Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Denmark, Sweden, and Norway
Related Articles: Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Denmark, Sweden, and Norway
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Denmark, Sweden, and Norway. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Denmark, Sweden, and Norway
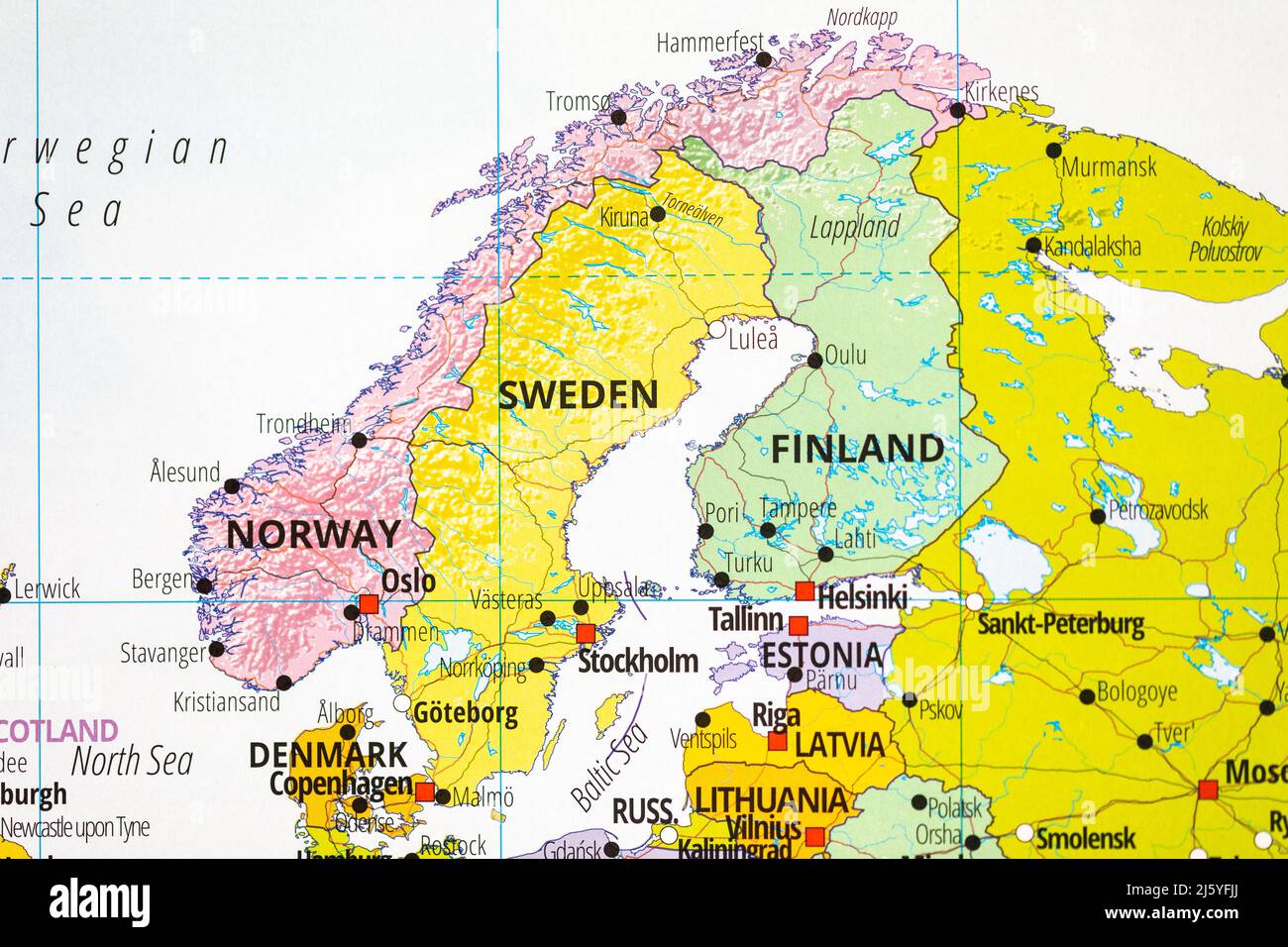
The Scandinavian Peninsula, a land of breathtaking landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures, encompasses three distinct nations: Denmark, Sweden, and Norway. Understanding the geographical relationships between these countries is crucial for appreciating their unique identities and interconnectedness. This comprehensive guide explores the map of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway, providing a detailed overview of their geographical features, historical connections, and cultural nuances.
Denmark: The Gateway to Scandinavia
Denmark, the southernmost of the three countries, holds a unique position as the bridge between continental Europe and the Scandinavian Peninsula. Located on the Jutland Peninsula and numerous islands, Denmark is characterized by its flat terrain, fertile land, and extensive coastline. Its proximity to Germany and its historical role as a trading hub have shaped its cultural identity and economic development.
Key Geographical Features of Denmark:
- Jutland Peninsula: The largest landmass of Denmark, Jutland is characterized by its flat landscape, fertile soil, and sandy beaches.
- Danish Islands: The country comprises over 400 islands, with the largest being Zealand, Funen, and Lolland. These islands are connected by bridges and ferries, facilitating travel and trade within the country.
- The Little Belt and The Great Belt: These two straits separate the Jutland Peninsula from the islands of Funen and Zealand, respectively. They are vital waterways for maritime trade and transportation.
- The Baltic Sea: Denmark’s eastern coastline borders the Baltic Sea, a large inland sea with a rich history and significant economic importance.
Sweden: The Land of Lakes and Forests
Sweden, the largest of the three Nordic nations, occupies the eastern portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. Its landscape is dominated by vast forests, numerous lakes, and rugged mountains, providing a stark contrast to Denmark’s flatter terrain. Sweden’s history is intertwined with its natural resources, particularly its timber and mineral deposits.
Key Geographical Features of Sweden:
- Scandinavian Mountains: The Scandinavian Mountains, stretching along the western border of Sweden, are a defining feature of the country’s landscape.
- The Swedish Highlands: This region, located in the central and northern parts of Sweden, is characterized by its vast forests, numerous lakes, and rugged terrain.
- The Baltic Sea: Sweden shares a long coastline with the Baltic Sea, providing access to international trade and maritime transportation.
- The Gulf of Bothnia: A large arm of the Baltic Sea, the Gulf of Bothnia separates Sweden from Finland.
Norway: The Land of Fjords and Mountains
Norway, occupying the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, is renowned for its dramatic coastline, towering mountains, and deep fjords. Its rugged terrain and abundant natural resources have shaped its history, culture, and economy. Norway’s distinctive landscape is a testament to the powerful forces of nature that have sculpted its land over millennia.
Key Geographical Features of Norway:
- The Norwegian Fjords: Deep, narrow inlets carved by glaciers, the fjords are a defining feature of Norway’s coastline. Their majestic beauty attracts tourists from around the world.
- The Scandinavian Mountains: Norway shares the Scandinavian Mountains with Sweden, with peaks reaching heights of over 2,000 meters.
- The North Sea: Norway’s western coastline borders the North Sea, a vital waterway for maritime trade and fishing.
- The Arctic Circle: Northern Norway lies within the Arctic Circle, experiencing long periods of darkness in winter and daylight in summer.
Historical Connections and Cultural Influences
The geographical proximity of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway has fostered a long history of interaction and exchange. These countries have shared cultural influences, common historical experiences, and a strong sense of regional identity.
- The Viking Age: From the 8th to the 11th centuries, Vikings from these countries embarked on voyages of exploration and conquest, leaving a lasting impact on European history and culture.
- The Kalmar Union: In the 14th century, Denmark, Sweden, and Norway were united under a single monarch in the Kalmar Union, marking a period of shared governance and cultural exchange.
- The Scandinavian Languages: The languages spoken in these countries, Danish, Swedish, and Norwegian, are closely related, reflecting their shared linguistic heritage.
- The Nordic Council: Established in 1952, the Nordic Council is an inter-governmental organization that promotes cooperation and collaboration between Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands.
Economic Interdependence and Modern Connections
The close geographical proximity and historical connections between Denmark, Sweden, and Norway have fostered strong economic ties. These countries share a common market, collaborate on infrastructure projects, and engage in significant trade with each other.
- The Nordic Council of Ministers: This organization promotes cooperation between the Nordic countries in areas such as trade, transportation, environmental protection, and research.
- The Nordic Investment Bank: This financial institution provides loans and guarantees for infrastructure projects in the Nordic countries.
- The Nordic passport union: Citizens of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway can travel freely within the Nordic region without requiring visas or passports.
- The Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS): This airline provides a comprehensive network of flights connecting the major cities in Denmark, Sweden, and Norway.
Cultural Nuances and Shared Heritage
Despite their distinct identities, Denmark, Sweden, and Norway share a common cultural heritage rooted in their Nordic ancestry. This shared heritage is reflected in their languages, folklore, traditions, and social values.
- Folklore and Mythology: The countries share a rich tradition of folklore and mythology, featuring mythical creatures, ancient gods, and tales of bravery and adventure.
- Social Welfare Systems: Denmark, Sweden, and Norway have developed strong social welfare systems, providing universal healthcare, education, and social security benefits to their citizens.
- Design and Innovation: The Nordic countries are renowned for their minimalist design aesthetic and innovative approaches to technology and sustainability.
- Environmental Consciousness: The countries have a strong commitment to environmental protection and sustainability, reflected in their policies and lifestyles.
FAQs
1. What are the major cities in Denmark, Sweden, and Norway?
- Denmark: Copenhagen (capital), Aarhus, Odense, Aalborg.
- Sweden: Stockholm (capital), Gothenburg, Malmö, Uppsala.
- Norway: Oslo (capital), Bergen, Trondheim, Stavanger.
2. What are the main languages spoken in these countries?
- Denmark: Danish
- Sweden: Swedish
- Norway: Norwegian (Bokmål and Nynorsk)
3. What are the main religions practiced in these countries?
- Denmark: Lutheran Christianity is the dominant religion.
- Sweden: Lutheran Christianity is the dominant religion.
- Norway: Lutheran Christianity is the dominant religion.
4. What are some of the most popular tourist attractions in these countries?
- Denmark: Tivoli Gardens, The Little Mermaid statue, Rosenborg Castle.
- Sweden: Stockholm Palace, Vasa Museum, Gamla Stan (Old Town).
- Norway: The fjords (Geirangerfjord, Sognefjord), Preikestolen (Pulpit Rock), Trolltunga (Troll’s Tongue).
5. What are the currencies used in these countries?
- Denmark: Danish krone (DKK)
- Sweden: Swedish krona (SEK)
- Norway: Norwegian krone (NOK)
Tips for Traveling to Denmark, Sweden, and Norway
- Plan your trip in advance: Booking flights and accommodation well in advance can help you secure better deals and avoid disappointment.
- Learn a few basic phrases in the local language: This will be appreciated by the locals and can help you navigate everyday situations.
- Pack for all types of weather: The Nordic countries are known for their unpredictable weather, so be prepared for rain, wind, and cold temperatures.
- Embrace the local culture: Take advantage of the opportunity to experience local cuisine, traditions, and festivals.
- Respect the environment: Be mindful of your impact on the environment by following local guidelines and disposing of waste properly.
Conclusion
The map of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway tells a story of interconnectedness, shared heritage, and distinct identities. These countries, despite their geographical proximity and historical ties, have carved their own unique paths in the world. Understanding the geographical relationships between them is crucial for appreciating their diverse cultures, vibrant landscapes, and significant contributions to the global community. Whether exploring their historic cities, traversing their breathtaking landscapes, or delving into their rich cultural heritage, a journey through the map of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway is an enriching experience that offers a glimpse into the heart of Scandinavia.


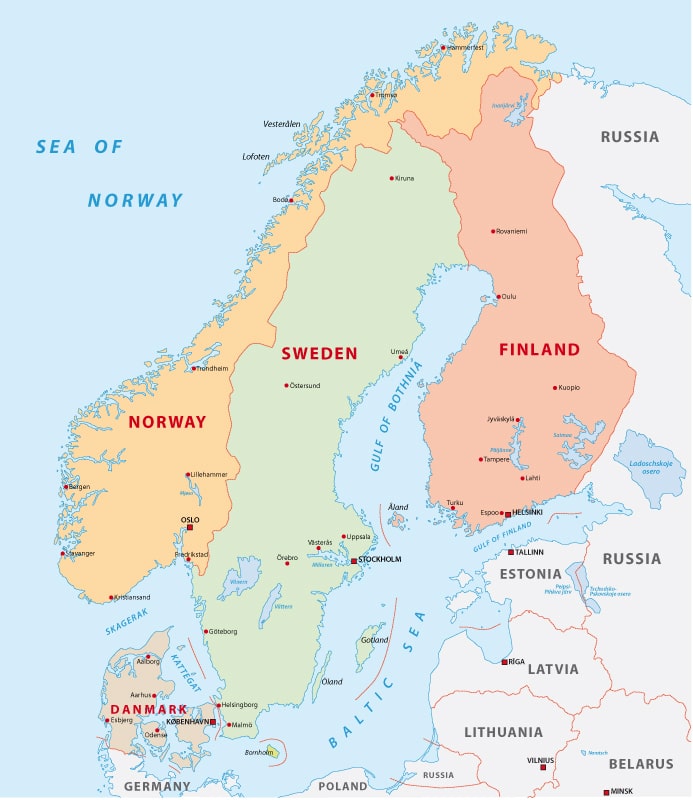



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Nordic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Denmark, Sweden, and Norway. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!