The Shifting Landscape of Germany: A Look at the Map of 1945
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Germany: A Look at the Map of 1945
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Germany: A Look at the Map of 1945. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape of Germany: A Look at the Map of 1945

The year 1945 marked a pivotal moment in German history, a year of both devastation and the beginning of a new era. The map of Germany in 1945 reflected the profound changes wrought by the Second World War, a war that left the country physically and politically fractured. Understanding this map is essential to grasping the complexities of post-war Germany, its subsequent division, and the eventual reunification.
The Aftermath of War: A Divided Nation
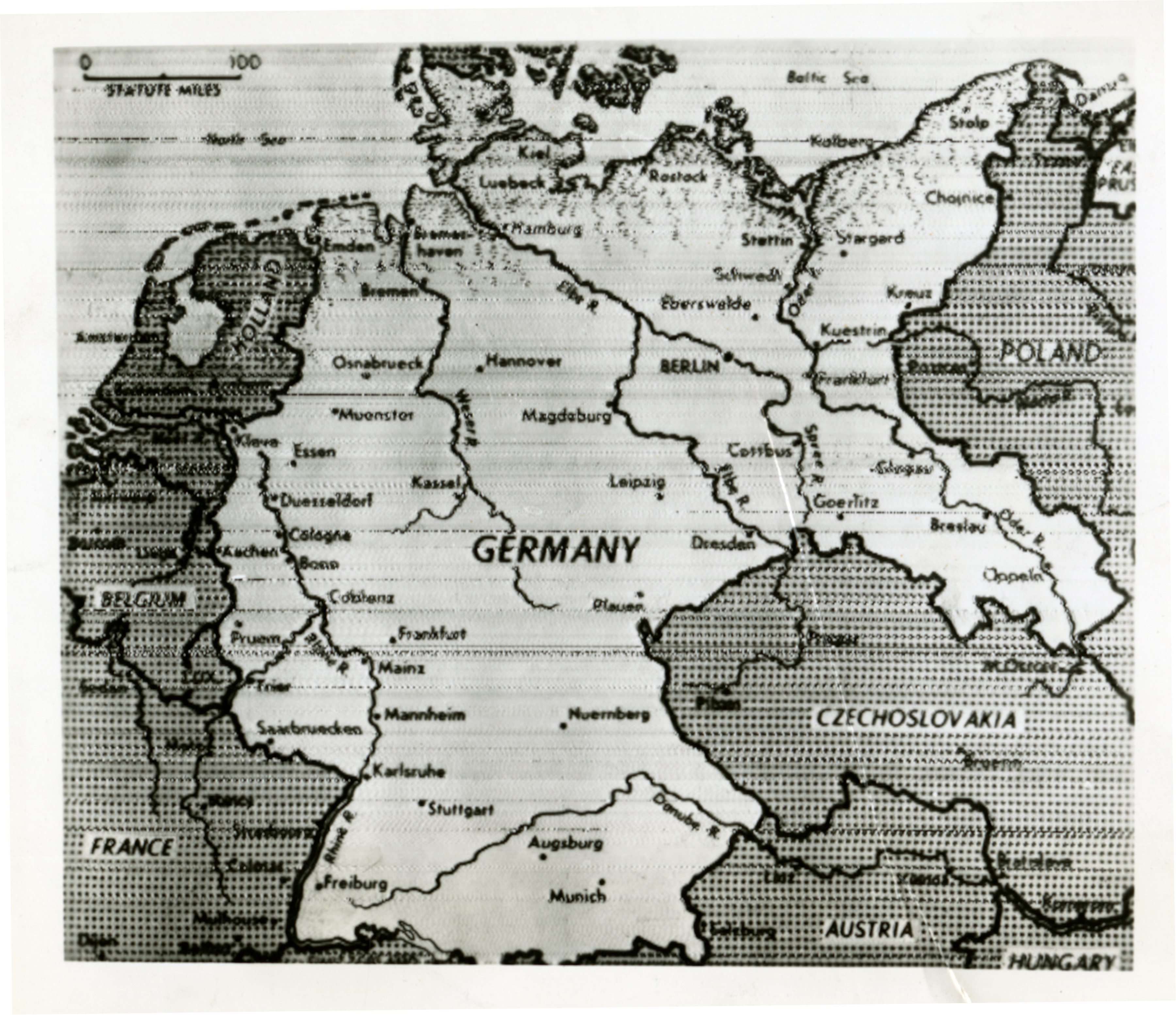
The map of Germany in 1945 showcased a nation divided into four occupation zones, each controlled by one of the Allied powers: the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France. This division was a direct consequence of the Potsdam Conference, where the victorious Allies agreed on the terms of Germany’s surrender and subsequent occupation.
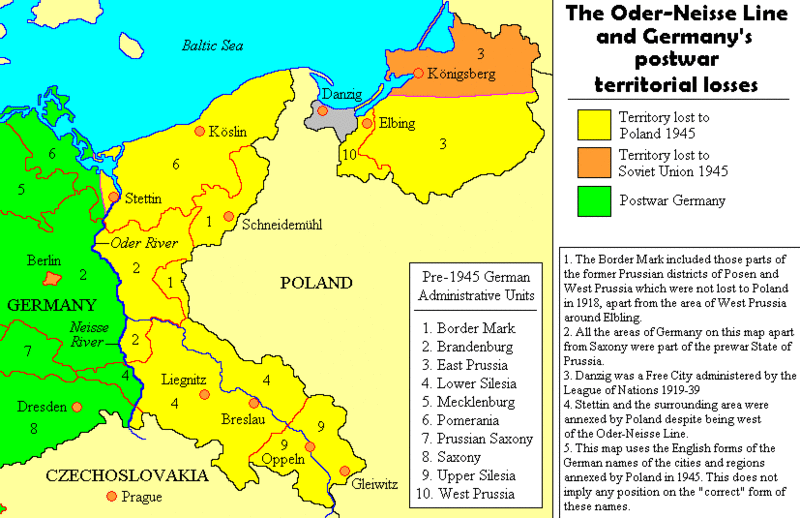
The Soviet Union controlled the eastern zone, encompassing East Prussia, Pomerania, and Silesia, territories that had been historically German but were now annexed by Poland. The western zones, controlled by the Western Allies, included the remaining parts of pre-war Germany, including the industrial Ruhr region.
The Berlin Divide: A Symbol of Cold War Tensions
The division of Germany extended to its capital, Berlin. Despite being located within the Soviet zone, Berlin itself was also divided into four sectors, mirroring the occupation zones. This division, particularly the Berlin Wall erected in 1961, became a powerful symbol of the Cold War and the ideological divide between East and West.
The Birth of Two Germanys: East and West
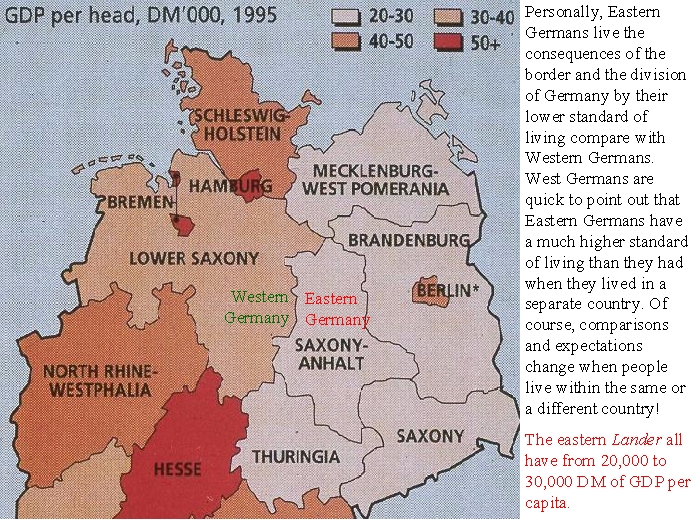
The post-war years saw the emergence of two distinct German states: the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in the east and the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) in the west. The GDR, under Soviet influence, adopted a communist system, while the FRG embraced a democratic and capitalist model. The map of 1945 laid the foundation for this division, setting the stage for a period of political and economic separation that would last for decades.
The Road to Reunification: From Division to Unity
The reunification of Germany in 1990, after decades of division, was a landmark event. The map of 1945, once a symbol of division, became a testament to the power of historical transformation. The reunification process involved dismantling the Berlin Wall, unifying the two Germanys, and integrating the former GDR into the Federal Republic.
The Legacy of 1945: A Map of Transformation
The map of 1945 serves as a powerful reminder of the devastating impact of war and the enduring consequences of political division. It highlights the complexities of post-war Germany, the struggle for national identity, and the eventual path towards unity. Studying this map provides a valuable lens through which to understand the history of Germany, its geopolitical complexities, and its remarkable journey from division to unity.
FAQs
Q: What were the key features of the map of Germany in 1945?
A: The map of Germany in 1945 showed the country divided into four occupation zones, controlled by the Allied powers: the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France. This division extended to Berlin, which was also divided into four sectors.
Q: How did the map of Germany in 1945 reflect the outcome of the Second World War?
A: The map reflected the Allied victory and the subsequent division of Germany into occupation zones. It also showed the territorial changes, with East Prussia, Pomerania, and Silesia annexed by Poland.
Q: What were the long-term consequences of the division of Germany?
A: The division of Germany led to the emergence of two distinct German states, the GDR and the FRG, with different political systems and economic models. This division also contributed to the Cold War and the ideological conflict between East and West.
Q: How did the map of Germany in 1945 influence the future of the country?
A: The map served as a foundation for the division of Germany and the subsequent development of two separate states. It also shaped the political landscape of Europe and influenced the course of the Cold War.
Q: What is the significance of the map of Germany in 1945 today?
A: The map serves as a reminder of the devastating impact of war and the enduring consequences of political division. It also highlights the resilience of the German people and their eventual journey towards unity.
Tips
- Study maps of Germany before and after 1945: Comparing these maps will help you understand the territorial changes and the impact of the war.
- Research the Potsdam Conference: This conference laid the foundation for the division of Germany and shaped the post-war landscape.
- Explore the history of the Cold War: Understanding the Cold War context will provide a deeper insight into the division of Germany and the Berlin Wall.
- Read about the reunification process: Learn about the events that led to the reunification of Germany and the challenges faced by the country.
Conclusion
The map of Germany in 1945 is a powerful visual representation of a nation in transition. It reveals the devastating impact of war, the complexities of political division, and the eventual path towards unity. By studying this map and understanding its historical context, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and triumphs of post-war Germany and the enduring legacy of this pivotal year.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Germany: A Look at the Map of 1945. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!