Navigating Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to House District Maps
Related Articles: Navigating Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to House District Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to House District Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to House District Maps
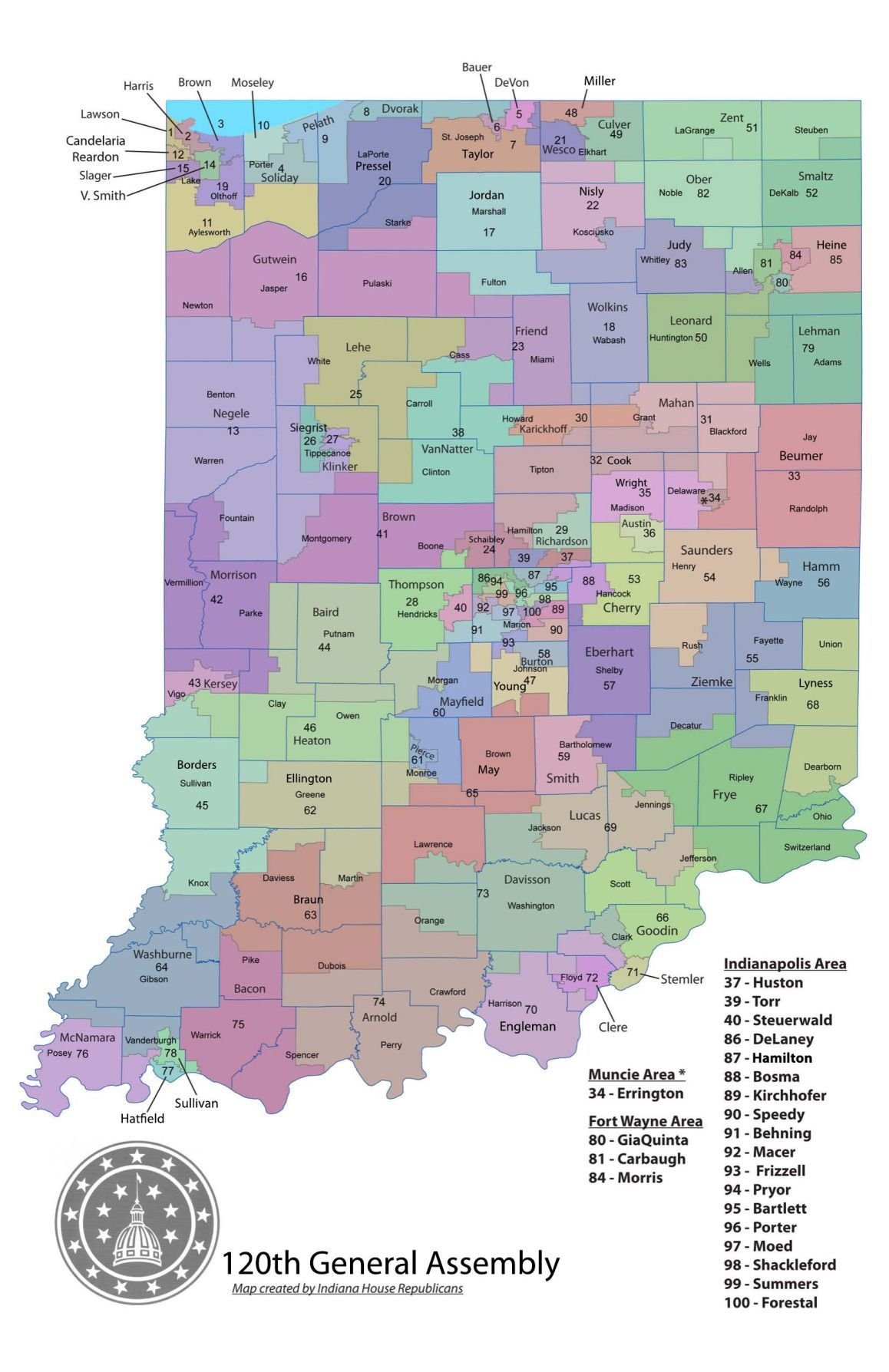
Understanding the intricate web of political representation in Indiana requires a clear grasp of its legislative districts. This guide delves into the significance of Indiana House district maps, providing a comprehensive overview of their structure, purpose, and impact on the state’s political landscape.
The Foundation of Representation: A Look at Indiana House Districts
Indiana’s House of Representatives, with 100 members, serves as the lower chamber of the state legislature. The state is divided into 100 districts, each represented by a single member. These districts are defined by House district maps, which are created through a process of redistricting following each decennial census.
Redistricting: The Process of Shaping Districts
Redistricting is the process of redrawing electoral boundaries to ensure that districts are roughly equal in population. This process is crucial for maintaining fair representation and ensuring that each voter’s voice carries equal weight. In Indiana, the redistricting process is overseen by the Indiana Legislative Redistricting Commission, a bipartisan body comprised of members of both the House and Senate.
Key Considerations in District Map Creation
The redistricting process is guided by several key principles:
- Population Equality: Districts must be as close as possible in population size, adhering to the principle of "one person, one vote."
- Contiguity: Each district must be a contiguous geographic area, meaning that all parts of the district are connected.
- Preservation of Communities of Interest: The redistricting process aims to avoid dividing communities of interest, such as cities, towns, or neighborhoods, across district lines.
- Compactness: Districts should be geographically compact, minimizing the distance between voters and their representatives.
- Minority Representation: The redistricting process aims to ensure that minority groups have fair representation in the legislature.
The Impact of House District Maps: Shaping the Political Landscape
House district maps have a profound impact on the political landscape of Indiana, influencing:
- Electoral Outcomes: The way districts are drawn can significantly influence the outcome of elections. A map that favors one party over another can create a partisan advantage, potentially leading to a skewed representation in the legislature.
- Representation of Specific Interests: District maps can be drawn to favor certain interests, such as specific industries, geographic regions, or demographic groups. This can lead to a legislature that is more responsive to certain groups than others.
- Public Policy: The makeup of the legislature, which is shaped by the district maps, influences the types of public policies that are considered and enacted.
Navigating the Indiana House District Map: A Guide for Citizens
Understanding the significance of House district maps is essential for active citizenship. Citizens can use this information to:
- Identify their House district: Determining the district they reside in allows citizens to engage with their elected representatives, participate in local elections, and stay informed about issues affecting their community.
- Track redistricting efforts: Staying informed about the redistricting process allows citizens to advocate for fair and equitable representation and ensure that the process is transparent and accountable.
- Advocate for their interests: By understanding the impact of district maps on political outcomes and public policy, citizens can advocate for their interests and ensure that their voices are heard in the legislative process.
Frequently Asked Questions about Indiana House District Maps
Q: How often are House district maps redrawn?
A: House district maps are redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for drawing the House district maps in Indiana?
A: The Indiana Legislative Redistricting Commission, a bipartisan body comprised of members of both the House and Senate, is responsible for drawing the House district maps.
Q: What are the criteria used to draw House district maps in Indiana?
A: The Indiana Legislative Redistricting Commission must follow several criteria when drawing House district maps, including population equality, contiguity, preservation of communities of interest, compactness, and minority representation.
Q: How can I find out which House district I live in?
A: You can find out which House district you live in by using the Indiana Legislative Redistricting Commission’s online district locator tool or by contacting your local election officials.
Q: What are the potential consequences of gerrymandering?
A: Gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries for partisan advantage, can have several negative consequences, including:
- Reduced voter choice: Gerrymandered districts can create safe seats for one party, limiting voter choice and making it difficult for challengers to win elections.
- Increased polarization: Gerrymandering can exacerbate political polarization by creating districts where one party dominates, leading to a lack of compromise and cooperation.
- Undermining public trust: Gerrymandering can erode public trust in the electoral process, as voters may perceive the system as rigged in favor of one party.
Tips for Engaging with House District Maps
- Stay informed: Follow the news and attend public hearings to stay informed about the redistricting process.
- Advocate for fair representation: Contact your elected officials and advocate for fair and equitable representation in the legislature.
- Participate in the redistricting process: Attend public meetings and submit feedback to the Indiana Legislative Redistricting Commission.
- Support organizations working to ensure fair redistricting: There are numerous organizations working to promote fair redistricting practices. Consider supporting these organizations through donations or volunteer work.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding House District Maps
Indiana House district maps are not just lines on a map; they are the foundation of the state’s political landscape, shaping representation, influencing electoral outcomes, and impacting public policy. By understanding the significance of these maps and engaging in the redistricting process, citizens can ensure that their voices are heard and that they have fair and equitable representation in the state legislature. The future of Indiana’s political landscape depends on a citizenry that is informed, engaged, and committed to upholding the principles of fair representation.
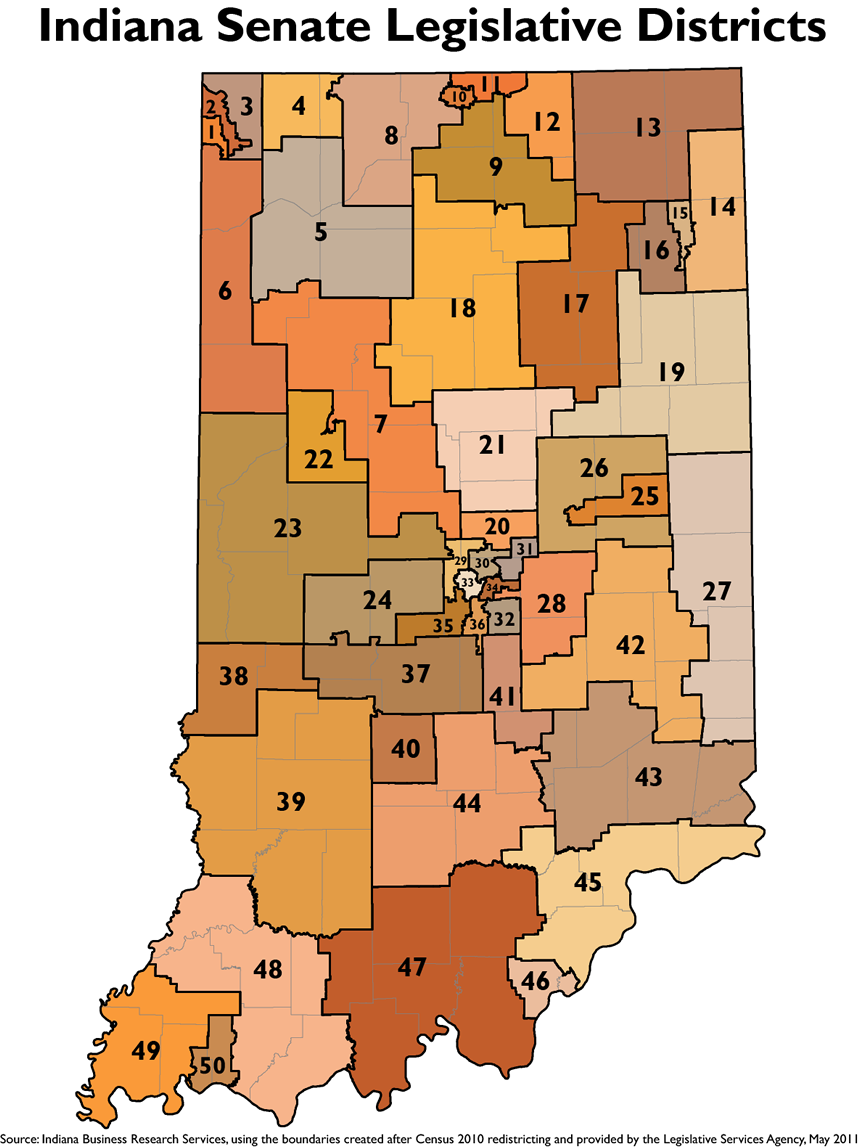
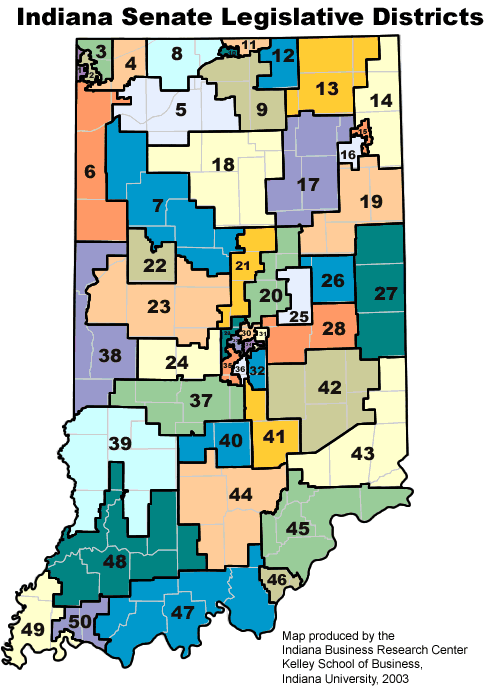
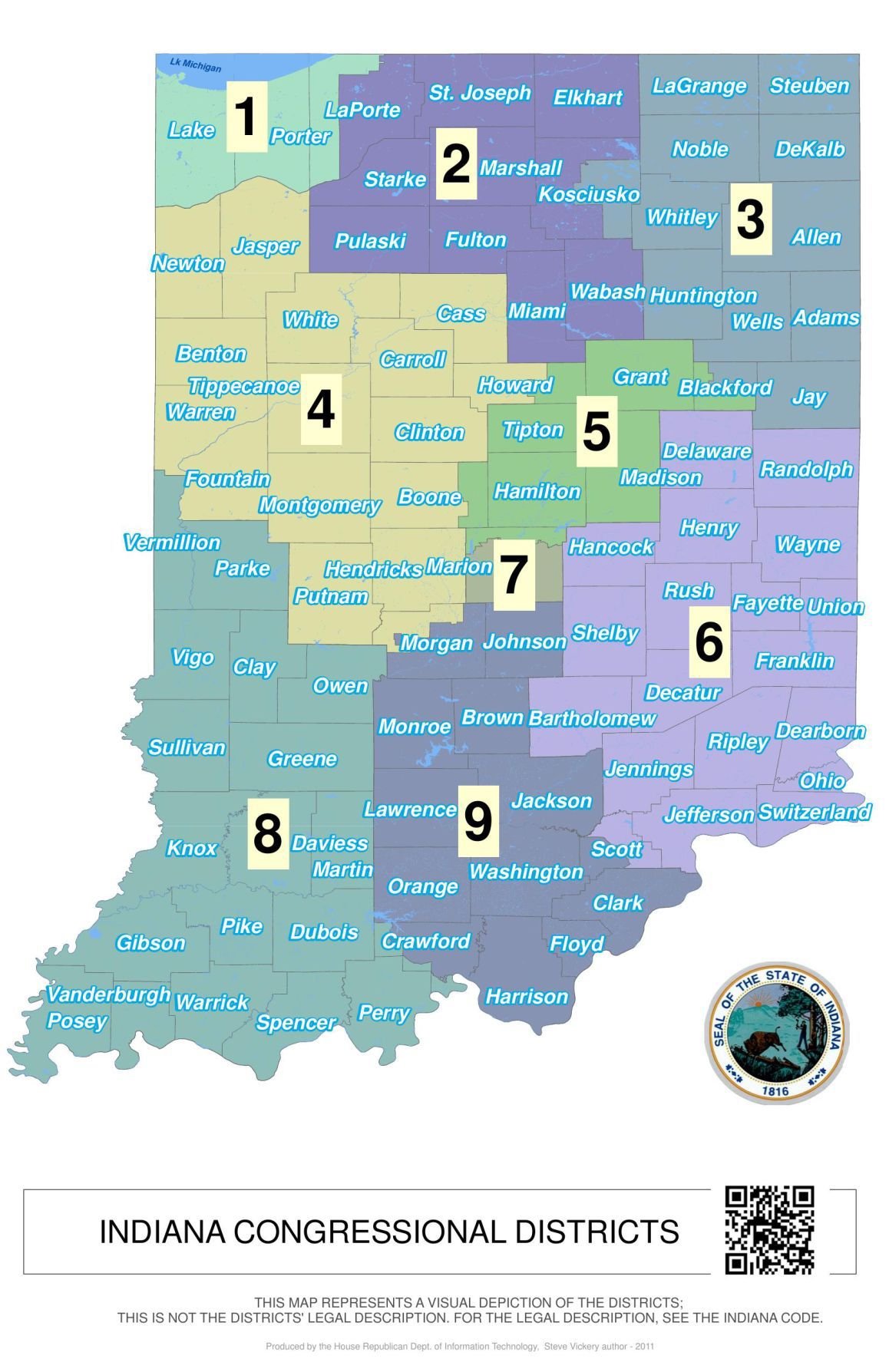
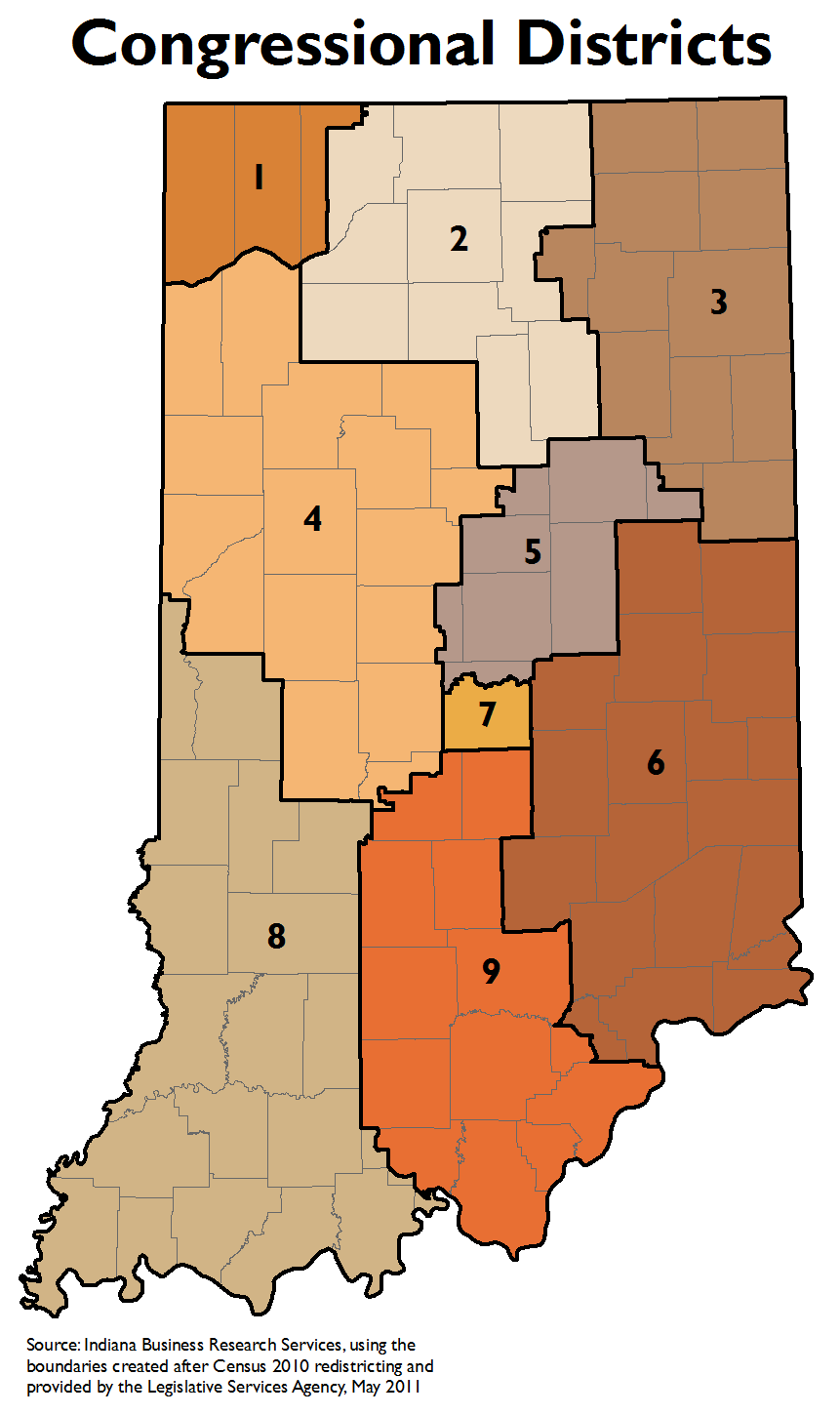
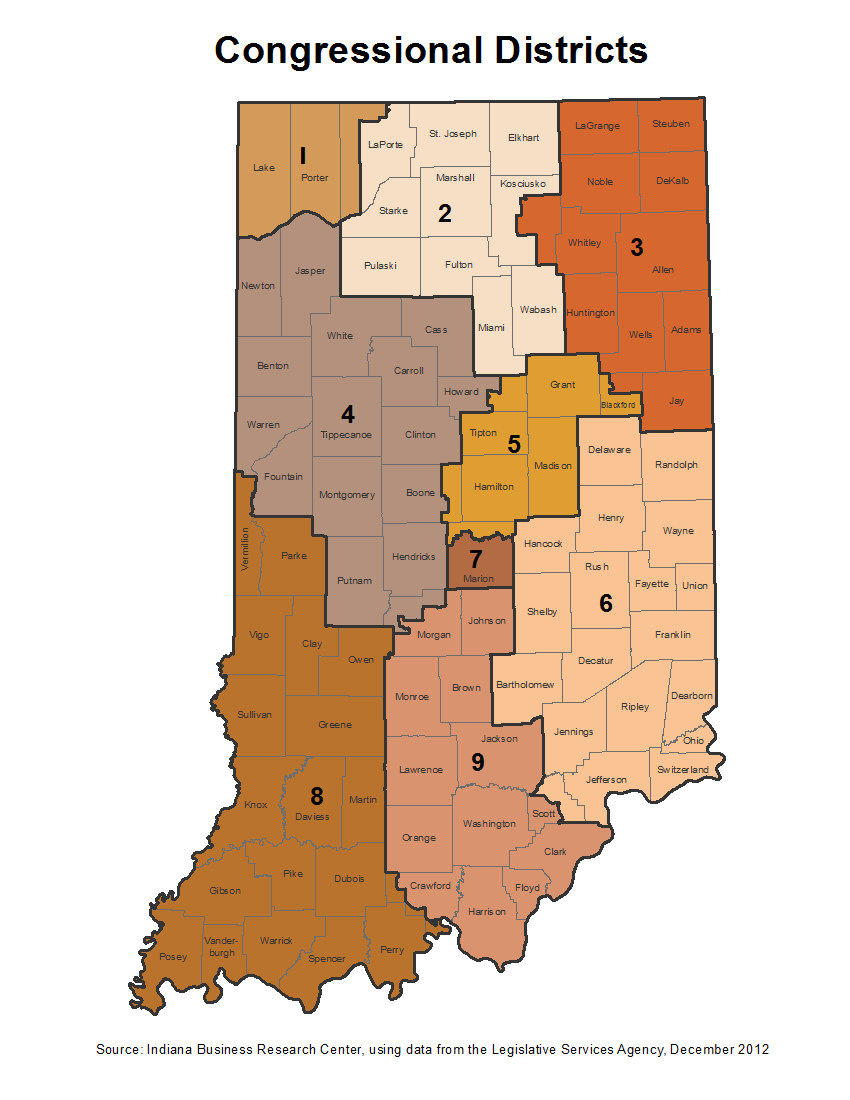

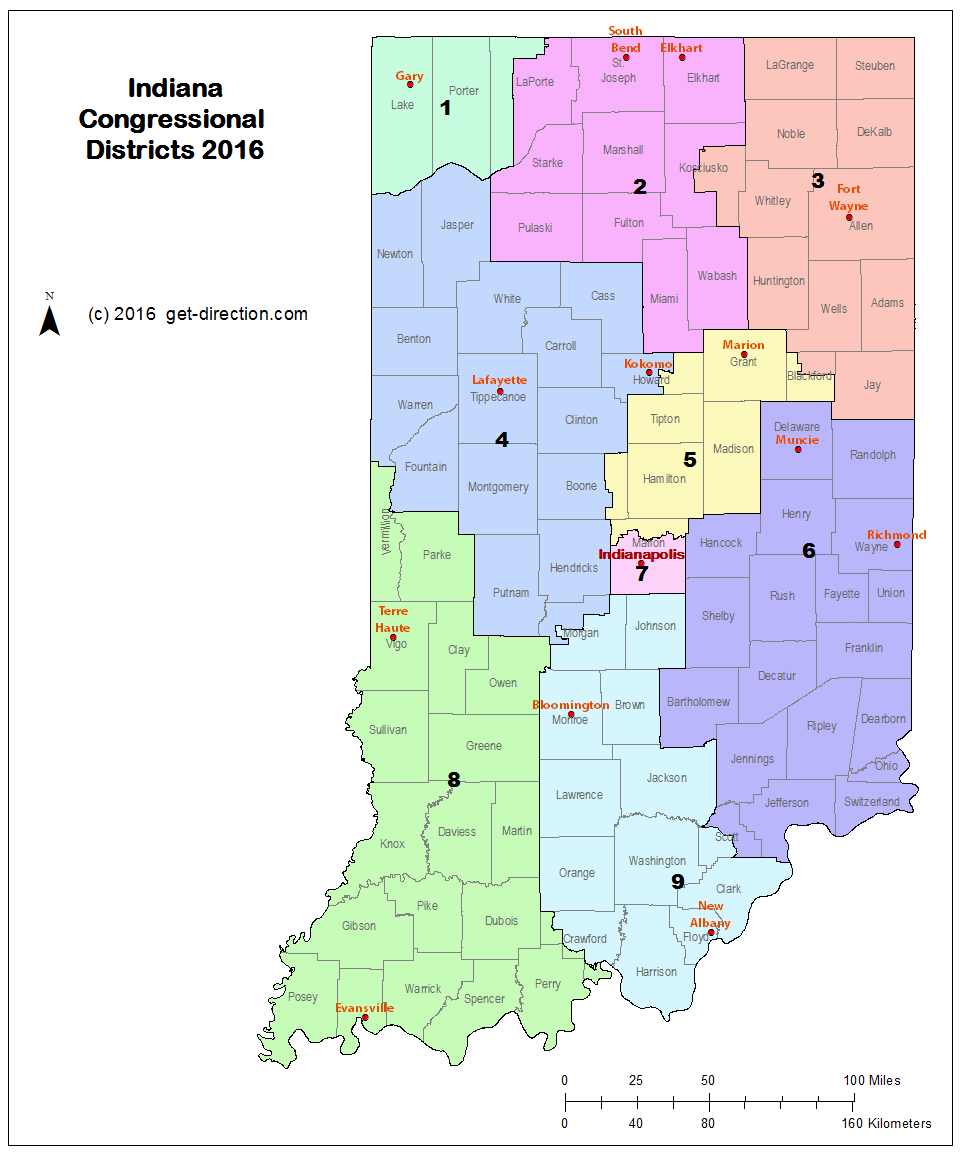

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Indiana’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to House District Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!