Navigating the Elements: A Comprehensive Guide to Nationwide Weather Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Elements: A Comprehensive Guide to Nationwide Weather Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Elements: A Comprehensive Guide to Nationwide Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Elements: A Comprehensive Guide to Nationwide Weather Maps

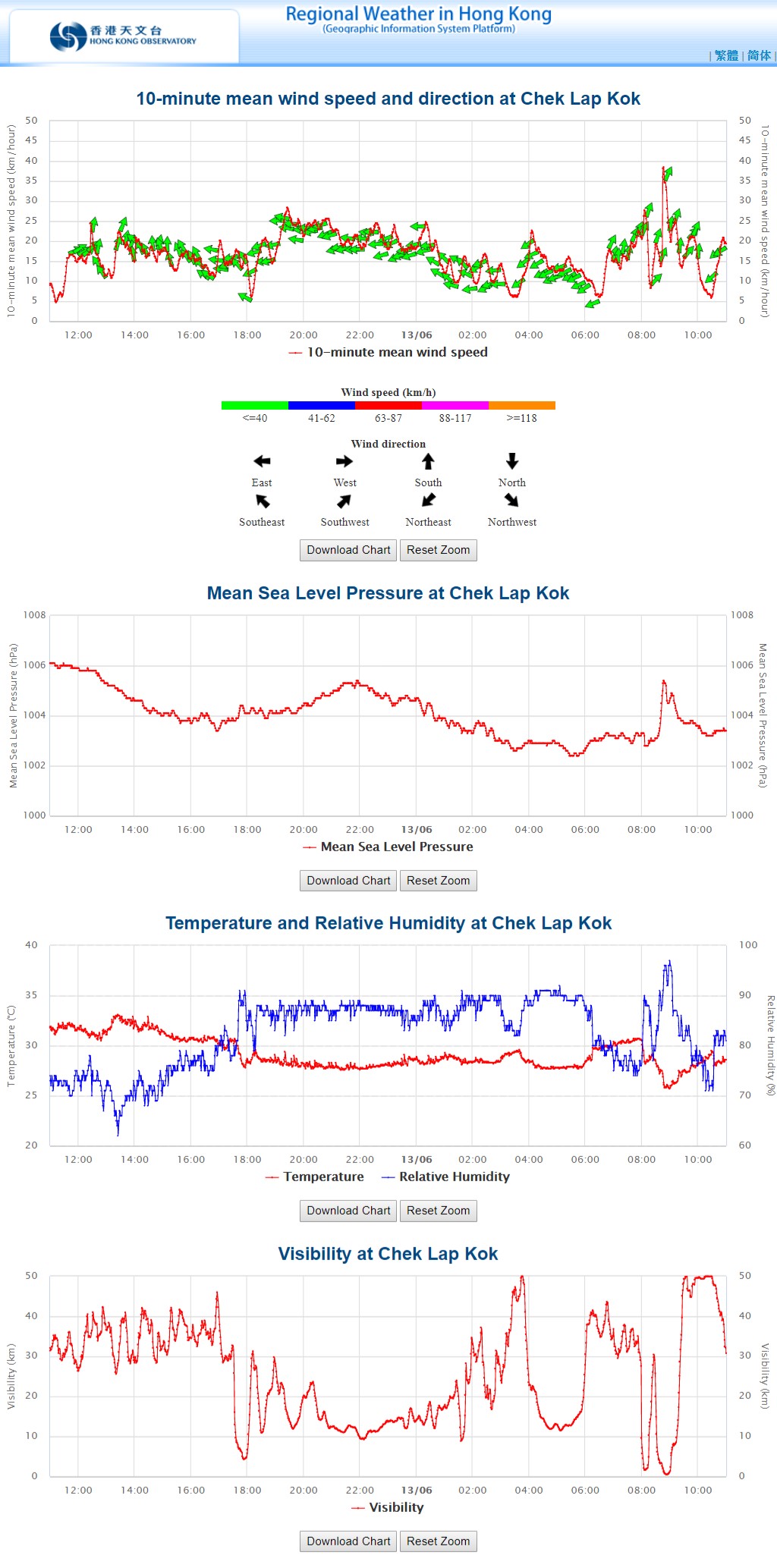
Understanding the weather is a fundamental human need. From daily decisions about clothing to preparing for extreme events, accurate weather information plays a crucial role in our lives. Nationwide weather maps, with their intricate tapestry of colors and symbols, provide a visual representation of atmospheric conditions across vast regions, empowering individuals and organizations to make informed decisions.
Unveiling the Layers of a Weather Map:
A nationwide weather map is a complex yet intuitive tool, offering a snapshot of current weather patterns and forecasting future conditions. The key components of a weather map include:
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. Closely spaced isobars indicate strong pressure gradients, often associated with windy conditions.
- Fronts: Boundaries between air masses of different temperatures and humidity. These boundaries often trigger precipitation and significant shifts in weather patterns.
- Temperature: Displayed using color gradients, with warmer areas represented by reds and oranges, and cooler areas by blues and purples.
- Precipitation: Shown as symbols representing different types of precipitation, such as rain, snow, or thunderstorms.
- Wind: Indicated by arrows, with the length and direction of the arrow reflecting wind speed and direction.
- Cloud Cover: Depicted using symbols that represent different cloud types and coverage.
Beyond the Visual: Understanding the Data:
While the visual representation of weather maps is essential for quick comprehension, the data behind these maps is crucial for accurate forecasting and informed decision-making. Weather maps are generated using data from various sources, including:
- Surface Weather Stations: These stations across the country provide real-time readings of temperature, pressure, wind speed and direction, humidity, and precipitation.
- Radars: Emit electromagnetic waves to detect precipitation, allowing meteorologists to track storms and predict their movement.
- Satellites: Provide a wide-angle view of the Earth’s atmosphere, capturing data on cloud cover, temperature, and moisture.
- Weather Balloons: Released twice daily from hundreds of locations, these balloons carry instruments that measure atmospheric conditions at various altitudes.
The Vital Role of Weather Maps in Our Lives:
Weather maps are not merely static representations; they are dynamic tools that play a vital role in numerous aspects of our lives. Here are some key applications:
- Public Safety: Weather maps are essential for forecasting severe weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards, allowing authorities to issue timely warnings and evacuate vulnerable areas.
- Transportation: Airlines, shipping companies, and road authorities rely on weather maps to navigate safely, avoiding hazardous conditions and optimizing routes.
- Agriculture: Farmers utilize weather maps to plan planting and harvesting schedules, ensuring optimal conditions for crop growth and minimizing losses due to adverse weather.
- Energy Production: Power companies use weather maps to predict energy demand and optimize energy production, considering factors like wind and solar potential.
- Public Health: Weather maps help monitor heat waves, cold snaps, and other extreme weather events that can impact public health, allowing for timely interventions.
- Tourism and Recreation: Individuals planning outdoor activities rely on weather maps to choose appropriate attire, prepare for potential weather changes, and ensure safe and enjoyable experiences.
Navigating the Information: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a surface weather map and an upper-air weather map?
A: A surface weather map depicts weather conditions at the Earth’s surface, while an upper-air weather map shows conditions at various altitudes. Upper-air maps provide valuable information about jet streams, high-altitude winds, and other atmospheric phenomena that influence surface weather.
Q: How accurate are weather forecasts?
A: The accuracy of weather forecasts varies depending on the time frame and the complexity of the weather system. Short-term forecasts (up to a few days) are generally more accurate than long-term forecasts (weeks or months). Advances in technology and data analysis have significantly improved forecast accuracy over time.
Q: How can I interpret a weather map?
A: Start by focusing on the key symbols and data points. Pay attention to the location of fronts, the direction and strength of winds, and the areas of precipitation. Consult the legend accompanying the map to understand the specific symbols and their meanings.
Q: Where can I find reliable weather maps?
A: Numerous online resources, including government agencies like the National Weather Service (NWS) and private weather companies, provide free and accurate weather maps. Many weather apps also offer detailed weather maps and forecasts.
Tips for Effective Weather Map Utilization:
- Consider the time frame: Weather maps provide snapshots of current conditions and forecasts for specific time periods. Ensure you are using a map that corresponds to your needs.
- Focus on relevant information: Identify the data points most relevant to your situation, such as temperature, precipitation, or wind speed.
- Cross-reference with other sources: Combine weather map information with other data sources, such as local news reports or weather alerts, for a comprehensive understanding of weather conditions.
- Stay informed: Monitor weather updates regularly, especially during periods of potential severe weather.
Conclusion:
Nationwide weather maps are powerful tools that provide a visual representation of atmospheric conditions, enabling informed decision-making across a wide range of applications. By understanding the components of a weather map, interpreting the data, and utilizing these maps effectively, individuals and organizations can navigate the elements with greater awareness and preparedness, fostering safety, efficiency, and informed decision-making in a world increasingly impacted by weather.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Elements: A Comprehensive Guide to Nationwide Weather Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!