The West Bank: A Complex Landscape of Settlements
Related Articles: The West Bank: A Complex Landscape of Settlements
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The West Bank: A Complex Landscape of Settlements. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The West Bank: A Complex Landscape of Settlements
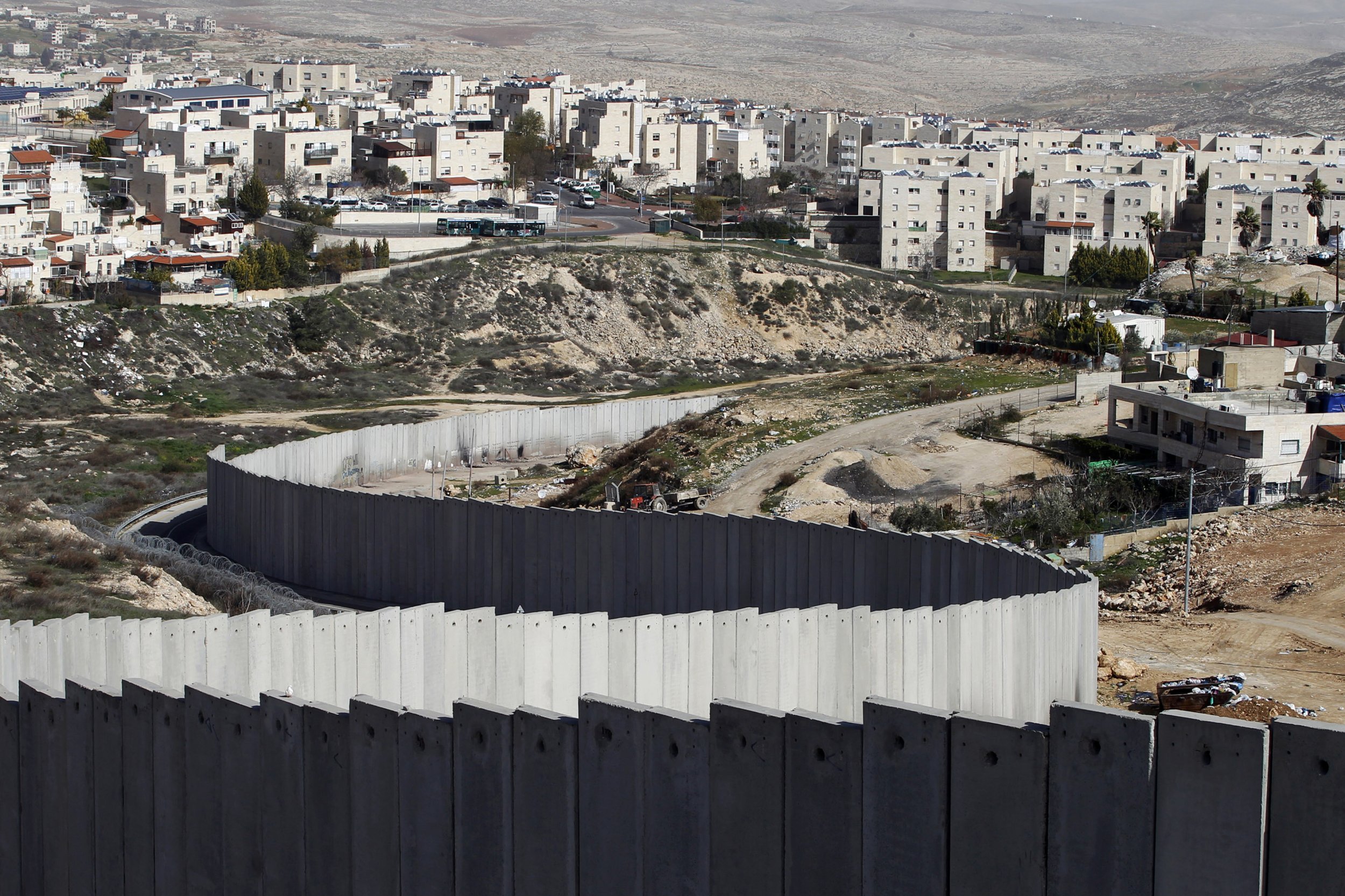

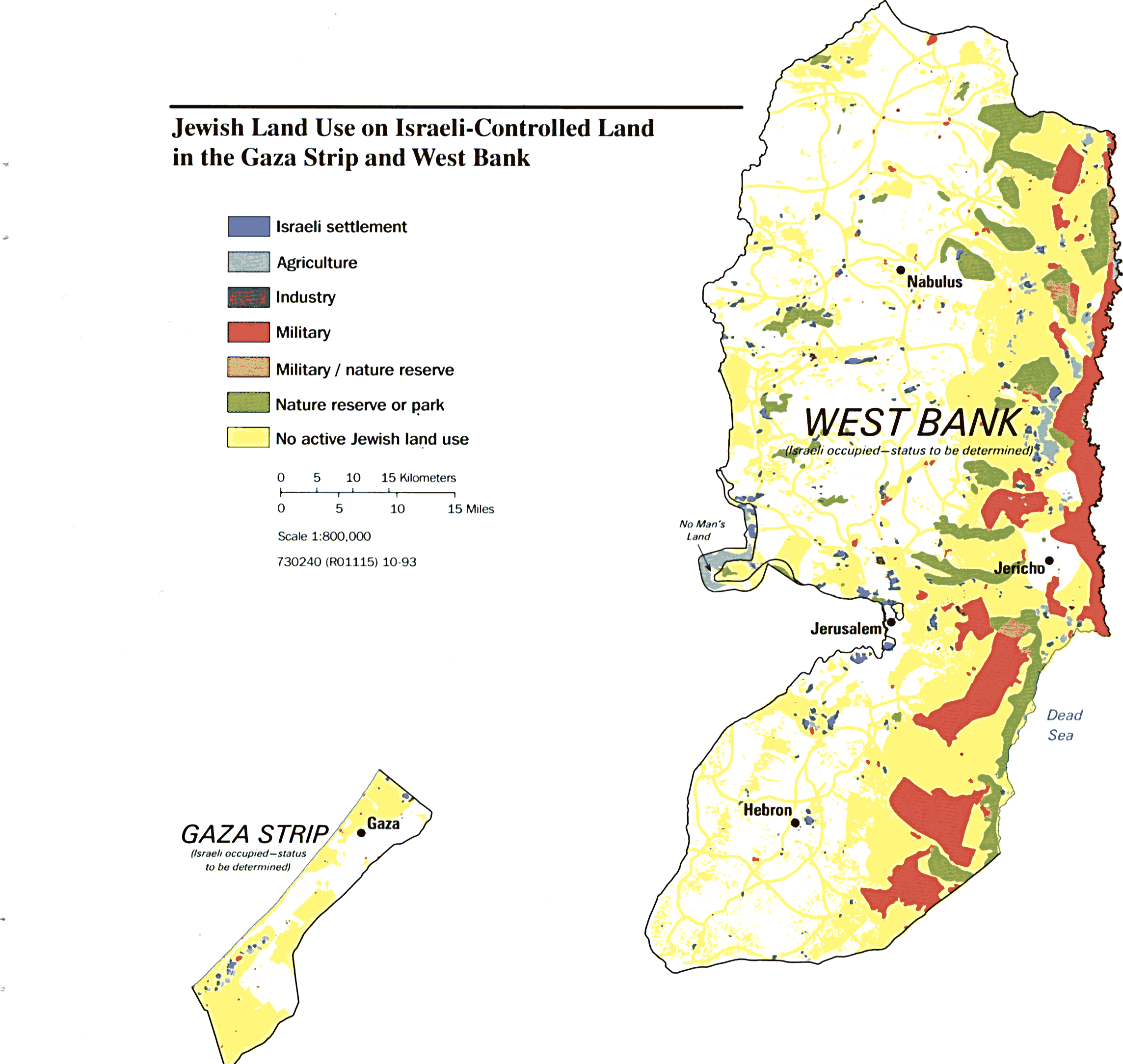
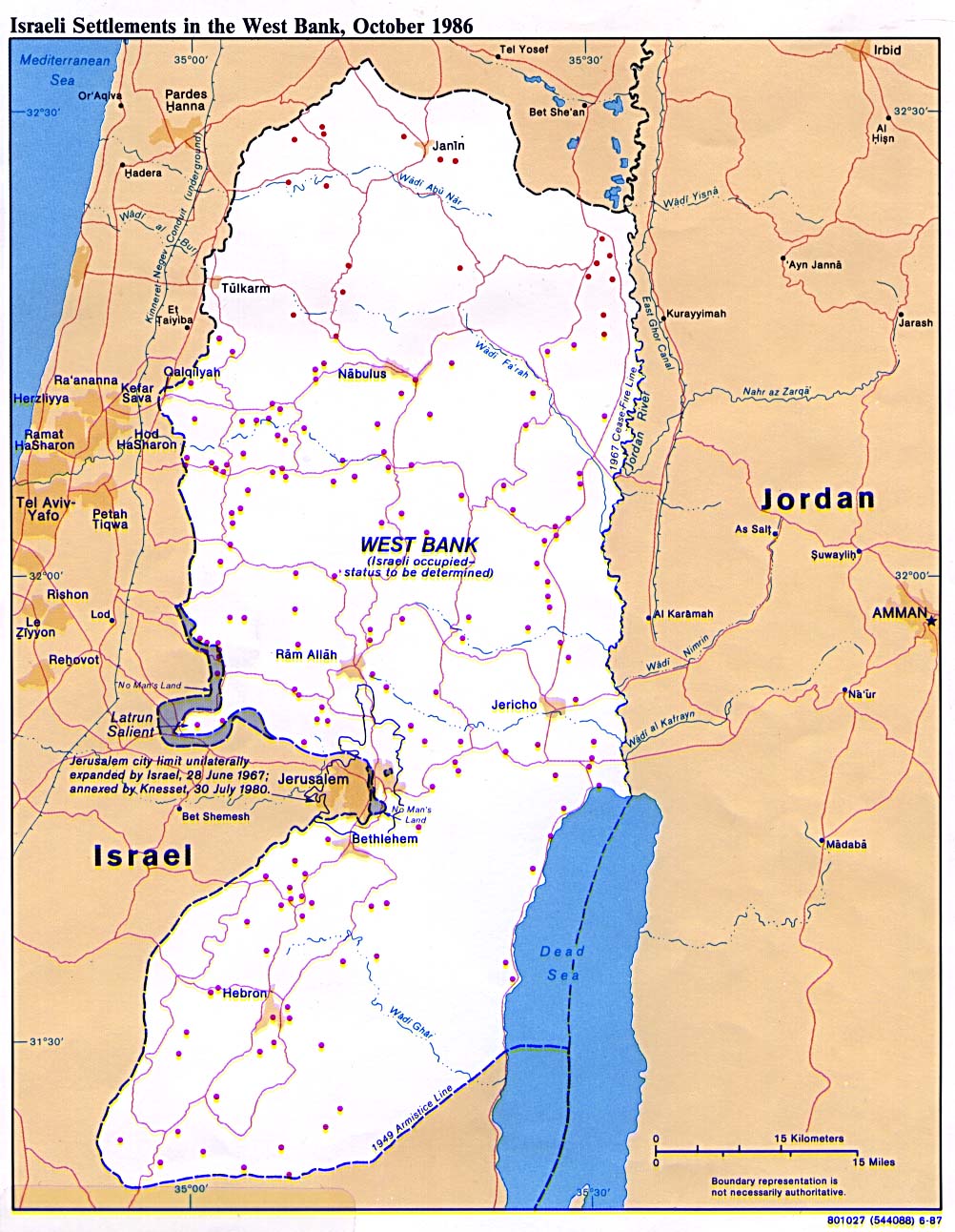
The West Bank, a territory situated between Israel and Jordan, is a focal point of international attention due to its intricate geopolitical landscape. Within this territory lie Israeli settlements, a significant component of the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Understanding the distribution and significance of these settlements requires a comprehensive examination of their historical context, legal status, and the impact they have on the region.
Historical Background:
The establishment of Israeli settlements in the West Bank began in the aftermath of the 1967 Six-Day War, when Israel captured the territory from Jordan. Initially, settlements were primarily established in areas with strategic military importance. However, over time, the settlement movement gained momentum, driven by a range of factors, including:
- Religious and ideological motivations: Some settlers believe that the West Bank is biblically ordained as part of the land of Israel, justifying their presence.
- Security concerns: Proponents of settlements argue that they bolster Israel’s security by creating a buffer zone against potential threats.
- Economic benefits: Settlements have provided economic opportunities for Israelis, particularly in agriculture and tourism.
Legal Status:
The legal status of Israeli settlements in the West Bank is highly contested. The international community, including the United Nations Security Council, considers settlements illegal under international law, citing the Fourth Geneva Convention, which prohibits an occupying power from transferring its own civilian population into occupied territory.
Israel, however, maintains that its settlements are legal, arguing that the West Bank is not an occupied territory but rather disputed land with historical and religious claims.
Geographical Distribution:
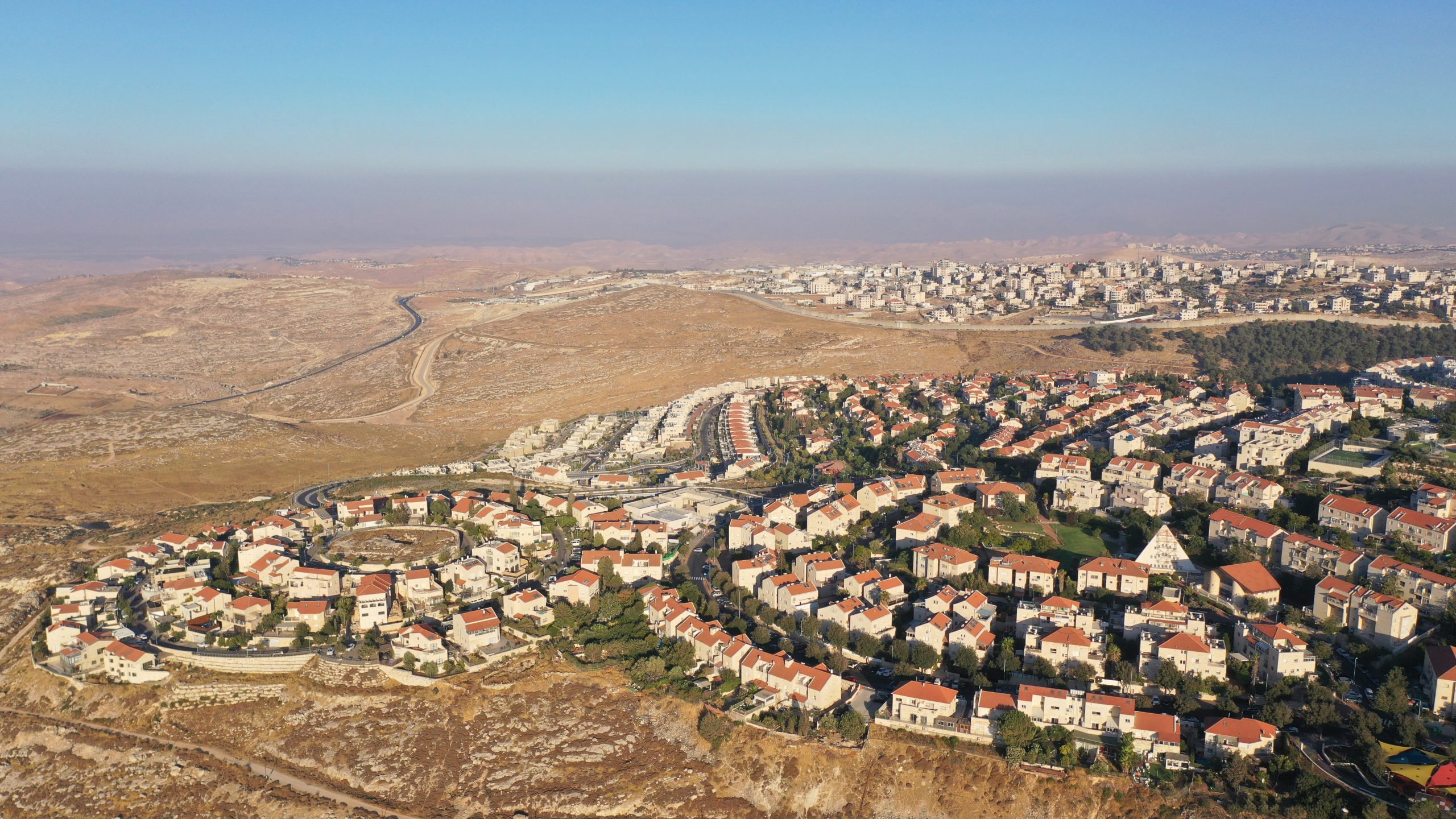
Israeli settlements are scattered throughout the West Bank, with varying densities and sizes. The majority of settlements are clustered in the following areas:
- The Jordan Valley: This strategically important area bordering Jordan holds significant agricultural potential and is home to a number of large settlements.
- Jerusalem: The city of Jerusalem, considered sacred by both Jews and Muslims, is a major focal point of settlement activity.
- The Gush Etzion Bloc: This area, located south of Jerusalem, is a densely populated region with a significant number of settlements.
- The Samaria region: This region, located north of Jerusalem, is home to a large number of settlements, including the city of Ariel.
Impact on the Palestinian Population:
The presence of Israeli settlements in the West Bank has a significant impact on the Palestinian population. Key concerns include:
- Land confiscation: The expansion of settlements often involves the confiscation of Palestinian land, hindering their ability to develop their own communities.
- Restrictions on movement: The presence of settlements and associated security measures create barriers to Palestinian movement, making it difficult for them to access their land, jobs, and essential services.
- Water resources: Settlements have access to a disproportionate amount of water resources, impacting the availability of water for Palestinian communities.
- Political and economic limitations: The presence of settlements hinders the creation of a viable Palestinian state, limiting economic opportunities and political autonomy.
International Reactions and Responses:
The international community has condemned the establishment and expansion of Israeli settlements in the West Bank. Numerous resolutions have been passed by the United Nations Security Council and General Assembly, calling for their dismantling.
The European Union has implemented a policy of labeling products produced in settlements, and many countries have imposed sanctions on companies operating in them.
The Future of Settlements:
The future of settlements in the West Bank is uncertain and hinges on the outcome of the Israeli-Palestinian peace process.
- Continued expansion: Proponents of settlements argue for their continued expansion, citing security and economic benefits.
- Negotiated solution: Advocates for a two-state solution emphasize the need to dismantle settlements as a precondition for peace.
- International pressure: The international community continues to exert pressure on Israel to halt settlement expansion, hoping to create an environment conducive to peace negotiations.
Conclusion:
The settlement map of the West Bank is a complex and dynamic landscape that reflects the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Understanding the historical, legal, and social dimensions of settlements is crucial for comprehending the challenges facing the region and the potential for a peaceful resolution. The future of the West Bank, and the fate of its Palestinian and Israeli inhabitants, will likely be determined by the choices made regarding the future of settlements.
FAQs about Israeli Settlements in the West Bank:
1. What is the legal status of Israeli settlements in the West Bank?
The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal under international law, citing the Fourth Geneva Convention, which prohibits an occupying power from transferring its own civilian population into occupied territory. Israel, however, maintains that its settlements are legal, arguing that the West Bank is not an occupied territory but rather disputed land with historical and religious claims.
2. What are the main motivations behind the establishment of Israeli settlements?
Motivations for establishing settlements in the West Bank are multifaceted and include religious and ideological beliefs, security concerns, and economic benefits. Some settlers believe that the West Bank is biblically ordained as part of the land of Israel, while others argue that settlements strengthen Israel’s security by creating a buffer zone against potential threats. Additionally, settlements have provided economic opportunities for Israelis, particularly in agriculture and tourism.
3. How do settlements impact the Palestinian population?
The presence of Israeli settlements in the West Bank has significant negative impacts on the Palestinian population, including land confiscation, restrictions on movement, water resource limitations, and political and economic constraints. The expansion of settlements often involves the confiscation of Palestinian land, hindering their ability to develop their own communities. Security measures associated with settlements create barriers to Palestinian movement, making it difficult for them to access their land, jobs, and essential services. Settlements also have access to a disproportionate amount of water resources, impacting the availability of water for Palestinian communities. Moreover, the presence of settlements hinders the creation of a viable Palestinian state, limiting economic opportunities and political autonomy.
4. What are the international reactions to Israeli settlements?
The international community has condemned the establishment and expansion of Israeli settlements in the West Bank. Numerous resolutions have been passed by the United Nations Security Council and General Assembly, calling for their dismantling. The European Union has implemented a policy of labeling products produced in settlements, and many countries have imposed sanctions on companies operating in them.
5. What are the potential future scenarios for settlements in the West Bank?
The future of settlements in the West Bank is uncertain and hinges on the outcome of the Israeli-Palestinian peace process. Proponents of settlements argue for their continued expansion, citing security and economic benefits. Advocates for a two-state solution emphasize the need to dismantle settlements as a precondition for peace. The international community continues to exert pressure on Israel to halt settlement expansion, hoping to create an environment conducive to peace negotiations.
Tips for Understanding the Settlement Map of the West Bank:
- Consult reliable sources: Utilize reputable academic journals, news organizations, and international organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
- Consider multiple perspectives: Acknowledge the perspectives of both Israelis and Palestinians, as well as the international community, to gain a balanced perspective.
- Analyze maps and data: Visualize the geographical distribution of settlements and their impact on surrounding Palestinian communities.
- Engage in critical thinking: Question assumptions, evaluate evidence, and consider the potential consequences of different policy options.
- Stay informed about current developments: The situation in the West Bank is constantly evolving, so it is important to stay informed about the latest developments and events.
Conclusion:
The settlement map of the West Bank is a complex and sensitive issue with significant implications for the future of the region. Understanding the historical context, legal status, and impact of settlements is crucial for appreciating the challenges and opportunities for peace in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The choices made regarding the future of settlements will have profound consequences for the lives of both Palestinians and Israelis.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The West Bank: A Complex Landscape of Settlements. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!