The Power of Mapping: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Related Articles: The Power of Mapping: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Mapping: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Mapping: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
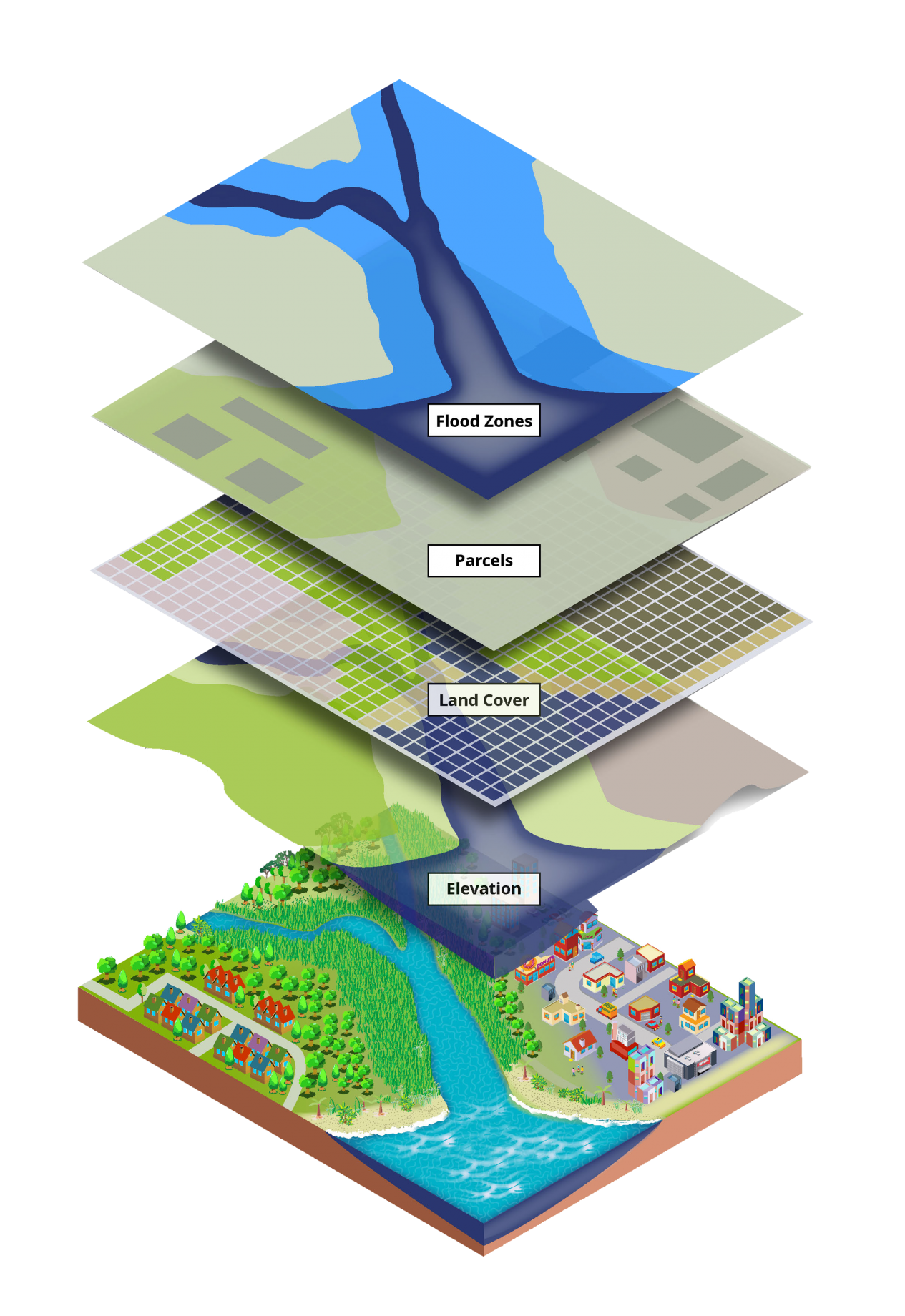
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have revolutionized the way we understand and interact with our world. This powerful technology combines geographic data with analytical tools to create insightful maps that reveal patterns, trends, and relationships hidden within complex datasets. GIS is not merely about creating static maps; it’s about using spatial data to solve real-world problems across various sectors.
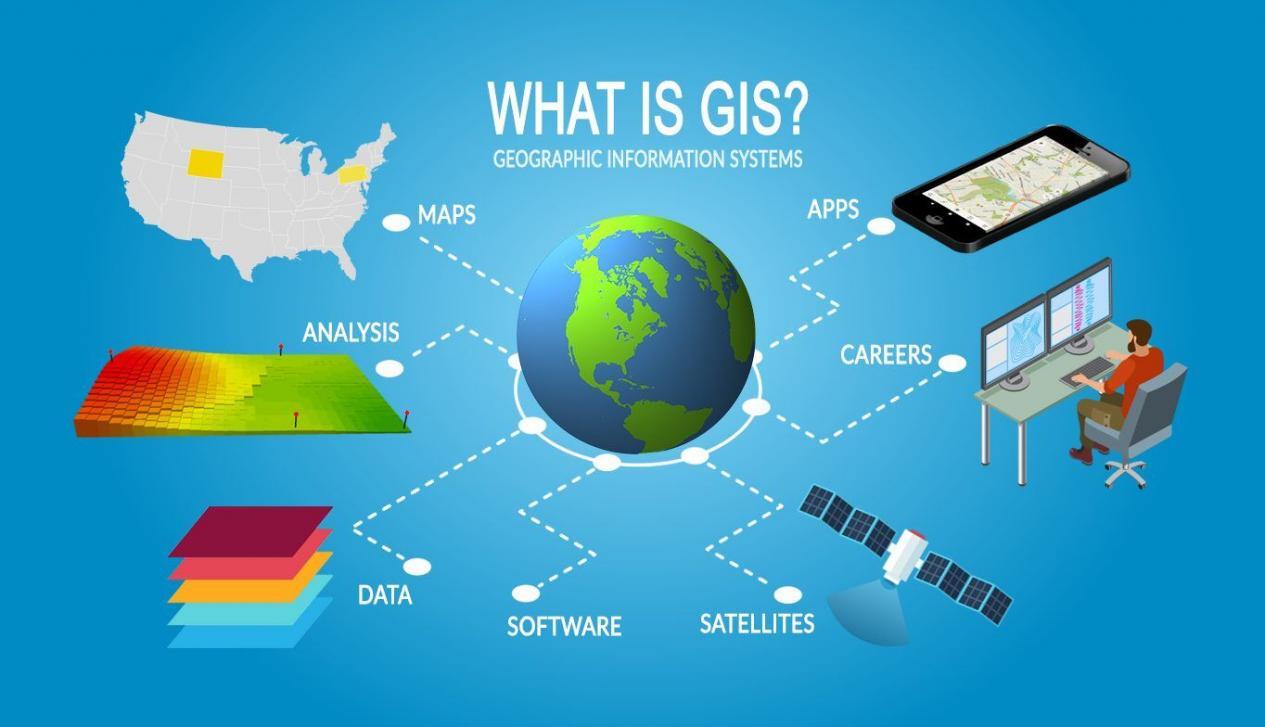
What is GIS?
GIS is a system that integrates hardware, software, data, and personnel to capture, store, manage, analyze, and present spatial information. At its core, GIS uses location as the fundamental organizing principle for data. This allows for the visualization of geographic data in a way that traditional spreadsheets or databases cannot achieve.
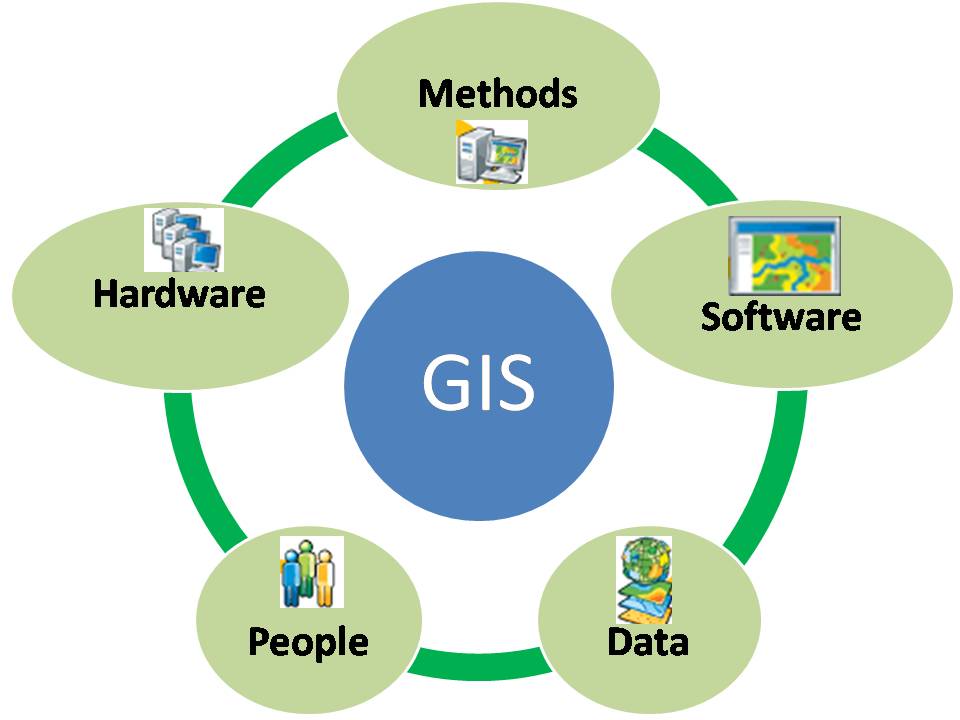
Key Components of a GIS
- Hardware: This includes computers, scanners, GPS devices, and other equipment used to collect and process spatial data.
- Software: GIS software provides the tools for data management, analysis, and visualization. Examples include ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo.
- Data: This is the heart of a GIS, comprising geographic information such as points, lines, polygons, and raster data. Data sources range from satellite imagery and aerial photographs to census data and environmental monitoring reports.
- Personnel: Skilled GIS professionals are essential for designing, implementing, and maintaining GIS systems, as well as for interpreting and communicating results.
The Power of Spatial Analysis
The true power of GIS lies in its ability to analyze spatial data. By leveraging the relationships between geographic features, GIS can:
- Identify patterns and trends: For example, GIS can analyze crime data to identify hotspots, enabling targeted crime prevention strategies.
- Model and predict future scenarios: GIS can model the spread of diseases, simulate urban growth, or assess the impact of climate change on coastal communities.
- Optimize resource allocation: GIS can help determine the most efficient routes for delivery services, identify optimal locations for new infrastructure, or manage natural resources effectively.
- Support decision-making: By providing clear visualizations and insightful analyses, GIS empowers informed decision-making in various fields.
Applications of GIS Across Industries
GIS is a versatile technology with applications across numerous sectors:
- Environmental Management: GIS helps monitor deforestation, track wildlife populations, manage natural disasters, and assess environmental impacts of development projects.
- Urban Planning: GIS aids in urban development, transportation planning, infrastructure management, and creating sustainable cities.
- Agriculture: GIS supports precision farming, crop yield analysis, and efficient resource management, leading to increased agricultural productivity.
- Business and Marketing: GIS helps businesses locate optimal store locations, analyze customer demographics, and optimize delivery routes.
- Public Health: GIS plays a crucial role in disease surveillance, outbreak response, and public health interventions.
- Emergency Management: GIS provides real-time situational awareness during emergencies, facilitates resource allocation, and assists in disaster recovery efforts.
- Military and Defense: GIS is used for mission planning, terrain analysis, and intelligence gathering in military operations.
Benefits of Using GIS
- Improved Decision-Making: GIS provides insights and visualizations that support data-driven decisions.
- Increased Efficiency: Automating tasks and optimizing workflows leads to greater efficiency in various sectors.
- Better Communication: GIS facilitates clear and concise communication of complex spatial information through maps and visualizations.
- Enhanced Collaboration: GIS platforms allow for collaborative work on projects involving multiple stakeholders.
- Cost Savings: GIS can help identify cost-effective solutions and optimize resource allocation.
FAQs About GIS
Q: What is the difference between GPS and GIS?
A: GPS (Global Positioning System) is a technology that determines the precise location of a device on Earth’s surface. GIS, on the other hand, is a system that integrates and analyzes spatial data, including data obtained from GPS devices.
Q: Is GIS only used for mapping?
A: While mapping is a prominent aspect of GIS, its capabilities extend far beyond simple visualization. GIS involves analyzing spatial data, modeling scenarios, and deriving insights that inform decision-making.
Q: What are some popular GIS software programs?
A: Some widely used GIS software programs include ArcGIS, QGIS, MapInfo, and Google Earth Pro. The choice of software depends on the specific needs and budget of the user.
Q: What are the career opportunities in GIS?
A: GIS professionals are in high demand across various industries. Career paths include GIS analysts, cartographers, spatial data specialists, and GIS managers.
Tips for Learning GIS
- Start with online resources: Numerous websites and online courses offer introductory materials on GIS.
- Explore free software: QGIS is a powerful and free open-source GIS software that’s ideal for beginners.
- Join online communities: Online forums and social media groups provide opportunities to connect with other GIS enthusiasts and professionals.
- Practice with real-world data: Use publicly available datasets to apply GIS techniques and explore real-world applications.
Conclusion
GIS is a transformative technology that empowers us to understand and interact with our world in unprecedented ways. Its ability to analyze spatial data, model scenarios, and support informed decision-making makes it a valuable tool in various fields. As technology continues to advance, GIS will play an increasingly vital role in addressing global challenges and shaping a sustainable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Mapping: Understanding Geographic Information Systems (GIS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!