisticated analytical techniques to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Community Engagement: Involving communities in the mapping process is crucial for ensuring the relevance and usability of these tools. This includes promoting understanding of mapping data and fostering local ownership of control efforts.
Looking Ahead: A Collaborative Approach to Malaria Control
The future of malaria mapping lies in collaborative efforts that combine expertise from diverse fields. This includes:
- Technological Advancements: Integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and remote sensing can enhance data analysis and prediction capabilities.
- Cross-Sectoral Collaboration: Collaboration between health ministries, research institutions, and international organizations is essential to overcome data gaps and ensure the effective use of mapping information.
- Community Participation: Empowering communities to participate in data collection and interpretation is crucial for building ownership and ensuring the relevance of mapping efforts.
FAQs on Malaria Maps in Africa
Q: What is the purpose of malaria maps in Africa?
A: Malaria maps serve as vital tools to understand the geographical distribution of malaria, identify areas with high transmission rates, and guide the allocation of resources and interventions for effective control and elimination.
Q: How are malaria maps created?
A: Malaria maps are developed using data from various sources, including surveillance systems, surveys, climate and environmental data. Mapping techniques like choropleth maps, point maps, and risk maps are employed to visualize the data.
Q: How do malaria maps benefit public health?
A: Malaria maps enable targeted interventions, prioritize research, monitor program effectiveness, predict outbreaks, and educate communities about malaria prevention.
Q: What are the challenges associated with malaria mapping?
A: Challenges include data availability and quality, resource constraints, integrating diverse data, and community engagement.
Q: What are the future directions for malaria mapping in Africa?
A: The future holds promise for technological advancements, cross-sectoral collaboration, and community participation to enhance mapping capabilities and guide malaria control efforts.
Tips for Using Malaria Maps Effectively
- Understand the data sources and limitations of the map.
- Consider the temporal and spatial scales of the map.
- Use the map in conjunction with other data sources and expert knowledge.
- Involve communities in the interpretation and application of the map.
- Continuously update and refine the map based on new data and insights.
Conclusion: A Map for a Healthier Future
Malaria maps are not just visual representations; they are powerful tools for understanding, controlling, and ultimately eliminating malaria in Africa. By leveraging the insights gleaned from these maps, researchers, policymakers, and communities can work together to build a healthier future for the continent. Through collaborative efforts, continuous innovation, and a commitment to data-driven decision-making, the fight against malaria can be strengthened, paving the way for a future free from this debilitating disease.



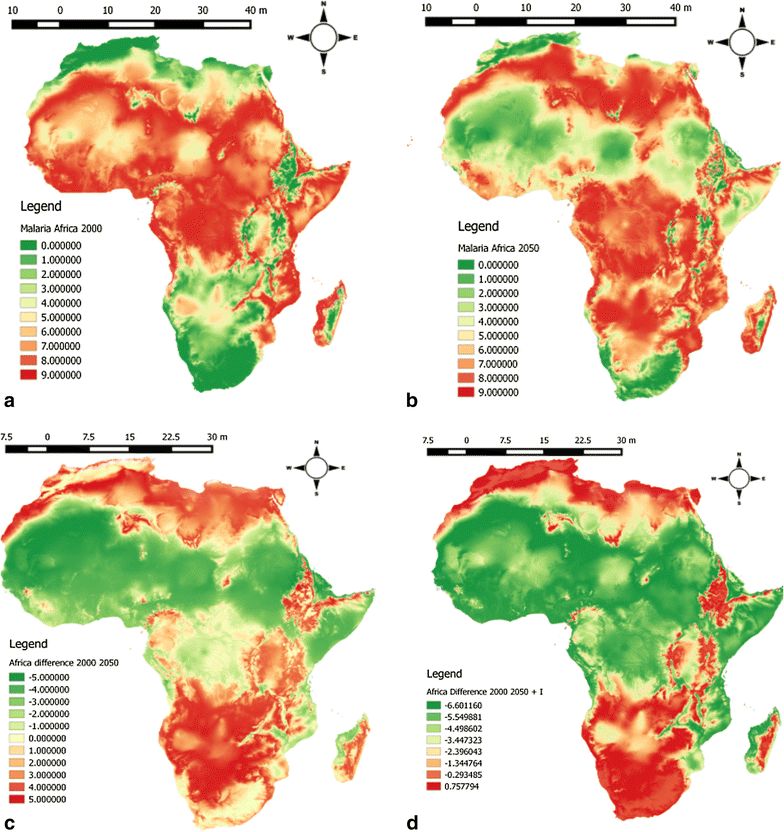
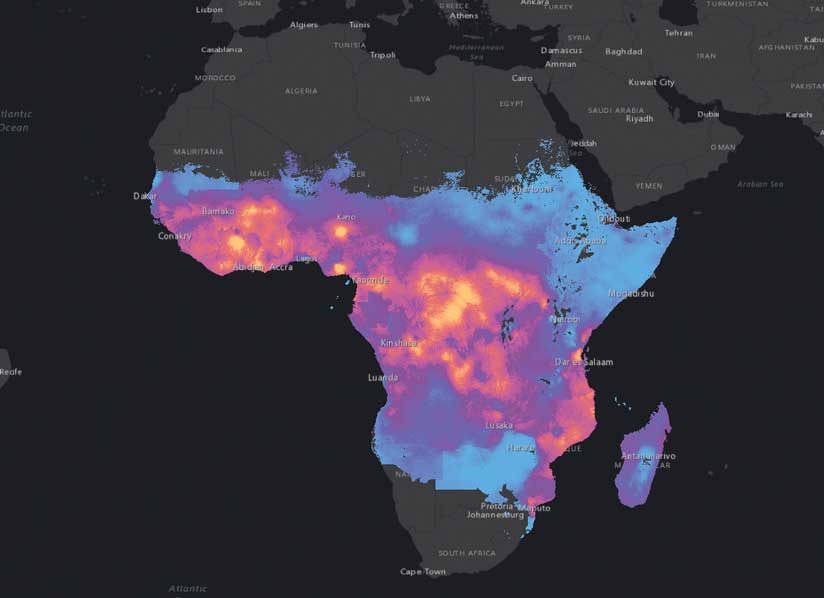



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Enemy: Understanding Malaria in Africa through Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!