The Seneca Nation: A Geographical and Historical Overview
Related Articles: The Seneca Nation: A Geographical and Historical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Seneca Nation: A Geographical and Historical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Seneca Nation: A Geographical and Historical Overview

The Seneca Nation, one of the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy, occupies a significant place in the history and geography of the northeastern United States. Their traditional territory, spanning parts of New York, Pennsylvania, and Ontario, Canada, has been shaped by centuries of treaties, conflict, and resilience. Understanding the Seneca Nation’s map, both historically and presently, provides crucial insights into their cultural identity, political landscape, and ongoing efforts to preserve their sovereignty and heritage.
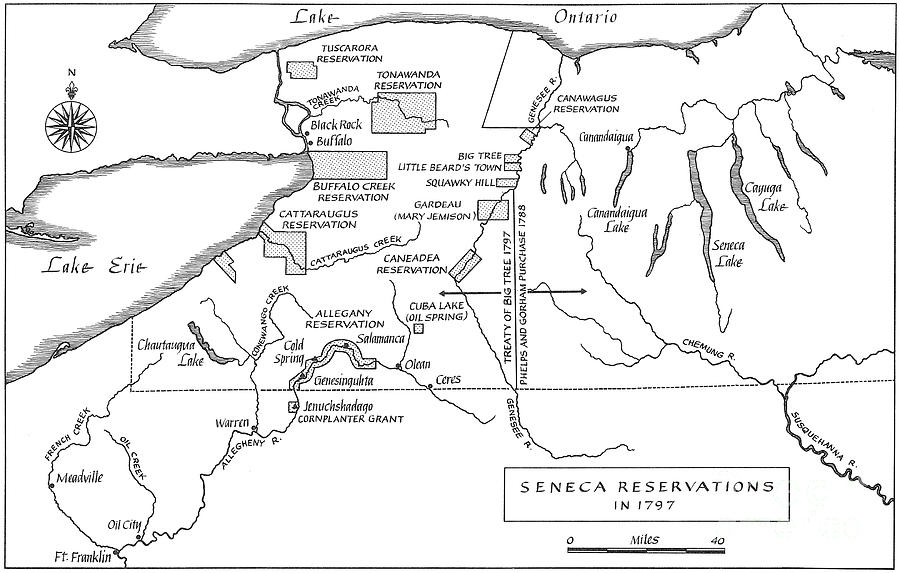
Historical Geography:
Prior to European colonization, the Seneca Nation’s territory encompassed a vast expanse of land, stretching from the Genesee River in New York to the Allegheny River in Pennsylvania. They were known as the "Keepers of the Western Door," guarding the Iroquois Confederacy’s western frontier. This strategic location played a key role in their political and economic influence, as they controlled crucial trade routes and resources.
Treaties and Land Cessions:
The arrival of European settlers in the 17th and 18th centuries drastically altered the Seneca Nation’s geographical reality. Through a series of treaties, often negotiated under duress, the Seneca Nation ceded significant portions of their ancestral lands. These treaties, while often viewed as legal documents, are contested by the Seneca Nation, who argue that they were coerced and did not reflect true consent.
Modern-Day Territories:
Today, the Seneca Nation’s territory is divided into six reservations located in New York State:
- Allegany Reservation: Situated in Cattaraugus County, it is the largest Seneca reservation and home to the Seneca Nation’s government headquarters.
- Cattaraugus Reservation: Also located in Cattaraugus County, it shares a border with the Allegany Reservation.
- Tonawanda Reservation: Situated in Erie County, it is the smallest Seneca reservation.
- Oil Springs Reservation: Located in Chautauqua County, it is known for its historical oil production.
- Tuscarora Reservation: While not officially part of the Seneca Nation, the Tuscarora Nation, another member of the Iroquois Confederacy, shares a close relationship with the Seneca and has a reservation located in Niagara County.
- The Seneca Nation of Indians at Cattaraugus and Allegany: This entity manages the Allegany and Cattaraugus reservations, providing essential services and governance.
The Importance of the Seneca Nation Map:
The Seneca Nation’s map is not merely a geographical representation; it is a living testament to their history, resilience, and ongoing struggles for self-determination. It highlights the following crucial aspects:
- Sovereignty and Self-Governance: The map showcases the Seneca Nation’s sovereign territories, emphasizing their right to self-government and autonomy.
- Cultural Preservation: The Seneca Nation’s lands hold profound cultural and spiritual significance, serving as repositories of ancestral knowledge, traditions, and language.
- Economic Development: The map showcases the Seneca Nation’s economic activities, including gaming, agriculture, and cultural tourism, which play a vital role in their self-sufficiency and community well-being.
- Environmental Stewardship: The Seneca Nation has a deep connection to the natural world, actively engaging in environmental protection and sustainable resource management.
- Historical and Legal Context: The map provides a visual representation of the Seneca Nation’s historical and legal claims to their ancestral lands, highlighting the ongoing challenges they face in protecting their rights.
FAQs about the Seneca Nation Map:
Q: What is the total land area of the Seneca Nation’s reservations?
A: The total land area of the Seneca Nation’s six reservations in New York State is approximately 30,000 acres.
Q: Are there any Seneca Nation territories outside of New York State?
A: Historically, the Seneca Nation’s territory extended into parts of Pennsylvania and Ontario, Canada. However, through treaties and land cessions, they have lost most of their original territory outside of New York State.
Q: What are the major economic activities on the Seneca Nation’s reservations?
A: The Seneca Nation’s primary economic activities include gaming, agriculture, tourism, and cultural heritage preservation.
Q: What is the role of the Seneca Nation government?
A: The Seneca Nation government is responsible for governing the reservations, providing essential services to its citizens, and negotiating with the United States government on matters related to sovereignty, land rights, and economic development.
Q: How does the Seneca Nation protect its cultural heritage?
A: The Seneca Nation actively promotes cultural preservation through language revitalization programs, traditional arts and crafts, and community-based cultural events.
Tips for Understanding the Seneca Nation Map:
- Explore Historical Maps: Examining historical maps of the Seneca Nation’s territory provides valuable insights into their past land holdings and the impact of colonization.
- Consult Official Resources: The Seneca Nation’s website and government publications offer comprehensive information about their reservations, governance, and cultural heritage.
- Engage with Local Communities: Visiting Seneca Nation reservations and interacting with community members provides a firsthand understanding of their culture, history, and ongoing challenges.
- Support Seneca Nation Businesses: Patronizing businesses owned and operated by Seneca Nation members contributes to their economic development and self-sufficiency.
- Educate Yourself on Treaty Rights: Understanding the historical context of treaties and their impact on the Seneca Nation’s land rights is crucial for informed advocacy and support.
Conclusion:
The Seneca Nation’s map is a powerful symbol of their resilience, cultural heritage, and ongoing struggles for self-determination. It serves as a reminder of their historical connection to the land, their commitment to preserving their cultural identity, and their ongoing fight for recognition and respect. By understanding the Seneca Nation’s map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for their history, culture, and ongoing efforts to shape their future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Seneca Nation: A Geographical and Historical Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!