The Evolution of Maps: Exploring the Movement of Information and Understanding
Related Articles: The Evolution of Maps: Exploring the Movement of Information and Understanding
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of Maps: Exploring the Movement of Information and Understanding. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of Maps: Exploring the Movement of Information and Understanding

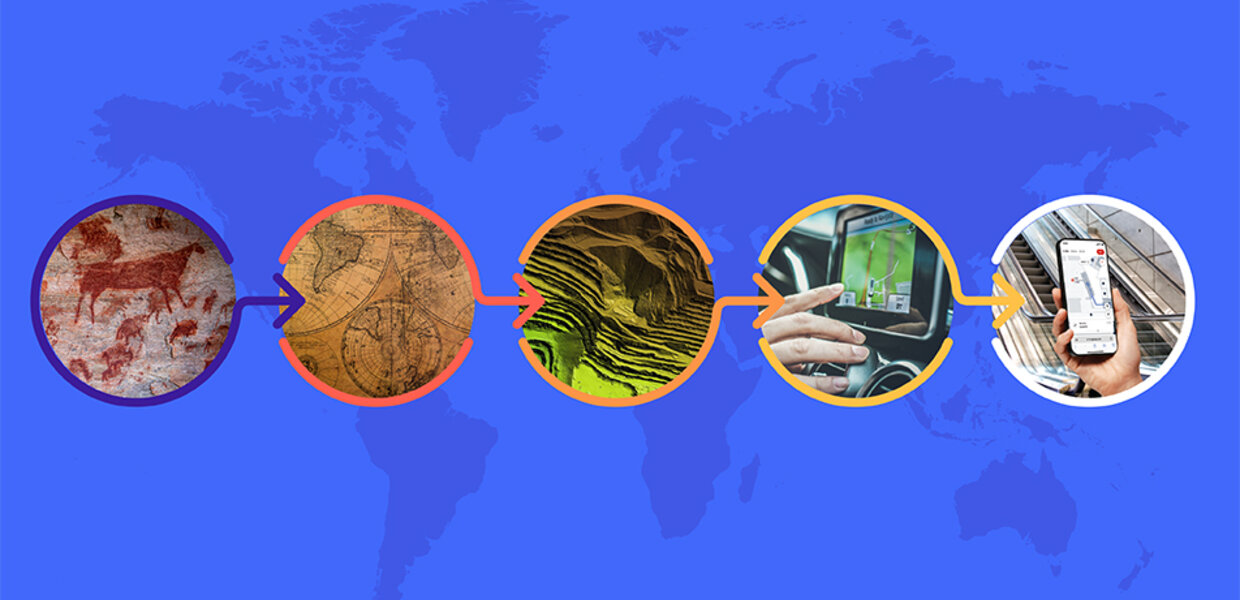
Maps, in their diverse forms, have long been instrumental in navigating the physical world. From ancient cave paintings depicting hunting grounds to intricate nautical charts guiding explorers across vast oceans, maps have served as powerful tools for spatial understanding and exploration. However, the evolution of maps extends far beyond their physical representations. The movement of information encoded within maps, the way we interact with them, and the technology driving their creation have all undergone significant transformations, resulting in a dynamic landscape where maps are no longer static but dynamic and interactive.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted concept of "map movement," examining its various dimensions and highlighting its profound impact on how we perceive and interact with the world around us.
1. The Digital Revolution: From Static to Interactive
The advent of digital technology marked a watershed moment in the history of mapmaking. Static, paper-based maps gave way to interactive, digital representations, ushering in a new era of map movement.
a. The Rise of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS, a powerful suite of tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing geographic data, revolutionized how maps are created and utilized. GIS allows for the integration of diverse datasets, enabling the creation of highly detailed and informative maps that go beyond simple visual representations.
b. Web Mapping and Online Platforms
The emergence of web mapping platforms, such as Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap, democratized access to maps and fostered a collaborative approach to map creation. Users can now access and interact with maps online, contributing to their development and sharing their knowledge.
c. Interactive Features and Dynamic Visualization
Digital maps offer a level of interactivity previously unimaginable. Users can zoom in and out, pan across vast distances, and explore various layers of information, revealing intricate details and patterns. Dynamic visualization techniques, such as heat maps and 3D models, enhance the visual storytelling capabilities of maps, providing a more engaging and informative experience.
2. Navigating the Digital Landscape: Embracing the Mobile Revolution
The proliferation of smartphones and tablets has further transformed the way we interact with maps. Mobile navigation apps, powered by GPS technology, have become ubiquitous, providing real-time location information and turn-by-turn directions, transforming the way we navigate our daily lives.
a. Location-Based Services and Personalized Experiences
Mobile maps leverage location data to provide personalized experiences, tailoring information to individual users’ needs. From finding nearby restaurants and shops to accessing real-time traffic updates, mobile maps have become integral to our daily routines.
b. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Integration
The integration of AR and VR technologies is pushing the boundaries of map movement even further. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, allowing users to see virtual objects superimposed on their surroundings. VR immerses users in a virtual environment, creating a more immersive and interactive experience.
3. Data-Driven Insights and the Power of Analysis
Maps are no longer simply visual representations of geographical features. They have become powerful tools for analyzing data and extracting insights.
a. Data Visualization and Spatial Analysis
By overlaying data onto maps, analysts can identify patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise remain hidden. This enables informed decision-making in various fields, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and public health.
b. Predictive Analytics and Modeling
Advanced mapping tools incorporate predictive analytics and modeling capabilities, allowing users to simulate scenarios and predict future outcomes based on historical data and user-defined parameters.
4. The Future of Map Movement: Exploring New Horizons
The movement of maps continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and a growing demand for more sophisticated and personalized experiences.
a. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming mapmaking by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and personalizing user experiences. AI-powered maps can learn from user interactions, providing personalized recommendations and predictions.
b. The Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensor Networks
The proliferation of IoT devices and sensor networks is generating vast amounts of real-time data, enriching map content and enabling dynamic updates. This data can be used to monitor environmental conditions, track traffic flow, and provide real-time information on various aspects of the physical world.
c. Metaverse Integration and Spatial Computing
The metaverse, a shared virtual space, promises to further revolutionize map movement. Spatial computing, which allows users to interact with digital objects in the real world, will enable the creation of immersive and interactive maps that blur the lines between the physical and digital realms.
FAQs about Map Movement
1. What are the key benefits of map movement?
Map movement offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced spatial understanding: Interactive maps allow users to explore and understand spatial relationships in a more engaging and informative way.
- Improved decision-making: Data visualization and analysis capabilities enable informed decision-making in various fields.
- Personalized experiences: Mobile maps and location-based services tailor information to individual needs, enhancing user experiences.
- Increased accessibility: Web mapping platforms and mobile apps democratize access to maps, making them readily available to a wider audience.
2. How is map movement impacting various industries?
Map movement is transforming industries across the board, including:
- Transportation: Navigation apps and real-time traffic updates improve efficiency and safety.
- Urban planning: Spatial analysis helps to optimize urban development and infrastructure planning.
- Environmental monitoring: Maps are used to track environmental changes and manage natural resources.
- Healthcare: Location data can be used to track disease outbreaks and allocate resources effectively.
- Marketing and advertising: Location-based marketing allows businesses to target customers more effectively.
3. What are the ethical considerations surrounding map movement?
Map movement raises ethical considerations, including:
- Privacy concerns: Location data collected by mobile apps can raise privacy concerns.
- Data security: The storage and use of sensitive location data require robust security measures.
- Bias and discrimination: Algorithmic biases in mapping systems can perpetuate existing inequalities.
Tips for Effective Map Movement
- Choose the right tool for the task: Select a mapping platform that best suits your needs and the type of data you are working with.
- Use clear and concise visualization techniques: Ensure that your maps are visually appealing and easy to understand.
- Consider accessibility: Design maps that are accessible to users with disabilities.
- Stay informed about ethical considerations: Be aware of the potential ethical implications of using location data and ensure that your practices are responsible and transparent.
Conclusion
The movement of maps, from static representations to interactive, data-driven platforms, reflects a profound shift in how we understand and interact with the world around us. The evolution of maps is driven by technological advancements, changing user needs, and a growing demand for more sophisticated and personalized experiences. As technology continues to advance, map movement is poised to play an even more central role in shaping our future, enabling us to navigate the physical and digital worlds with greater ease, insight, and understanding.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of Maps: Exploring the Movement of Information and Understanding. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!