Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Military Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Military Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Military Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Military Maps
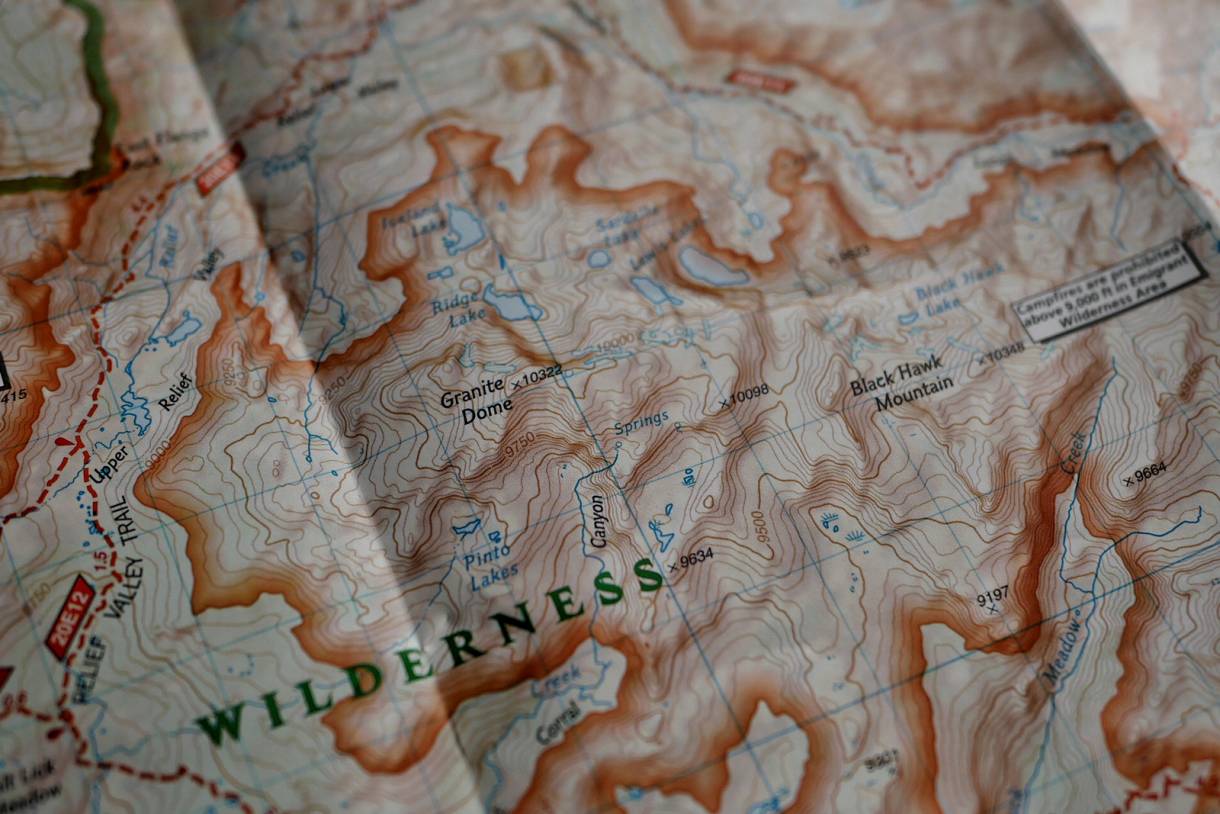
Topographic maps, particularly those tailored for military use, are essential tools for planning, navigating, and executing operations in diverse environments. These maps provide a detailed and accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, offering a wealth of information crucial for military decision-making. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of topographic military maps, exploring their construction, features, and applications in a clear and informative manner.
Understanding the Foundation: The Essence of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are distinguished by their ability to depict the Earth’s surface with remarkable accuracy, capturing both the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the terrain. They utilize a standardized system of symbols, colors, and contours to represent features such as:
- Elevation: Contours lines, which connect points of equal elevation, provide a visual representation of the terrain’s slopes and valleys.
- Relief: Shading techniques and contour lines depict the three-dimensional nature of the landscape, highlighting hills, ridges, and depressions.
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, and other water bodies are precisely mapped, including their flow direction and depth.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation are represented with specific symbols, indicating areas of forest, grassland, or cultivated land.
- Infrastructure: Roads, railways, bridges, and other man-made structures are meticulously depicted, providing crucial information for navigation and logistics.
- Cultural Features: Towns, villages, and other settlements are marked, along with important landmarks and points of interest.
Tailoring Maps for Military Operations: The Unique Characteristics of Military Topographic Maps
Military topographic maps are designed to meet the specific needs of armed forces, incorporating features and details crucial for planning and executing military operations. Some key characteristics distinguish them from standard topographic maps:
- Detailed Representation: Military maps prioritize accuracy and detail, often incorporating larger scales than civilian maps to facilitate precise planning and navigation.
- Emphasis on Tactical Features: They highlight features of tactical significance, such as potential defensive positions, firing points, and concealed routes.
- Military Grid System: A military grid system, typically based on the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) grid, provides a universal reference system for precise location determination and target designation.
- Overlays and Annotations: Military maps often incorporate overlays and annotations, such as troop movements, enemy positions, or planned attack routes, to facilitate operational planning and coordination.
- Security Considerations: Military maps are subject to strict security protocols, with access limited to authorized personnel to prevent sensitive information from falling into enemy hands.
Deciphering the Symbols: A Key to Understanding the Terrain
The ability to interpret the symbols and conventions used on topographic maps is essential for effectively utilizing their information. Military maps utilize a standardized system of symbols, each representing a specific feature or object. Some key symbols include:
- Contour Lines: Contour lines are the most prominent feature of topographic maps, representing points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
- Relief Shading: Relief shading uses light and dark tones to depict the three-dimensional nature of the terrain, highlighting hills, valleys, and other features.
- Vegetation Symbols: Different types of vegetation are represented with specific symbols, such as trees, shrubs, and cultivated land.
- Cultural Features: Towns, villages, and other settlements are marked with specific symbols, along with important landmarks and points of interest.
- Military Symbols: Military maps utilize a comprehensive system of symbols to represent military units, equipment, fortifications, and other military-specific features.
Navigating the Terrain: Utilizing Topographic Maps for Operational Planning
Topographic maps are indispensable tools for military planning and operations, providing crucial information for:
- Mission Planning: Maps facilitate the planning of operations by allowing commanders to visualize the terrain, assess potential routes, and identify advantageous positions.
- Route Selection: Maps assist in selecting optimal routes, considering factors such as terrain, obstacles, and enemy positions.
- Target Identification: Maps help identify potential targets, assess their vulnerability, and determine the best approach for attack or defense.
- Logistics and Supply: Maps aid in planning logistics and supply routes, ensuring the timely delivery of resources and equipment.
- Command and Control: Maps serve as a common reference for coordinating operations and maintaining situational awareness among different units.
Beyond the Battlefield: The Broader Applications of Topographic Maps
While primarily associated with military applications, topographic maps find diverse uses in various fields, including:
- Civil Engineering: Topographic maps are essential for planning infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and dams, providing detailed information about the terrain and existing structures.
- Environmental Management: Maps assist in assessing environmental conditions, identifying areas susceptible to natural hazards, and planning conservation efforts.
- Urban Planning: Topographic maps are valuable for urban planning, providing information about the terrain, existing infrastructure, and potential development sites.
- Recreation and Tourism: Maps are widely used by hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts, providing guidance for navigation, identifying points of interest, and understanding the terrain.
FAQs about Topographic Military Maps
1. What is the difference between a topographic map and a military topographic map?
While both types of maps depict the Earth’s surface, military topographic maps prioritize detail, accuracy, and tactical information relevant for military operations. They often use larger scales, incorporate specific military symbols, and are subject to strict security protocols.
2. How are topographic maps created?
Topographic maps are created using various surveying techniques, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys. Data is collected, processed, and then transformed into a two-dimensional representation of the terrain.
3. What is the importance of scale in topographic maps?
The scale of a map determines the level of detail and the area covered. Larger scales provide more detailed information but cover a smaller area, while smaller scales cover a larger area but provide less detail. Military maps often utilize larger scales to facilitate precise planning and navigation.
4. How can I learn to read and interpret topographic maps?
Several resources are available to learn about topographic maps, including online tutorials, books, and workshops. The key is to understand the symbols and conventions used, practice interpreting the information, and apply your knowledge to real-world situations.
5. Are topographic maps still relevant in the age of GPS and satellite imagery?
While GPS and satellite imagery provide valuable information, topographic maps remain essential for planning and operations, particularly in areas with limited or unreliable GPS coverage. They offer a comprehensive overview of the terrain, provide a permanent record of the landscape, and are less susceptible to electronic interference.
Tips for Utilizing Topographic Military Maps
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s scale and legend: Understanding the map’s scale and the meaning of its symbols is crucial for interpreting the information correctly.
- Use a protractor and ruler for accurate measurements: Measuring distances and angles on the map is essential for planning routes and determining target locations.
- Consider the terrain and elevation: The terrain’s features, such as hills, valleys, and obstacles, can significantly impact movement and operations.
- Utilize overlays and annotations: Overlays and annotations provide additional information, such as troop movements, enemy positions, or planned attack routes.
- Maintain map security: Military maps contain sensitive information and should be handled with care and protected from unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Topographic military maps remain indispensable tools for military operations, providing a detailed and accurate representation of the terrain, essential for planning, navigation, and decision-making. Their ability to depict the Earth’s surface with remarkable accuracy, incorporate tactical information, and facilitate communication and coordination makes them invaluable assets for armed forces worldwide. As technology continues to evolve, topographic maps will likely continue to play a vital role in military operations, adapting to new challenges and evolving alongside the demands of modern warfare.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Military Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!