Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Massachusetts
Related Articles: Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Massachusetts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Massachusetts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Massachusetts
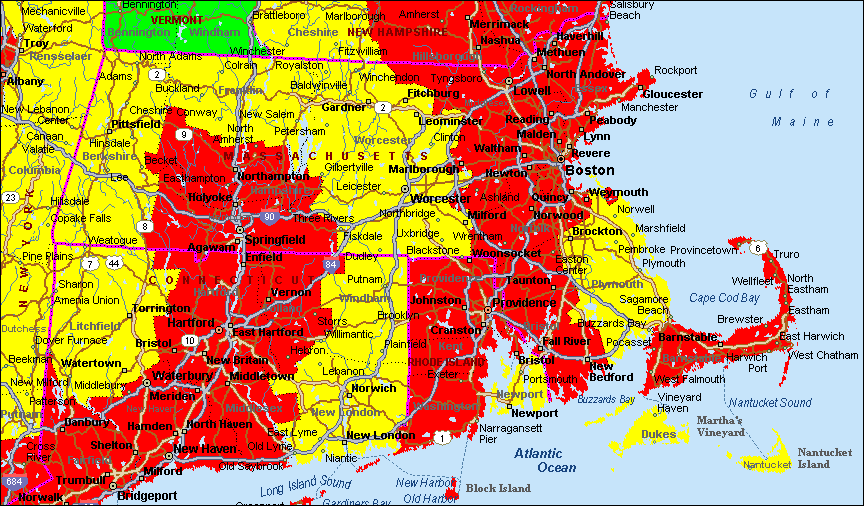
The air we breathe is an essential element of human life, yet its quality can significantly impact our health and well-being. In Massachusetts, a state known for its vibrant cities, sprawling countryside, and diverse population, understanding the nuances of air quality is paramount. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the air quality map of Massachusetts, illuminating its significance and providing valuable insights for residents and visitors alike.
Decoding the Air Quality Map: A Visual Representation of Breath
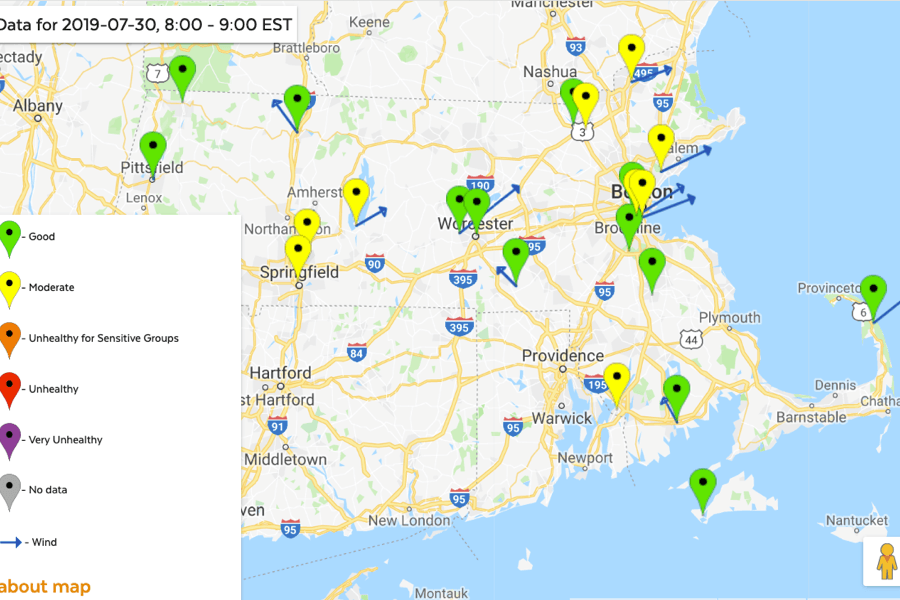
The air quality map of Massachusetts, a dynamic and informative tool, provides a real-time snapshot of air quality across the state. It utilizes a color-coded system, with different hues representing varying levels of air pollution. This visual representation empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and activities, particularly for those with respiratory sensitivities or pre-existing conditions.
The Pillars of Air Quality: Key Pollutants and Their Impacts
Air pollution is a complex issue, driven by a combination of factors, including industrial emissions, vehicular traffic, and even natural occurrences. The air quality map of Massachusetts focuses on key pollutants that pose the most significant health risks:
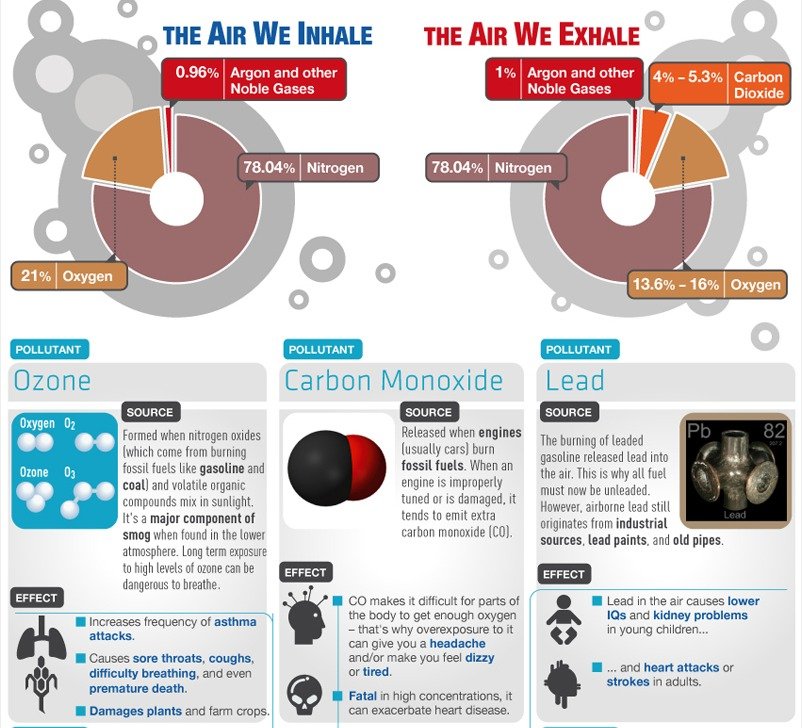
- Ozone (O3): This colorless gas forms in the atmosphere when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in the presence of sunlight. Ozone can cause respiratory irritation, chest pain, and reduced lung function, particularly in children, older adults, and individuals with asthma.
- Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5): These microscopic particles, smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, leading to cardiovascular disease, respiratory problems, and even premature death.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, carbon monoxide reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, potentially causing headaches, dizziness, and even death.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Primarily released from burning fossil fuels, sulfur dioxide can irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. It also contributes to acid rain, damaging ecosystems and infrastructure.
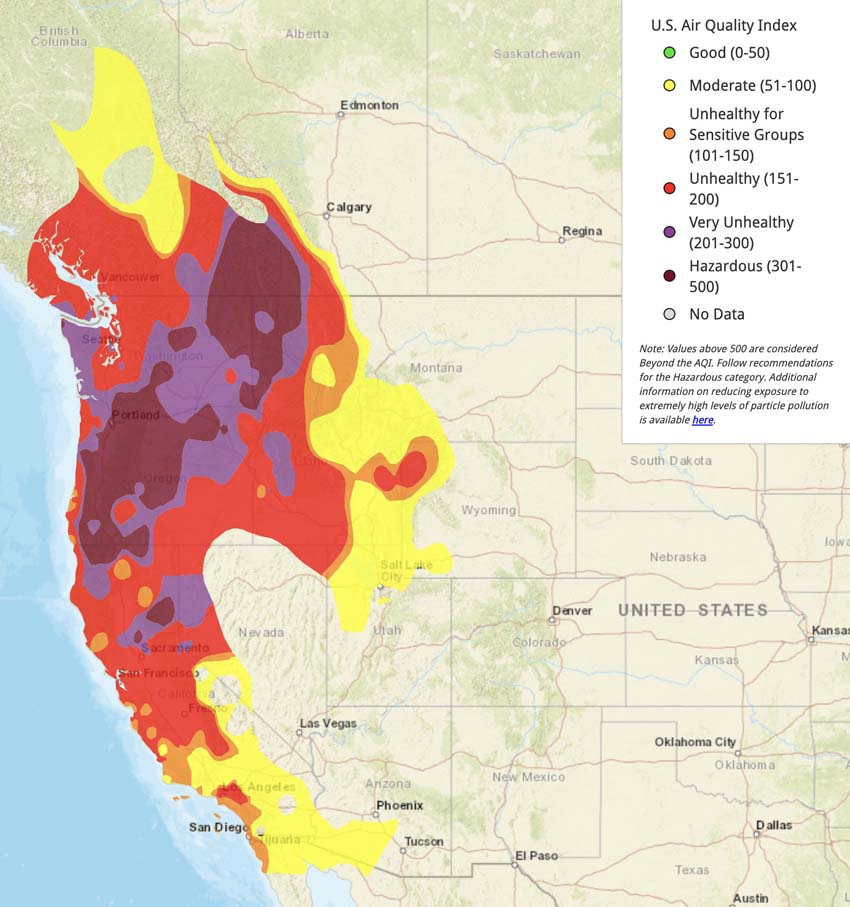
Understanding the Color-Coded System: A Guide to Air Quality Levels
The air quality map of Massachusetts uses a color-coded system to visually represent the concentration of pollutants in the air:
- Green: Air quality is good, posing minimal health risks.
- Yellow: Air quality is moderate, meaning some individuals may experience minor health effects.
- Orange: Air quality is unhealthy for sensitive groups, such as children, older adults, and individuals with respiratory conditions.
- Red: Air quality is unhealthy for everyone, and individuals should limit outdoor activities.
- Purple: Air quality is very unhealthy, and everyone should avoid prolonged exposure to outdoor air.
- Maroon: Air quality is hazardous, requiring immediate action to protect health.
Beyond the Map: Factors Influencing Air Quality in Massachusetts
While the air quality map provides a valuable overview, several factors can influence local air quality, including:
- Geography and Topography: The presence of valleys, mountains, and bodies of water can trap pollutants, leading to localized areas of poor air quality.
- Meteorological Conditions: Wind patterns, temperature inversions, and precipitation can impact pollutant dispersal and accumulation.
- Industrial Activities: Factories, power plants, and other industrial facilities contribute significantly to air pollution, particularly in urban areas.
- Traffic Congestion: Vehicular emissions are a major source of air pollution, especially in densely populated areas.
- Seasonal Variations: Air quality can fluctuate significantly throughout the year, with higher levels of pollutants often observed during the summer months due to increased ozone formation.
The Importance of Monitoring and Reporting: A Collaborative Effort
The air quality map of Massachusetts is the result of a collaborative effort between various agencies, including:
- The Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP): Responsible for regulating air quality and monitoring pollutant levels.
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Provides national standards for air quality and collaborates with state agencies to ensure compliance.
- Local Air Quality Monitoring Networks: These networks collect and analyze air quality data, providing real-time information for the air quality map.
Benefits of the Air Quality Map: Empowering Individuals and Communities
The air quality map of Massachusetts offers numerous benefits for individuals, communities, and the environment:
- Informed Decision-Making: The map empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and activities, particularly during periods of poor air quality.
- Health Protection: By understanding air quality trends, individuals can take steps to minimize their exposure to pollutants, reducing the risk of respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Environmental Awareness: The map raises awareness about the importance of air quality and encourages individuals to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Public Health Planning: The map provides valuable data for public health officials to develop strategies for protecting vulnerable populations and mitigating the health impacts of air pollution.
- Policy Development: The data collected for the air quality map informs policy decisions related to air quality regulations, emission control measures, and public health interventions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the Air Quality Map of Massachusetts
1. Where can I find the air quality map of Massachusetts?
The air quality map of Massachusetts is readily available online through the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) website.
2. What are the health risks associated with different air quality levels?
The health risks associated with different air quality levels are clearly outlined on the air quality map, providing specific information about the potential effects on sensitive groups and the general population.
3. How often is the air quality map updated?
The air quality map of Massachusetts is updated regularly, often in real-time, to reflect the latest air quality data.
4. What can I do to improve air quality in my community?
Individuals can contribute to improving air quality by adopting environmentally friendly practices, such as reducing car usage, using public transportation, and supporting policies that promote clean energy.
5. How can I stay informed about air quality alerts and advisories?
The MassDEP website, as well as local news outlets, provide regular updates on air quality alerts and advisories, enabling individuals to stay informed and take appropriate precautions.
Tips for Using the Air Quality Map Effectively
- Check the map regularly: Make it a habit to check the air quality map before engaging in outdoor activities, particularly during periods of high pollution.
- Pay attention to color-coded alerts: Be aware of the different color codes and their corresponding health risks.
- Limit outdoor activities during periods of poor air quality: Avoid strenuous outdoor activities when air quality is unhealthy, especially if you have respiratory sensitivities.
- Consider indoor activities: Choose indoor activities, such as going to the movies or visiting a museum, during periods of poor air quality.
- Use air purifiers: Consider using air purifiers indoors to improve air quality, especially if you live in an area with high pollution levels.
Conclusion: A Shared Responsibility for Clean Air
The air quality map of Massachusetts serves as a vital tool for understanding and addressing the critical issue of air pollution. By providing a visual representation of air quality data, it empowers individuals, communities, and policymakers to make informed decisions that protect public health and the environment. It is a reminder that clean air is a shared responsibility, and everyone has a role to play in ensuring that the air we breathe is safe and healthy for generations to come.
![Air Quality in the contiguous United States [3500×2198] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/i3CuXwkonbxMyAjDJsBEqSJ_qMdv3_Dzwv1WtAlQF_w.gif?format=png8u0026s=d17f253bf79a8adb5fc36cb25cb8b5eede7bf531)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Air We Breathe: Understanding the Air Quality Map of Massachusetts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!