The Power of Spatial Intelligence: Unlocking Insights from Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Intelligence: Unlocking Insights from Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Intelligence: Unlocking Insights from Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Spatial Intelligence: Unlocking Insights from Maps
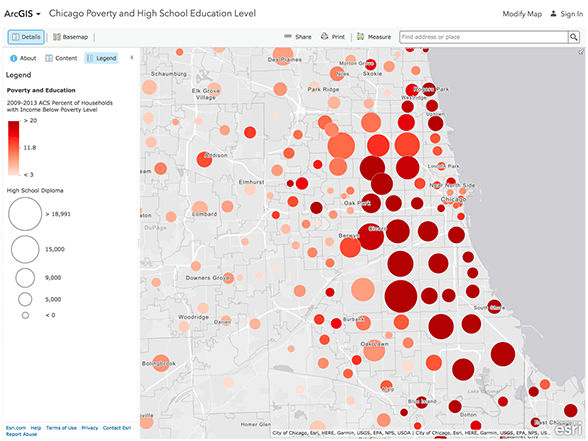
In today’s data-driven world, information is readily available, but extracting meaningful insights from it remains a significant challenge. Enter spatial intelligence, a powerful tool that leverages the visual language of maps to uncover hidden patterns and relationships within data. By integrating geographical context, spatial intelligence transforms raw data into actionable knowledge, enabling informed decision-making across various domains.
Understanding Spatial Intelligence
Spatial intelligence, often referred to as geo-spatial intelligence, goes beyond simply displaying data on a map. It involves analyzing and interpreting spatial relationships, patterns, and trends within geographic data. This analysis can encompass a vast array of data types, including demographic information, economic indicators, environmental data, and social media trends.
Key Components of Spatial Intelligence
The core components of spatial intelligence include:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software serves as the foundation for spatial analysis, providing tools to collect, store, analyze, and visualize geographic data.
- Remote Sensing: Utilizing satellite imagery and aerial photography, remote sensing captures data about Earth’s surface, providing valuable insights into land cover, vegetation, and infrastructure.
- Geocoding: This process converts addresses and place names into geographic coordinates, enabling the integration of spatial information with other datasets.
- Spatial Analysis Techniques: A wide range of statistical and analytical methods are employed to analyze spatial data, revealing patterns, trends, and relationships within geographic context.
The Importance of Spatial Intelligence
The application of spatial intelligence transcends various industries and sectors, offering valuable insights for:
- Business and Marketing: Identifying target markets, optimizing supply chains, and understanding consumer behavior.
- Urban Planning: Analyzing population growth, traffic patterns, and infrastructure needs to create sustainable and efficient urban environments.
- Environmental Management: Monitoring environmental changes, managing natural resources, and assessing the impact of climate change.
- Disaster Response: Predicting and mitigating natural disasters, coordinating relief efforts, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Public Health: Tracking disease outbreaks, identifying vulnerable populations, and deploying public health interventions effectively.
- Security and Intelligence: Identifying threats, analyzing crime patterns, and optimizing resource allocation for security operations.
Benefits of Utilizing Spatial Intelligence
Leveraging spatial intelligence provides numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By incorporating geographic context, spatial intelligence provides a holistic view of data, enabling more informed and strategic decisions.
- Improved Resource Allocation: By analyzing spatial patterns and trends, organizations can optimize resource allocation, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness.
- Data Visualization and Communication: Maps provide an intuitive and easily understandable way to communicate complex data, fostering collaboration and understanding.
- Identification of Opportunities: Spatial intelligence can uncover hidden opportunities by revealing spatial relationships and trends that might otherwise be missed.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation, spatial intelligence can significantly increase efficiency and productivity.
FAQs about Spatial Intelligence
Q: What are some real-world examples of spatial intelligence applications?
A:
- Retail Location Optimization: Retailers use spatial intelligence to analyze customer demographics, competition, and accessibility to identify optimal locations for new stores.
- Disease Surveillance: Public health organizations use spatial intelligence to track disease outbreaks, identify high-risk areas, and target public health interventions.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Environmental agencies utilize spatial intelligence to assess the impact of development projects on ecosystems and natural resources.
- Disaster Relief Planning: Emergency responders use spatial intelligence to map affected areas, identify evacuation routes, and allocate resources efficiently during natural disasters.
Q: How can I learn more about spatial intelligence?
A:
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Numerous online platforms offer courses and tutorials on GIS, remote sensing, and spatial analysis techniques.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations such as the Association for Geographic Information (AGI) and the Urban and Regional Information Systems Association (URISA) provide resources and networking opportunities.
- Industry Conferences and Events: Attending industry conferences and events allows for networking and learning about the latest advancements in spatial intelligence.
Q: What are the challenges associated with spatial intelligence?
A:
- Data Availability and Quality: Access to accurate and comprehensive spatial data is crucial for effective analysis.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing and utilizing spatial intelligence requires specialized technical skills.
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive geographic data is essential.
- Integration with Other Systems: Integrating spatial intelligence with existing systems and workflows can be challenging.
Tips for Implementing Spatial Intelligence
- Clearly Define Objectives: Identify specific goals and objectives that spatial intelligence can help achieve.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select appropriate GIS software and other tools based on specific needs and requirements.
- Ensure Data Quality: Validate and clean data to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage relevant stakeholders throughout the process to ensure alignment and buy-in.
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: Begin with pilot projects to demonstrate the value of spatial intelligence and gradually scale up implementations.
Conclusion
Spatial intelligence is a transformative tool that empowers organizations to unlock the power of geographic data. By analyzing spatial relationships and trends, organizations can gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and optimize their operations. As technology continues to evolve, the applications of spatial intelligence are expanding, offering endless possibilities for innovation and progress across diverse industries. Embracing spatial intelligence is essential for organizations seeking to harness the power of data and make a meaningful impact in a geographically interconnected world.

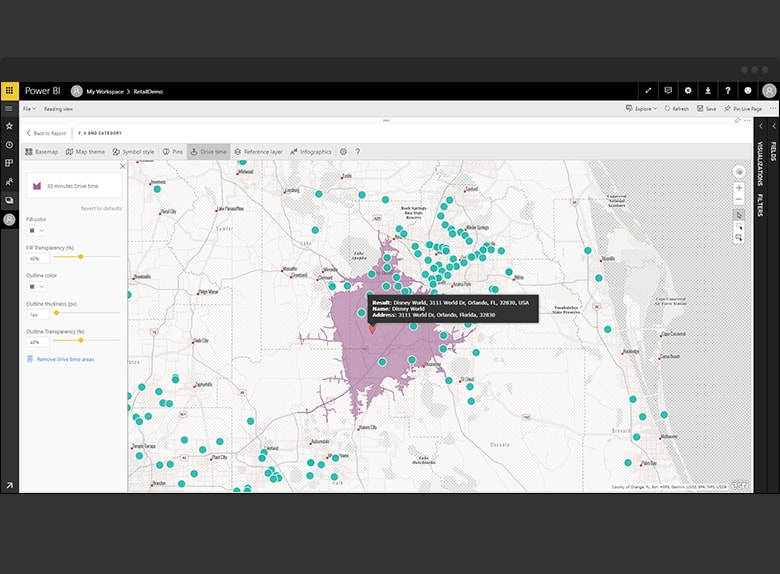

![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Intelligence: Unlocking Insights from Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!