The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels
Related Articles: The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels

Rome, the Eternal City, boasts a legacy that extends far beyond its iconic monuments and architectural wonders. Beneath the bustling metropolis lies a network of intricate, ancient engineering marvels – the aqueducts. These colossal structures, stretching for miles across the Roman countryside, played a pivotal role in the city’s growth and prosperity, supplying a constant flow of fresh water for centuries.
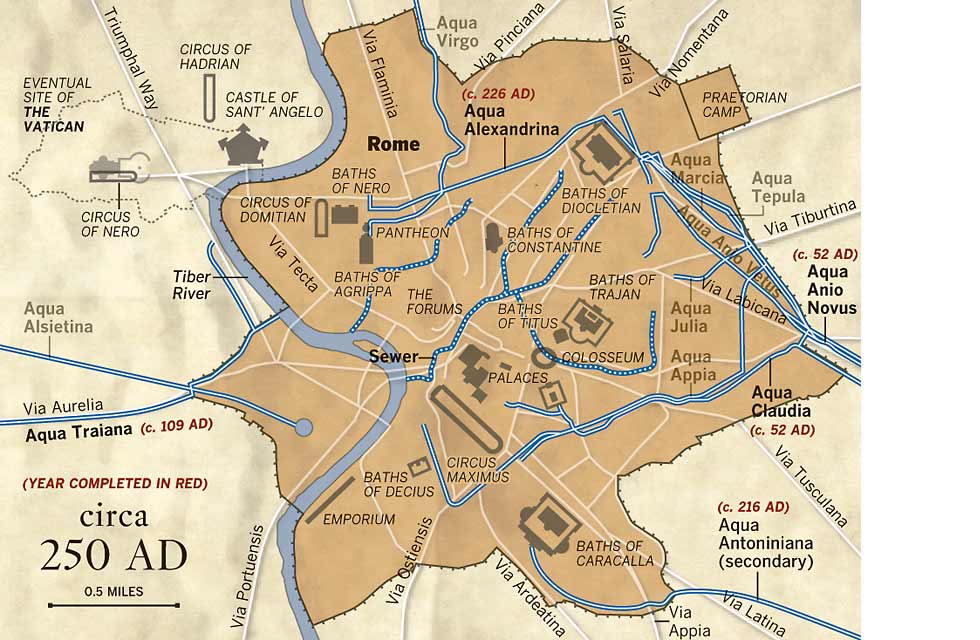
A Map Unveils the Network:
A map of the Roman aqueducts is more than just a visual representation; it’s a testament to the ingenuity and ambition of a civilization that dared to conquer nature itself. The map reveals a complex system of channels, tunnels, and bridges, each meticulously designed to transport water from distant sources to the heart of the city.
Tracing the Aqueducts:
The most prominent aqueducts, visible even today, include:
- Aqua Appia: The oldest of the aqueducts, built in 312 BCE, it sourced water from the springs of the Colline Hills and supplied the city with a steady flow of water.
- Aqua Marcia: Constructed in 144 BCE, this aqueduct stands out for its impressive length of 91 kilometers, bringing water from the Sabine Hills.
- Aqua Tepula: Built in 125 BCE, this aqueduct ran parallel to the Aqua Marcia, drawing water from the same source.
- Aqua Julia: Constructed in 33 BCE, this aqueduct tapped into the same source as the Aqua Marcia and Tepula, increasing the city’s water supply.
- Aqua Virgo: Built in 19 BCE, this aqueduct was unique in its source, drawing water from a spring near the Via Collatina, which flowed into the city.
- Aqua Alsietina: Completed in 2 BCE, this aqueduct supplied the city with water for agricultural use, drawing from the Alsietina Lake.
- Aqua Claudia: Constructed in 52 CE, this aqueduct was the longest, stretching over 69 kilometers, and drew water from the springs of the Simbruini Mountains.
- Anio Novus: Completed in 52 CE, this aqueduct ran parallel to the Aqua Claudia, drawing water from the Anio River.
The Importance of the Aqueducts:
The Roman aqueducts were far more than mere water conduits. They were a testament to the city’s ingenuity and ambition. They played a crucial role in the city’s growth and development, enabling:
- Population Growth: The constant supply of clean water allowed Rome’s population to swell, fueling the city’s rise to prominence.
- Public Health: The aqueducts ensured a consistent supply of clean water for drinking, bathing, and sanitation, contributing to the health and well-being of the city’s inhabitants.
- Economic Development: The aqueducts provided water for agriculture, industry, and public fountains, contributing to the city’s economic growth and prosperity.
- Social Stability: The aqueducts ensured a steady supply of water, preventing shortages and potential unrest among the population.
Exploring the Aqueduct System:
Today, remnants of the aqueducts are still visible throughout Rome, serving as a tangible link to the city’s ancient past. Visitors can:
- Visit the Parco degli Acquedotti: This park, located in the Appian Way Regional Park, offers a glimpse into the grandeur of the aqueduct system.
- Explore the Aqua Marcia: This aqueduct, still partially standing, offers a striking reminder of the engineering prowess of the Romans.
- See the Aqua Claudia: The remains of this aqueduct, visible along the Via Appia Antica, offer a fascinating glimpse into its construction and design.
- Visit the Baths of Caracalla: The ruins of these baths, once supplied by the Aqua Marcia, showcase the luxurious lifestyle made possible by the aqueduct system.
FAQs about the Aqueducts of Rome:
1. How did the Romans transport water over such long distances?
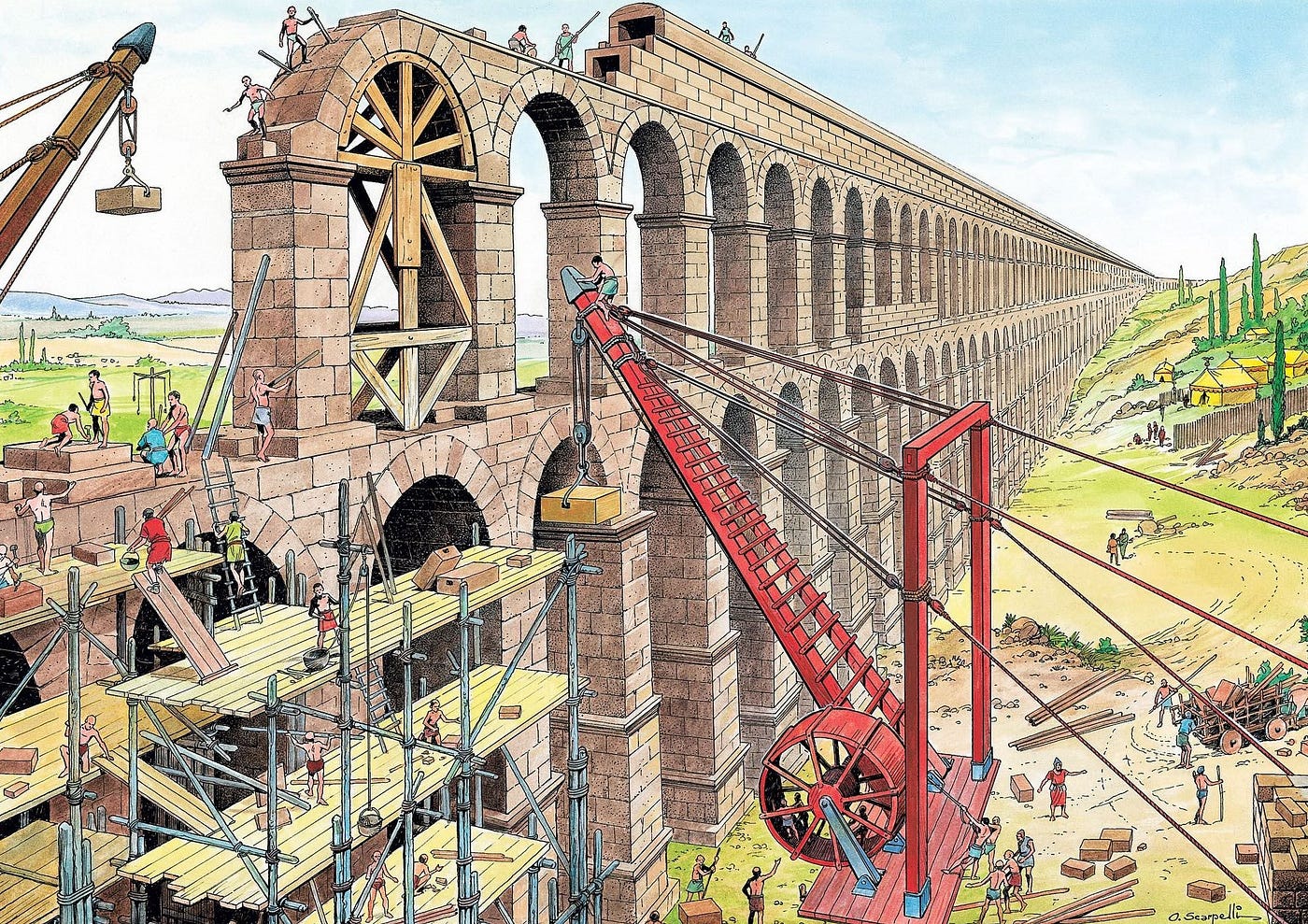
The Romans used a system of gravity-fed channels, tunnels, and bridges. The aqueducts were carefully designed with a slight incline, allowing water to flow naturally from the source to the city.
2. How did the Romans ensure the water was clean?
The Romans employed various techniques to ensure the water’s purity. They used sedimentation tanks to remove impurities, and they also built aqueducts in such a way that they avoided contamination from nearby sources.
3. What materials were used to build the aqueducts?
The Romans primarily used stone and concrete to build the aqueducts. The arches and bridges were constructed from stone, while the channels were lined with concrete to ensure watertightness.
4. How long did it take to build the aqueducts?
The construction of the aqueducts was a massive undertaking, often taking years to complete. The Aqua Marcia, for example, took 11 years to build.
5. What is the significance of the aqueducts today?
The aqueducts of Rome serve as a powerful reminder of the city’s ancient engineering prowess and its dedication to providing its citizens with a high quality of life. They are also a testament to the enduring legacy of Roman civilization.
Tips for Visiting the Aqueducts:
- Plan your visit in advance: The aqueducts are scattered throughout Rome, so it’s essential to plan your itinerary in advance.
- Wear comfortable shoes: The aqueducts are often located in rural areas, so it’s important to wear comfortable shoes for walking.
- Bring water and snacks: There are limited amenities at the aqueducts, so it’s best to bring your own water and snacks.
- Take advantage of guided tours: Guided tours can provide valuable insights into the history and engineering of the aqueducts.
- Be mindful of the environment: The aqueducts are ancient structures, so it’s important to respect the environment and avoid damaging the ruins.
Conclusion:
The map of the Roman aqueducts is a powerful testament to the ingenuity and ambition of a civilization that dared to conquer nature itself. These structures, stretching for miles across the Roman countryside, played a pivotal role in the city’s growth, prosperity, and well-being. They stand as a reminder of the Romans’ mastery of engineering and their commitment to providing their citizens with a high quality of life. Today, the aqueducts continue to fascinate and inspire visitors, offering a glimpse into the ingenuity and grandeur of a bygone era.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Aqueducts of Rome: A Map to Ancient Engineering Marvels. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!