The Ganges Delta: A Vital Lifeline in South Asia
Related Articles: The Ganges Delta: A Vital Lifeline in South Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ganges Delta: A Vital Lifeline in South Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ganges Delta: A Vital Lifeline in South Asia

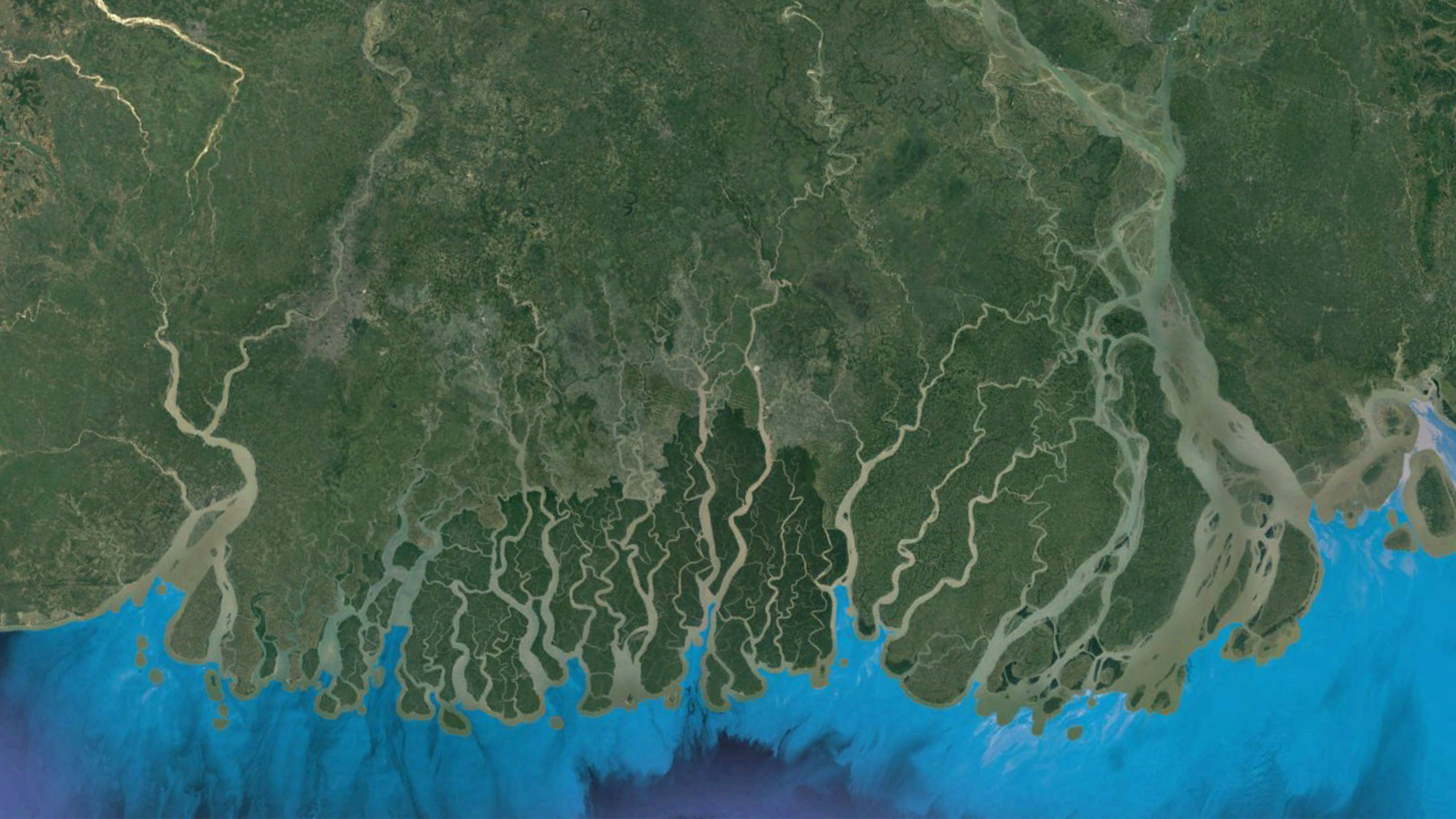
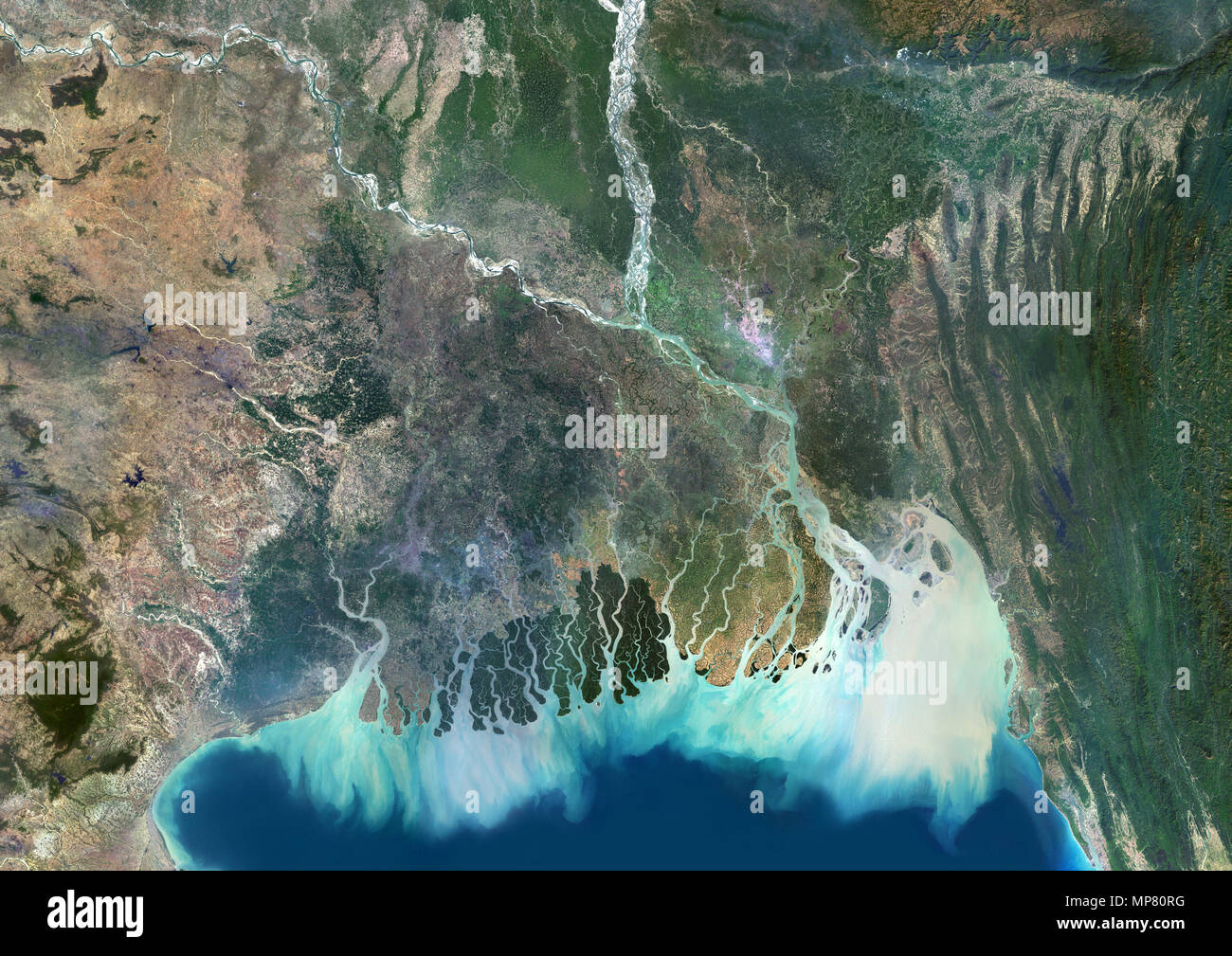
The Ganges Delta, a vast expanse of fertile land sculpted by the mighty Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, is a crucial geographical feature in South Asia. This intricate network of waterways, islands, and wetlands plays a vital role in the lives of millions, shaping the region’s cultural landscape, economic prosperity, and ecological balance. Understanding the Ganges Delta map is essential for appreciating its significance and the multifaceted challenges it faces.
A Riverine Tapestry: Understanding the Ganges Delta Map
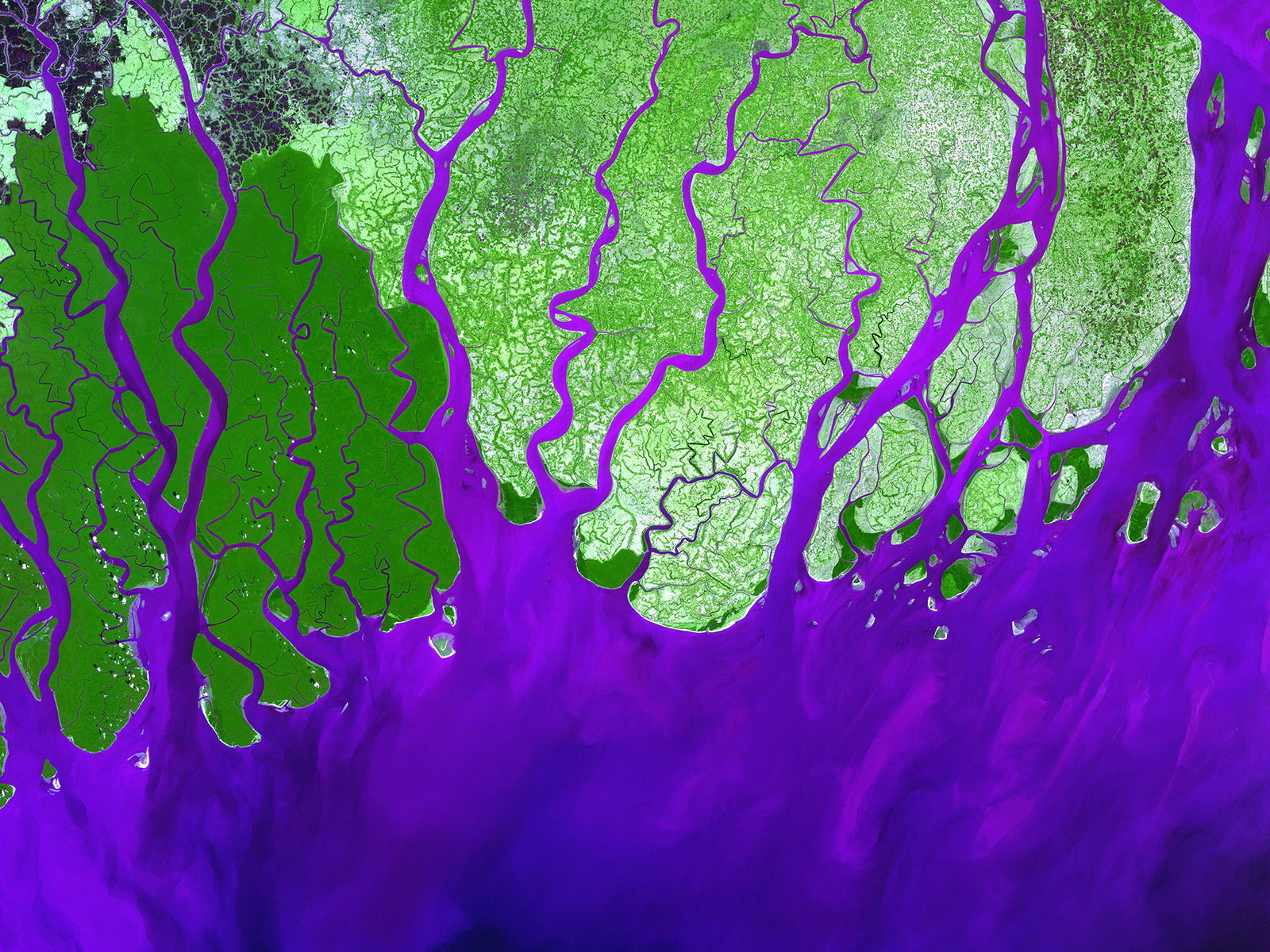
The Ganges Delta, often referred to as the "Bengal Delta," is one of the largest river deltas in the world, spanning across Bangladesh and parts of India. It is formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, their combined flow carving a complex network of distributaries, channels, and islands.
Key Features of the Ganges Delta Map:
- The Ganges River: Originating in the Gangotri glacier in the Himalayas, the Ganges flows eastward across northern India before entering Bangladesh and merging with the Brahmaputra.
- The Brahmaputra River: Rising in Tibet, the Brahmaputra flows south through India and then east through Bangladesh, joining the Ganges to form the Meghna River.
- The Meghna River: The largest river in Bangladesh, the Meghna is formed by the confluence of the Ganges and Brahmaputra. It flows through the heart of the delta before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Sundarbans: A UNESCO World Heritage site, the Sundarbans is a vast mangrove forest located in the southwestern part of the delta. It is home to a rich diversity of flora and fauna, including the Royal Bengal Tiger.
- The Islands: The Ganges Delta is dotted with numerous islands, some permanently inhabited, others emerging and disappearing with the changing river flows. These islands provide fertile land for agriculture and fishing.
- The Tidal Flats: The delta’s coastline is characterized by extensive tidal flats, which are submerged during high tide and exposed during low tide. These flats are important for marine life and provide a buffer against storm surges.
The Importance of the Ganges Delta Map:
The Ganges Delta map is not merely a geographical representation; it is a roadmap to understanding the region’s multifaceted importance:
- Agriculture and Food Security: The fertile soils of the delta provide the foundation for a thriving agricultural sector, producing rice, jute, and other essential crops that feed millions.
- Fisheries and Livelihoods: The vast network of waterways and coastal areas supports a vibrant fishing industry, providing employment and sustenance for a significant portion of the population.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Ganges Delta is a biodiversity hotspot, home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, including endangered species like the Ganges River Dolphin and the Bengal Tiger.
- Cultural Heritage: The delta is a cradle of ancient civilizations, with a rich cultural heritage reflected in its temples, mosques, and traditional arts and crafts.
- Economic Growth: The delta is a major economic hub, with thriving industries in textiles, shipping, and tourism.
Challenges Facing the Ganges Delta:
Despite its immense importance, the Ganges Delta faces a number of challenges:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased frequency of cyclones, and changing rainfall patterns threaten the delta’s agricultural productivity and coastal communities.
- Pollution: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge pollute the rivers and waterways, posing a threat to human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Overpopulation: Rapid population growth puts pressure on resources, leading to deforestation, land degradation, and depletion of freshwater resources.
- Coastal Erosion: The delta’s coastline is vulnerable to erosion caused by rising sea levels and strong tidal currents, leading to loss of land and displacement of communities.
- Deforestation: The Sundarbans mangrove forest is facing deforestation due to illegal logging, encroachment, and climate change, jeopardizing its ecological integrity and the livelihoods of local communities.
FAQs: Understanding the Ganges Delta Map
Q1: What is the geographical significance of the Ganges Delta?
A: The Ganges Delta is one of the largest river deltas in the world, formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers. It is a crucial geographical feature in South Asia, shaping the region’s cultural landscape, economic prosperity, and ecological balance.
Q2: What are the key features of the Ganges Delta map?
A: The Ganges Delta map encompasses the major rivers (Ganges, Brahmaputra, Meghna), the Sundarbans mangrove forest, numerous islands, extensive tidal flats, and the delta’s coastline along the Bay of Bengal.
Q3: Why is the Ganges Delta important?
A: The delta is vital for agriculture, fisheries, biodiversity, cultural heritage, and economic growth. It provides food security, livelihoods, and a unique ecosystem for millions of people.
Q4: What are the challenges facing the Ganges Delta?
A: The delta faces challenges from climate change, pollution, overpopulation, coastal erosion, and deforestation, threatening its ecological integrity and the well-being of its inhabitants.
Q5: How can the Ganges Delta be protected?
A: Sustainable development practices, environmental conservation efforts, and collaborative initiatives between governments and communities are crucial for safeguarding the delta’s future.
Tips for Understanding and Using the Ganges Delta Map:
- Study the map carefully: Pay attention to the major rivers, islands, and coastal areas.
- Explore different resources: Use online maps, satellite imagery, and geographical data to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Connect the map to real-world issues: Relate the features on the map to the challenges and opportunities facing the delta.
- Engage with local communities: Learn from the experiences and perspectives of those who live and work in the delta.
- Advocate for sustainable development: Support initiatives that promote environmental conservation and responsible resource management.
Conclusion: A Vital Resource for the Future
The Ganges Delta map is a powerful tool for understanding the complex interplay of nature, culture, and human activity in this vital region. It highlights the delta’s immense importance as a source of food, livelihood, and cultural heritage, while also revealing the challenges it faces. By understanding and appreciating the Ganges Delta, we can better appreciate its significance and contribute to its sustainable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ganges Delta: A Vital Lifeline in South Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!