Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel and the Middle East
Related Articles: Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel and the Middle East
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel and the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel and the Middle East

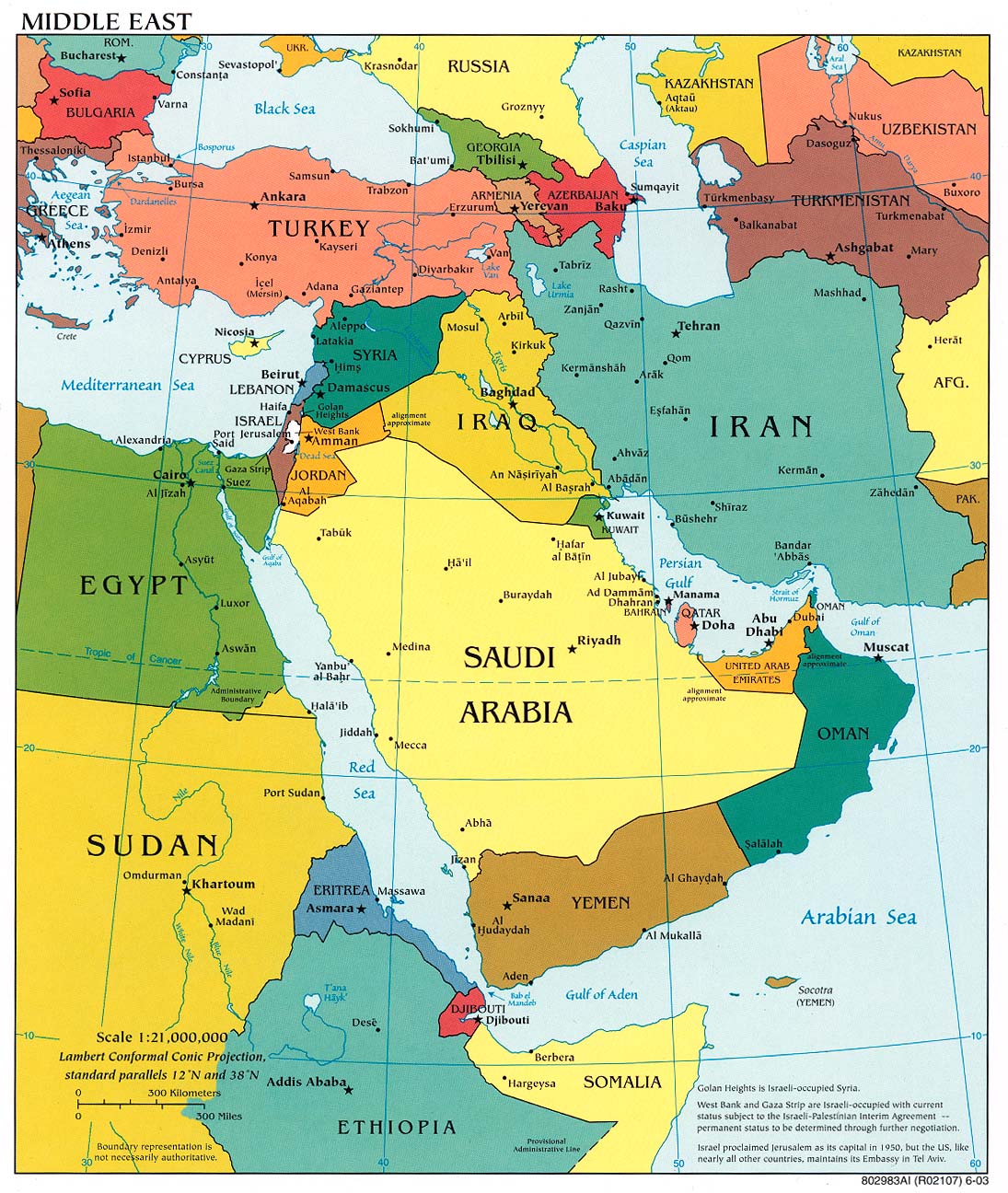
The Middle East, a region steeped in history, culture, and geopolitical complexities, presents a fascinating and often challenging landscape for understanding. At its core lies Israel, a nation whose presence and boundaries have sparked countless debates and controversies. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear and informative understanding of the map of Israel and the Middle East, exploring its historical context, geographical features, and the political dynamics that shape its current state.
Understanding the Geographic Context
The Middle East, a vast region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, and parts of Asia, is characterized by diverse landscapes, ranging from fertile river valleys to arid deserts. The region’s geography has played a significant role in shaping its history and influencing its political and economic development.
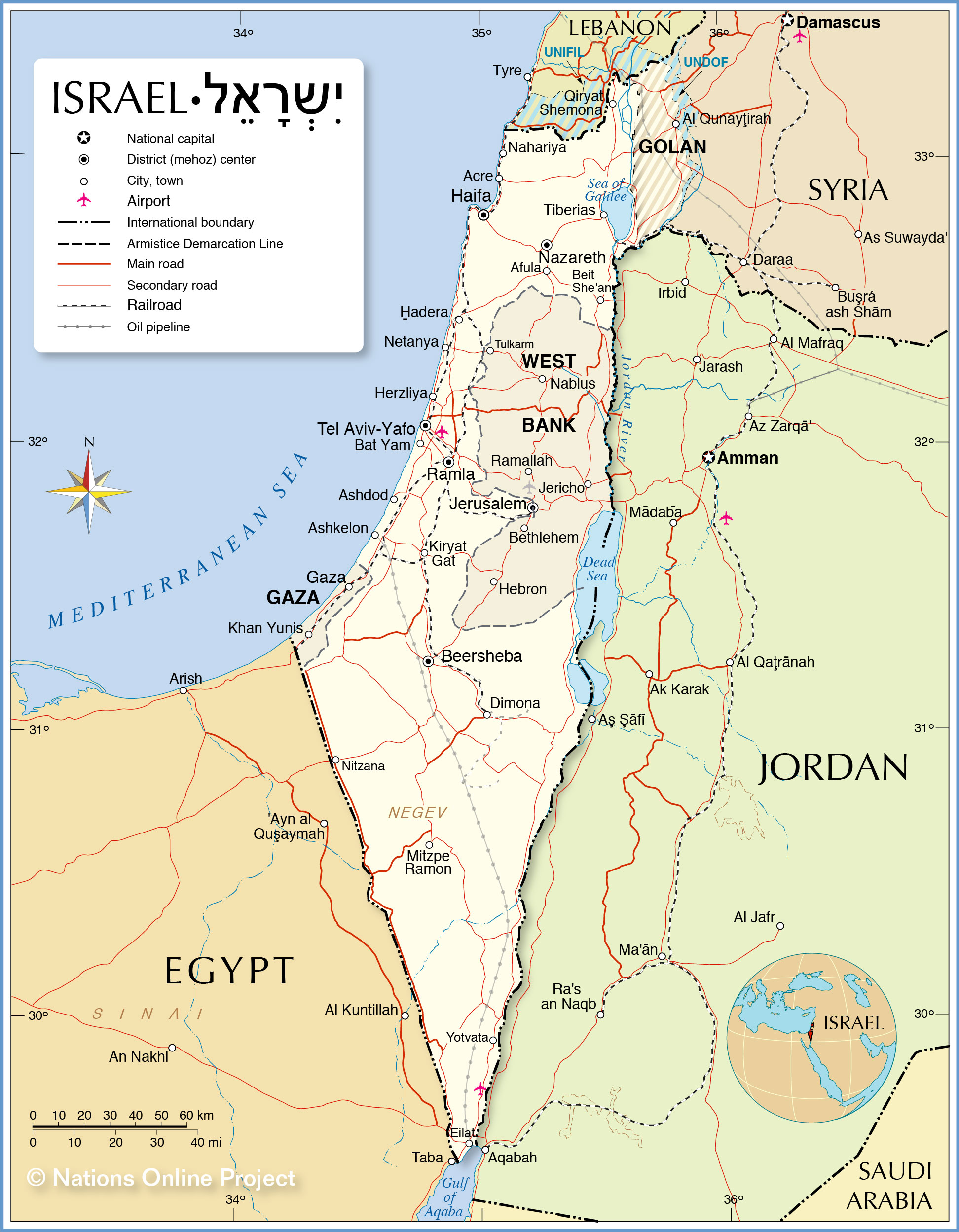
Israel’s Location and Borders
Israel, situated in the southeastern corner of the Mediterranean Sea, occupies a relatively small landmass. Its boundaries have been subject to constant change throughout history, with the modern state of Israel established in 1948 following the British withdrawal from Palestine.
Key Geographical Features
- The Mediterranean Sea: The Mediterranean Sea forms Israel’s western border, providing access to international trade and influencing its climate.
- The Jordan River: Flowing through the Jordan Valley, the Jordan River forms a natural boundary between Israel and Jordan.
- The Dead Sea: The Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, lies between Israel and Jordan, offering unique geological and environmental features.
- The Negev Desert: The Negev Desert, covering much of southern Israel, presents a vast and arid landscape.
- The Golan Heights: The Golan Heights, a strategically important plateau, is a disputed territory between Israel and Syria.
Historical Context: A Tapestry of Empires and Conflicts
The Middle East has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, each leaving its mark on the region’s cultural and political landscape. Understanding the historical context is crucial for grasping the complexities of the present.
Ancient Empires and the Birth of Judaism
The region was home to ancient civilizations like the Babylonians, Persians, and Romans. The emergence of Judaism in the Levant, with its roots in the Hebrew Bible, laid the groundwork for future religious and political developments.
Ottoman Rule and the Rise of Zionism
The Ottoman Empire ruled the region for centuries, until its decline in the late 19th century. During this period, the Zionist movement emerged, advocating for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
The British Mandate and the 1948 War
Following World War I, Britain was granted a mandate over Palestine. The tension between Jewish and Arab populations escalated, culminating in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, which led to the establishment of the state of Israel.
The Six-Day War and the Expansion of Israel
The Six-Day War of 1967 saw Israel seize control of the Sinai Peninsula, the Golan Heights, the West Bank, and East Jerusalem. This expansion significantly altered the map of the region and sparked ongoing disputes.
The Peace Process and the Oslo Accords
Efforts towards peace between Israel and its Arab neighbors have been ongoing for decades. The Oslo Accords, signed in the 1990s, aimed to establish a two-state solution, but these efforts have been hampered by political complexities and ongoing conflicts.
The Ongoing Conflicts and the Quest for Peace
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains one of the most intractable issues in the region, with ongoing disputes over land, resources, and political rights. The quest for a lasting peace remains a challenging but crucial endeavor.
The Palestinian Territories: Gaza and the West Bank
The Palestinian territories, encompassing Gaza and the West Bank, are under Israeli control, with varying degrees of autonomy. These territories are subject to ongoing disputes and conflicts, with a complex web of political and humanitarian issues.
Understanding the Political Landscape
The map of Israel and the Middle East reflects a complex political landscape, shaped by historical grievances, religious beliefs, and competing national aspirations.
Major Players and their Interests
- Israel: Israel, a democratic state with a strong military, seeks to maintain its security and territorial integrity while pursuing peace with its neighbors.
- Palestine: The Palestinian people aspire to establish an independent state in the West Bank and Gaza, with East Jerusalem as its capital.
- Arab States: Arab states, including Egypt, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon, hold diverse views on Israel, ranging from outright hostility to cautious diplomacy.
- International Actors: International actors, including the United States, the European Union, and the United Nations, play significant roles in mediating peace efforts and providing humanitarian aid.
The Role of Religion and Identity
Religion plays a profound role in shaping the identity and politics of the region. The intertwined histories of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam have shaped the region’s cultural landscape and fueled conflicts over holy sites and religious authority.
The Importance of Understanding the Map
Understanding the map of Israel and the Middle East is essential for comprehending the region’s history, its current state, and its future prospects. It provides a framework for analyzing the geopolitical dynamics, the role of religion, and the challenges to peace.
FAQs on the Map of Israel and the Middle East
1. What are the major disputed territories in the region?
The major disputed territories include the West Bank, East Jerusalem, the Golan Heights, and the Gaza Strip. These areas are claimed by both Israel and the Palestinians, with varying degrees of control and autonomy.
2. What are the main religious sites in the region?
The region is home to numerous religious sites, including the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, which is sacred to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam; the Western Wall in Jerusalem, a holy site for Judaism; the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, a Christian pilgrimage site; and the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, an Islamic shrine.
3. What are the main challenges to peace in the region?
The main challenges to peace include the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the territorial disputes, the security concerns of both sides, and the deep-rooted historical grievances.
4. What are the potential solutions to the conflict?
Potential solutions include a two-state solution, with the establishment of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel; a one-state solution, with a single state for both Israelis and Palestinians; or a confederation model, with a loose alliance between Israel and a Palestinian state.
5. What role do international actors play in the region?
International actors play a crucial role in mediating peace efforts, providing humanitarian aid, and promoting dialogue. They also impose sanctions and exert diplomatic pressure on both sides.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Israel and the Middle East
- Study the historical context: Understanding the historical events that shaped the region is essential for grasping the current situation.
- Analyze the geographical features: The region’s geography has played a significant role in its history and political dynamics.
- Consider the perspectives of all stakeholders: It is crucial to consider the perspectives of all parties involved, including Israelis, Palestinians, and neighboring Arab states.
- Stay informed about current events: The situation in the Middle East is constantly evolving, so staying informed about current events is essential for understanding the complexities of the region.
- Be critical of information sources: Be wary of biased or inaccurate information and seek out credible sources of news and analysis.
Conclusion
The map of Israel and the Middle East reflects a region of profound historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance. Understanding the intricate details of this map is crucial for navigating the complexities of the region, its conflicts, and its potential for peace. By studying the historical context, analyzing the geographical features, and considering the perspectives of all stakeholders, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in this dynamic and multifaceted region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel and the Middle East. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!