Navigating Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide to the HHS Regions
Related Articles: Navigating Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide to the HHS Regions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide to the HHS Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide to the HHS Regions

The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a vast organization with a wide-ranging portfolio of programs and initiatives that touch every aspect of healthcare in the nation. To effectively manage these responsibilities and ensure efficient service delivery, HHS is geographically divided into ten distinct regions. Understanding the HHS regional structure is crucial for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public alike.
The HHS Regional Structure: A Foundation for Healthcare Coordination
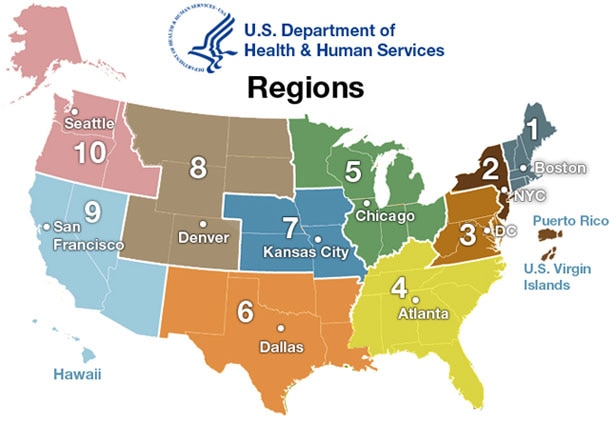
The HHS regional map is a vital tool for understanding the organization’s operational framework. Each region, numbered from I to X, is responsible for administering and overseeing various HHS programs within its designated geographic area. This regional structure provides a decentralized approach to healthcare management, allowing for tailored solutions to address specific needs and challenges within each region.
Understanding the Regions: A Geographical Breakdown
The ten HHS regions are:
Region I (Boston): Encompasses the states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
Region II (New York): Includes the states of New Jersey, New York, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands.
Region III (Philadelphia): Covers Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and Virginia.
Region IV (Atlanta): Includes the states of Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee.
Region V (Chicago): Encompasses Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin.
Region VI (Dallas): Includes Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Region VII (Kansas City): Covers Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska.
Region VIII (Denver): Includes Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Utah, and Wyoming.
Region IX (San Francisco): Encompasses Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, and the Pacific Territories.
Region X (Seattle): Covers Alaska, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington.
The Importance of Regionalization: Tailored Solutions for Diverse Needs
The HHS regional structure is not merely a geographical division but a strategic framework designed to address the unique healthcare needs of each region. This approach recognizes the diverse demographic, socioeconomic, and epidemiological characteristics that influence healthcare delivery across the nation.
- Regional Health Disparities: By dividing the country into ten regions, HHS can better identify and address health disparities that exist within each region. This includes factors such as access to healthcare, health insurance coverage, and the prevalence of chronic diseases.
- Local Expertise: Each region has a dedicated team of professionals with expertise in local health issues and challenges. This allows for tailored solutions and program implementation that effectively meet the needs of the region’s population.
- Community Partnerships: The regional structure fosters strong partnerships with local communities, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders. This collaborative approach ensures that HHS programs are relevant and responsive to the needs of the communities they serve.
Navigating the HHS Regional Structure: Resources and Information
For those seeking information about HHS programs and services, understanding the regional structure is essential. The HHS website provides comprehensive resources and information about each region, including:
- Regional Offices: Contact information and details about the various HHS programs and services offered in each region.
- Regional News and Events: Updates on local health initiatives, program announcements, and events organized by the regional offices.
- Regional Data and Statistics: Access to health data and statistics specific to each region, providing valuable insights into local health trends and needs.
FAQs about the HHS Regions
1. How do I find the HHS region I live in?
You can easily determine your HHS region by using the interactive map available on the HHS website. Simply enter your zip code or address, and the map will highlight the corresponding region.
2. What programs and services are offered by the HHS regions?
Each HHS region provides a wide range of programs and services, including:
- Medicare and Medicaid: Administration and oversight of these programs, ensuring access to healthcare for eligible individuals.
- Public Health: Support for local health departments, disease surveillance, and public health education initiatives.
- Mental Health and Substance Abuse: Programs to address mental health needs and substance abuse disorders within each region.
- Disaster Preparedness and Response: Coordination of disaster relief efforts and emergency preparedness initiatives.
- Health Information and Education: Dissemination of health information and resources to the public.
3. How can I contact the HHS regional office in my area?
You can find contact information for your regional office on the HHS website. This includes phone numbers, email addresses, and mailing addresses.
4. What are the benefits of the HHS regional structure?
The regional structure offers several benefits, including:
- Improved coordination and collaboration: Regional offices work together to ensure seamless service delivery and program implementation.
- Tailored solutions to local needs: The regional structure allows for flexible and responsive program design to address specific regional challenges.
- Enhanced accountability and transparency: Regional offices are accountable for their performance and are transparent in their operations.
Tips for Engaging with the HHS Regional Structure
- Utilize the HHS website: The HHS website provides a wealth of information about regional programs, services, and contact information.
- Connect with your regional office: Reach out to the HHS regional office in your area to learn about local health initiatives and resources.
- Participate in community health events: Engage in community health events and forums to learn about local health priorities and how to get involved.
- Share your feedback: Provide feedback to the HHS regional office about your experiences with their programs and services.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Health Equity and Access
The HHS regional structure is a vital component of the organization’s mission to improve the health and well-being of all Americans. By dividing the country into ten distinct regions, HHS can effectively address the unique healthcare needs of each area, fostering health equity and ensuring access to essential services. Understanding the HHS regional structure empowers individuals, healthcare providers, and policymakers to navigate the complex landscape of healthcare and advocate for the health of their communities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Healthcare: A Comprehensive Guide to the HHS Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!