The Shifting Landscape of Wolves in Wisconsin: A 2020 Perspective
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Wolves in Wisconsin: A 2020 Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Wolves in Wisconsin: A 2020 Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape of Wolves in Wisconsin: A 2020 Perspective
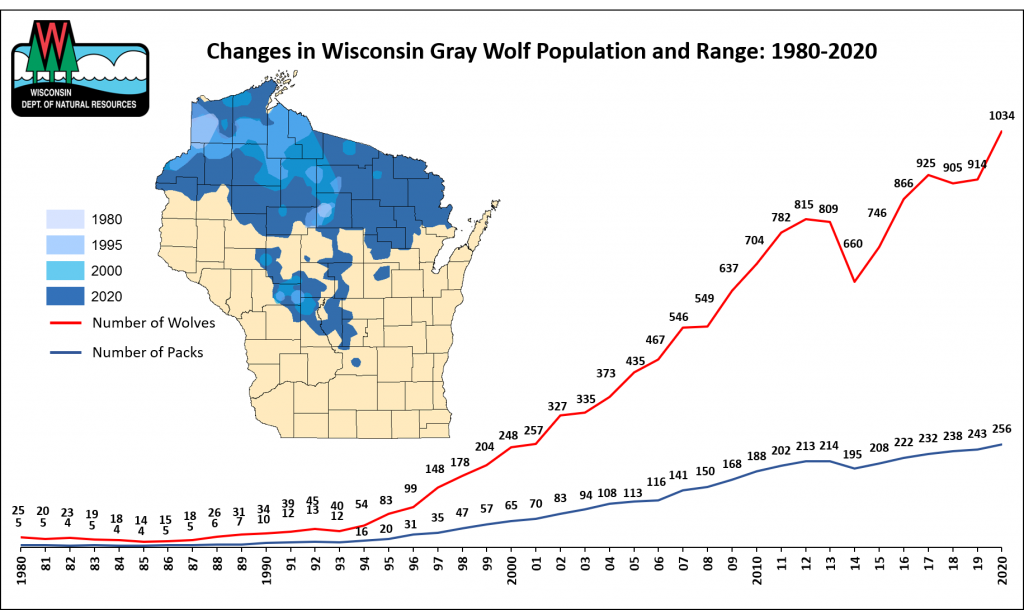
The presence of wolves in Wisconsin has been a subject of ongoing debate and fascination, with their populations experiencing significant fluctuations over time. Understanding the distribution and movement of these apex predators is crucial for managing their interactions with humans and the broader ecosystem. This exploration delves into the 2020 landscape of wolves in Wisconsin, providing insights into their geographic presence, population trends, and the implications for wildlife management.
A Historical Overview: From Near Extinction to Reintroduction
Wolves were once widespread throughout Wisconsin, playing a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. However, due to extensive hunting and trapping, their numbers dwindled significantly throughout the 20th century. By the 1960s, wolves were effectively extirpated from the state. Recognizing the ecological importance of wolves, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) listed them as an endangered species in 1974.
In the early 1980s, a reintroduction program was initiated, with wolves being brought in from Canada. These wolves successfully established themselves in the northern parts of the state, gradually expanding their range.
Mapping the Presence of Wolves in Wisconsin: A 2020 Snapshot
By 2020, wolves had re-established themselves in numerous counties across northern Wisconsin, with their presence concentrated in the forested areas. While their exact distribution varies from year to year, the following points highlight key characteristics:
- Core Areas: The core wolf population areas are located in the Chequamegon-Nicolet National Forest, the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore, and the northern portions of the Chippewa National Forest. These areas provide suitable habitat and ample prey for wolves.
- Expanding Range: While wolves are primarily found in the northern regions, they have been observed venturing further south in recent years, indicating a gradual expansion of their range.
- Human-Wolf Interactions: As wolves continue to expand their territory, encounters between humans and wolves are becoming more frequent. This highlights the importance of understanding wolf behavior and implementing strategies to minimize conflict.
Understanding the Dynamics of Wolf Populations: A Complex Ecosystem
The wolf population in Wisconsin is not static. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Habitat Availability: The availability of suitable habitat, particularly forested areas with ample prey, is a primary determinant of wolf population size.
- Prey Abundance: Wolves rely on a variety of prey species, including deer, moose, and smaller mammals. Fluctuations in prey populations can impact wolf survival and reproduction.
- Human Influence: Human activities, such as hunting, trapping, and habitat fragmentation, can significantly impact wolf populations.
- Disease and Parasitism: Like any other species, wolves are susceptible to disease and parasites, which can influence their health and survival.
The Importance of Monitoring and Management: Ensuring Sustainable Coexistence
Monitoring and managing wolf populations are essential for ensuring their long-term sustainability and mitigating potential conflicts with humans. The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) plays a critical role in this process, employing a range of methods:
- Population Estimates: The WDNR uses a variety of methods, including aerial surveys and genetic analysis, to estimate the size of the wolf population and track its changes over time.
- Habitat Management: The WDNR manages forest habitats to provide suitable conditions for wolves and their prey species.
- Conflict Mitigation: The WDNR works to minimize conflicts between wolves and humans by promoting responsible livestock management practices, educating the public about wolf behavior, and addressing concerns about livestock depredation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Wolves in Wisconsin
Q: How many wolves are there in Wisconsin?
A: The WDNR conducts regular population estimates, with the most recent estimate indicating a population of several hundred wolves.
Q: Are wolves dangerous to humans?
A: While wolves are wild animals, they are generally wary of humans and avoid contact. Attacks on humans are extremely rare. However, it is important to maintain a safe distance from wolves and to never approach them.
Q: What can I do if I encounter a wolf?
A: If you encounter a wolf, remain calm and do not approach it. Make yourself appear large by raising your arms and shouting. If the wolf does not retreat, back away slowly.
Q: How can I help protect wolves in Wisconsin?
A: You can support wolf conservation by educating yourself about their role in the ecosystem, supporting organizations that work to protect wolves, and advocating for responsible wildlife management practices.
Tips for Responsible Wildlife Viewing
- Observe from a distance: Never approach a wolf or any other wild animal.
- Use binoculars or a spotting scope: This allows you to view wildlife without disturbing them.
- Stay on designated trails: This helps to minimize your impact on the environment and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Keep noise levels down: Loud noises can scare wildlife and disrupt their natural behavior.
- Pack out everything you pack in: Leave no trace of your presence in the wild.
Conclusion: A Complex and Evolving Relationship
The presence of wolves in Wisconsin is a testament to the resilience of nature and the success of conservation efforts. While their reintroduction has brought ecological benefits, it has also posed challenges in terms of managing human-wildlife interactions. Understanding the dynamics of wolf populations and implementing responsible management strategies are crucial for ensuring the long-term health of wolves and the ecosystems they inhabit. By fostering a deeper understanding of these magnificent animals and promoting responsible interactions, we can continue to coexist with wolves in a manner that benefits both humans and wildlife.
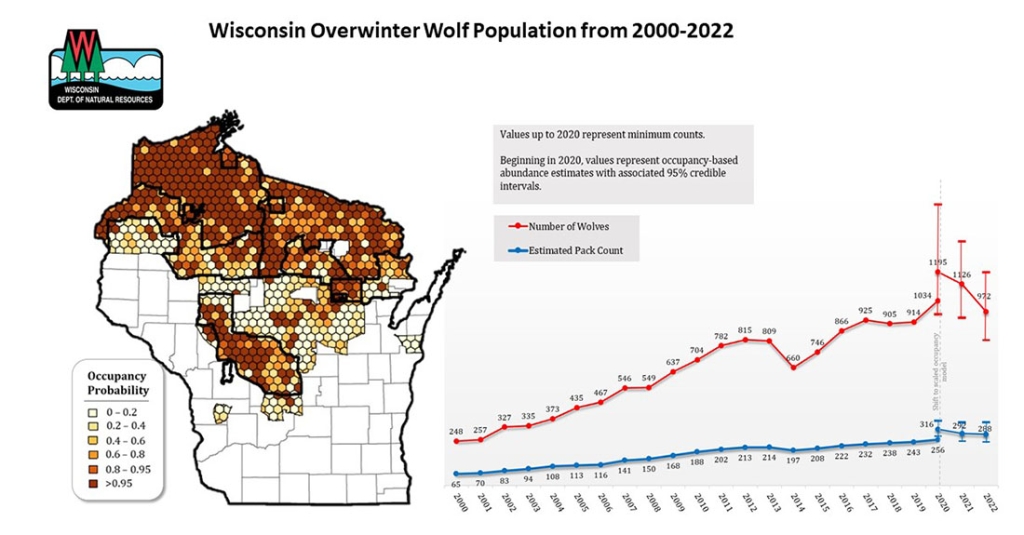







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Wolves in Wisconsin: A 2020 Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!