Tajikistan: A Landlocked Gem in Central Asia
Related Articles: Tajikistan: A Landlocked Gem in Central Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Tajikistan: A Landlocked Gem in Central Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tajikistan: A Landlocked Gem in Central Asia

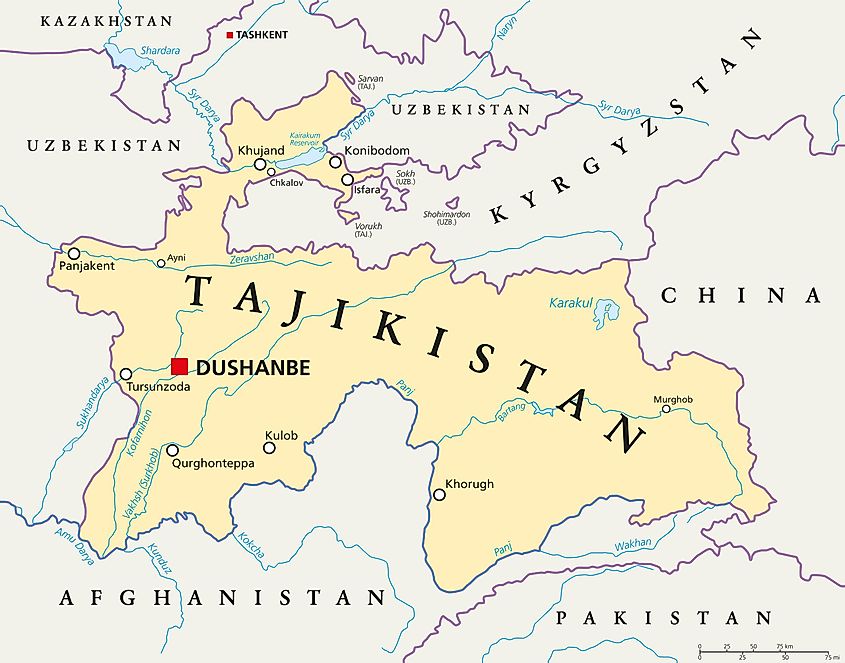
Nestled amidst the towering peaks of the Pamir Mountains, Tajikistan, a landlocked nation in Central Asia, boasts a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty. Its geographical location, bordering Afghanistan, China, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan, has shaped its unique identity and played a crucial role in its development. This article delves into the geography of Tajikistan, exploring its diverse landscapes, key cities, and strategic significance in the region.
A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes
Tajikistan’s terrain is characterized by dramatic contrasts, ranging from snow-capped mountain ranges to fertile valleys and vast deserts. The Pamir Mountains, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," dominate the eastern and southern regions, reaching heights exceeding 7,000 meters. The majestic peaks, including the legendary Peak Ismail Samani (formerly known as Communism Peak), the highest peak in the former Soviet Union, offer breathtaking views and challenge adventurous mountaineers.
The Heart of Tajikistan: The Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley, a fertile basin shared with Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan, cuts through the heart of Tajikistan. This region is renowned for its abundant agricultural production, supporting a significant population and providing essential resources. The valley is home to several key cities, including Khujand, the second-largest city in Tajikistan, and Istaravshan, known for its historical significance and ancient architecture.
Ancient Cities and Historical Treasures
Tajikistan’s history stretches back millennia, leaving behind a legacy of ancient cities and architectural marvels. The capital city, Dushanbe, is a modern metropolis, yet it retains traces of its past, evident in the National Museum of Tajikistan, housing a vast collection of artifacts from ancient civilizations.
Other historical gems include:
- Bukhara: Located in neighboring Uzbekistan, Bukhara was a prominent trading center on the Silk Road and boasts a rich history, evident in its numerous mosques, madrasas, and ancient bazaars.
- Samarkand: Another Silk Road gem in Uzbekistan, Samarkand was a major hub for trade and cultural exchange. Its iconic Registan Square, adorned with three magnificent madrasas, stands as a testament to its glorious past.
- The ancient city of Panjakent: Situated in the Sughd Region of Tajikistan, Panjakent is a testament to the country’s rich history, with archaeological evidence dating back to the 5th century BC.
Strategic Significance in the Region
Tajikistan’s strategic location at the crossroads of Central Asia has made it a vital player in regional politics and trade. The country’s access to natural resources, including significant reserves of water, has further increased its importance. The Amu Darya River, one of Central Asia’s major rivers, originates in Tajikistan and flows through neighboring countries, making it a crucial resource for agriculture and hydropower.
Hydropower: A Source of Energy and Development
Tajikistan’s mountainous terrain offers immense potential for hydropower development. The country possesses abundant water resources, and the government is actively investing in hydroelectric projects to meet domestic energy needs and export excess electricity to neighboring countries. This initiative aims to contribute to the country’s economic growth and improve living standards.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its rich potential, Tajikistan faces several challenges, including:
- Poverty: While economic growth has been observed in recent years, poverty remains a significant issue, especially in rural areas.
- Limited Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure, particularly in transportation and communication, hinders economic development and limits access to essential services.
- Environmental Concerns: Climate change poses a threat to Tajikistan’s fragile environment, impacting water resources and agricultural productivity.
Tourism: A Growing Sector
Tajikistan’s stunning natural beauty, diverse landscapes, and rich history offer immense potential for tourism. The country is home to numerous national parks, including the Pamir National Park, renowned for its breathtaking mountain scenery and rare wildlife. The development of tourism infrastructure and marketing initiatives can attract more visitors, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
FAQs
Q: What is the capital of Tajikistan?
A: The capital of Tajikistan is Dushanbe.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Tajikistan?
A: The official language of Tajikistan is Tajik, a Persian-based language. Russian is also widely spoken, particularly in urban areas.
Q: What is the currency of Tajikistan?
A: The currency of Tajikistan is the Tajikistani Somoni (TJS).
Q: What is the climate like in Tajikistan?
A: Tajikistan has a continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters. The climate varies significantly depending on altitude and location.
Q: Is Tajikistan a safe country to visit?
A: Tajikistan is generally considered a safe country for tourists. However, it is essential to be aware of local customs and follow safety guidelines, especially when traveling to remote areas.
Tips for Visiting Tajikistan
- Plan your trip in advance: Booking accommodations and transportation in advance is recommended, especially during peak season.
- Obtain a visa: Most visitors require a visa to enter Tajikistan.
- Pack appropriately: The climate in Tajikistan can vary significantly, so pack layers of clothing.
- Respect local customs: Dress modestly and be mindful of cultural sensitivities.
- Learn a few basic Tajik phrases: This will enhance your experience and facilitate communication with locals.
- Be prepared for altitude sickness: If traveling to higher elevations, be aware of the potential for altitude sickness and take necessary precautions.
Conclusion
Tajikistan, a landlocked nation in Central Asia, is a land of contrasts, boasting majestic mountains, fertile valleys, and ancient cities. Its strategic location and abundant natural resources offer significant potential for development. While the country faces challenges such as poverty and limited infrastructure, its rich culture, diverse landscapes, and growing tourism sector present opportunities for a brighter future. As Tajikistan navigates the challenges and embraces its potential, its unique position in Central Asia will continue to shape its destiny and contribute to the region’s dynamic landscape.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tajikistan: A Landlocked Gem in Central Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!