Navigating the Complexities of the Rosewood Trade: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rosewood Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of the Rosewood Trade: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rosewood Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of the Rosewood Trade: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rosewood Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of the Rosewood Trade: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rosewood Map
The rosewood map is not a physical map in the traditional sense, but rather a metaphorical representation of the intricate and often controversial global trade in rosewood. It encompasses the diverse species of rosewood trees, their geographical distribution, the economic forces driving their exploitation, and the environmental and social consequences of this trade. Understanding the complexities of this map is crucial for navigating the ethical and sustainable use of rosewood, a valuable and highly sought-after wood.
The Rosewood Family: A Diverse and Valuable Resource
Rosewood encompasses a wide range of tree species belonging to the genera Dalbergia, Pterocarpus, and Machaerium, among others. These trees are native to tropical and subtropical regions across the globe, with significant populations found in Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America.
The unique properties of rosewood, including its durability, beautiful grain patterns, and rich, aromatic scent, have made it highly prized for centuries. Its uses range from high-end furniture and musical instruments to traditional medicine and incense.
Navigating the Map: A Global Perspective
The global trade in rosewood is a complex tapestry woven from various threads:
- Demand: The demand for rosewood is driven by a combination of factors, including its aesthetic appeal, cultural significance, and perceived value. The increasing wealth and urbanization in Asia, particularly China, has significantly fueled the demand for rosewood furniture and other products.
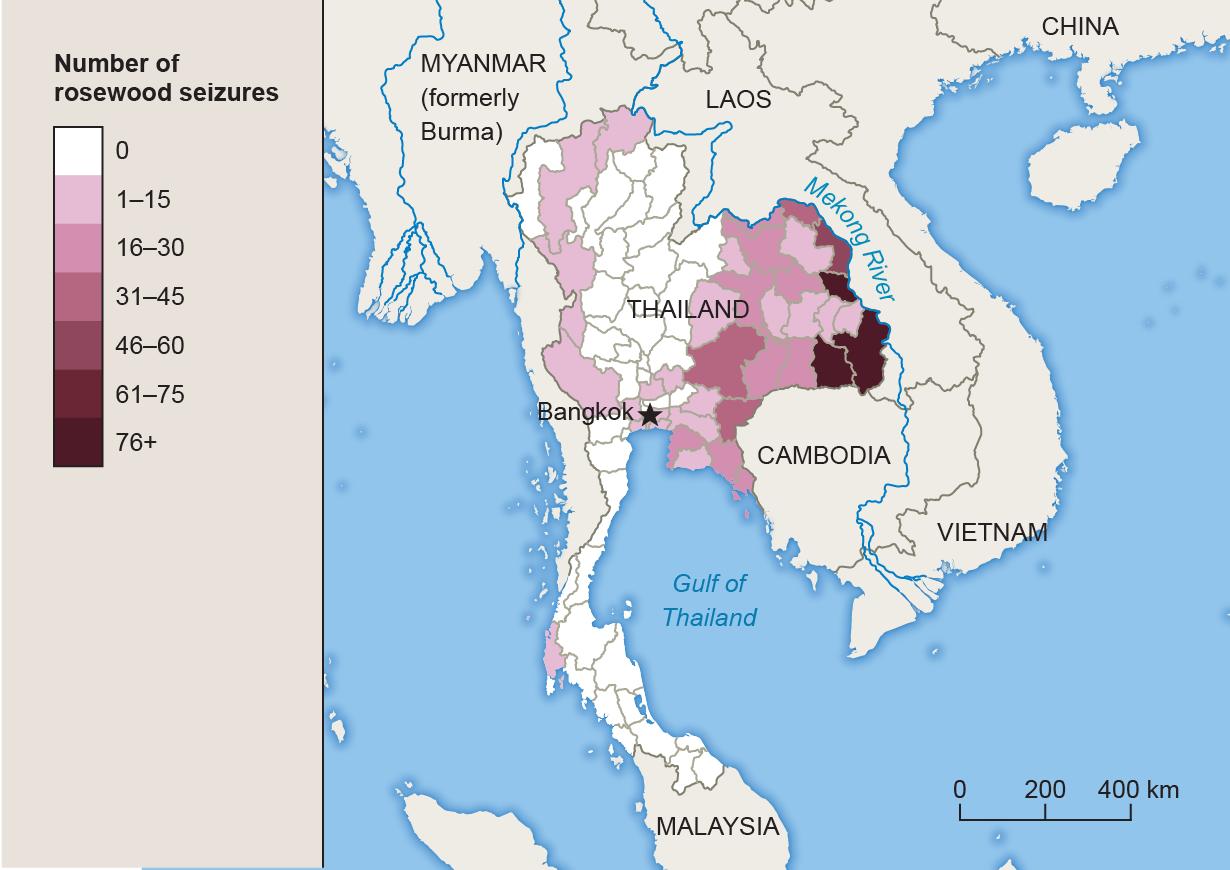
- Supply: The supply of rosewood is geographically diverse, with various species found in different regions. However, the distribution of these species is uneven, and many are now facing overexploitation due to unsustainable harvesting practices.
- Trade Routes: Rosewood travels along intricate trade routes, often passing through multiple countries before reaching its final destination. This complex network makes it difficult to track the origin of the wood and ensure its legal and sustainable sourcing.
- Regulation: International and national regulations aim to control the trade in rosewood, including CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Flora and Fauna) listings and national laws. However, enforcement of these regulations is often challenging, and illegal trade remains a significant issue.
The Shadows on the Map: Environmental and Social Impacts
The unsustainable exploitation of rosewood has significant environmental and social impacts:
- Deforestation: The illegal logging of rosewood contributes to widespread deforestation, threatening biodiversity and ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration and water regulation.
- Habitat Loss: The loss of rosewood forests has severe consequences for wildlife, including endangered species that rely on these habitats for survival.
- Community Displacement: Local communities often bear the brunt of the environmental and social consequences of rosewood exploitation, experiencing displacement, loss of livelihoods, and conflicts over land rights.
- Corruption: The illegal trade in rosewood is often intertwined with corruption and organized crime, further exacerbating the negative impacts.
The Path Forward: Towards Sustainable Use
Navigating the complexities of the rosewood map requires a multi-faceted approach to ensure its sustainable use:
- Stricter Regulation: Strengthening international and national regulations, including effective enforcement mechanisms, is crucial for curbing illegal trade and promoting sustainable harvesting practices.
- Sustainable Forestry Management: Implementing sustainable forestry practices, such as selective logging, reforestation, and community-based forest management, is essential for conserving rosewood resources and ensuring their long-term availability.
- Consumer Awareness: Raising awareness among consumers about the environmental and social impacts of unsustainable rosewood trade is crucial for driving demand for ethically sourced products.
- Alternative Materials: Exploring and promoting alternative materials for furniture and other products can reduce the pressure on rosewood resources and encourage sustainable alternatives.
- Collaboration: Collaborative efforts between governments, conservation organizations, industry stakeholders, and local communities are essential for addressing the complex challenges of the rosewood trade.
FAQs on Rosewood Map
1. What are the most endangered rosewood species?
Several rosewood species are classified as critically endangered by the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature), including Dalbergia cochinchinensis, Dalbergia nigra, and Dalbergia latifolia.
2. How can I ensure the rosewood I purchase is sustainably sourced?
Look for certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or CITES permits to verify the legality and sustainability of the product.
3. What are the alternatives to rosewood for furniture and other products?
Sustainable alternatives include teak, mahogany, walnut, and recycled materials like reclaimed wood.
4. How can I contribute to the conservation of rosewood forests?
Support organizations working on rosewood conservation and sustainable forestry, and choose products made from sustainably sourced materials.
5. Is there a way to track the origin of rosewood products?
Technological advancements like blockchain and DNA barcoding are being explored to improve traceability and combat illegal trade.
Tips for Navigating the Rosewood Map
- Be Informed: Educate yourself about the environmental and social impacts of the rosewood trade and the different species involved.
- Choose Wisely: Select products made from sustainably sourced rosewood or explore alternative materials.
- Support Conservation: Donate to organizations working on rosewood conservation and sustainable forestry.
- Advocate for Change: Encourage businesses and policymakers to adopt sustainable practices and stricter regulations.
- Spread Awareness: Share information about the rosewood trade and its consequences with your network.
Conclusion
The rosewood map is a complex and evolving landscape. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for navigating the ethical and sustainable use of this valuable resource. By promoting responsible practices, raising awareness, and supporting conservation efforts, we can contribute to a future where rosewood is sustainably managed and enjoyed for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of the Rosewood Trade: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rosewood Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!