A World Transformed: Navigating the Globe in 1750
Related Articles: A World Transformed: Navigating the Globe in 1750
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World Transformed: Navigating the Globe in 1750. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World Transformed: Navigating the Globe in 1750

The year 1750 marks a pivotal moment in human history. The world was on the cusp of dramatic change, driven by technological advancements, burgeoning empires, and the burgeoning global trade. This era, often referred to as the "Age of Enlightenment," witnessed a surge in scientific exploration and cartographic innovation.
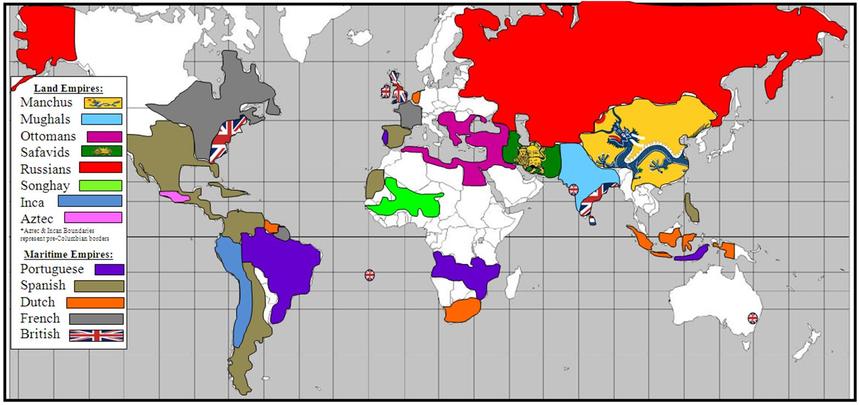
A map of the world from 1750 offers a fascinating glimpse into the state of global knowledge and the prevailing geopolitical landscape. It reveals a world vastly different from the one we know today, with continents and empires defined by distinct boundaries and power dynamics. Examining this historical map provides a unique opportunity to understand the historical context shaping the world we inhabit today.
The Shifting Sands of Empire:
The 1750 map reveals a world dominated by empires. European powers, particularly Great Britain, France, and Spain, held vast colonial possessions across the globe. The British Empire, at its zenith, stretched from North America to India, while France controlled territories in North America, the Caribbean, and Africa. Spain, despite its waning power, still held vast swathes of Latin America.
These empires exerted significant influence on the global political and economic landscape. Trade routes crisscrossed the oceans, connecting distant continents and fueling the growth of European economies. Colonial exploitation, however, brought immense suffering to indigenous populations, leaving an enduring legacy of inequality and conflict.
The Rise of the European Powers:
The 1750 map underscores the growing dominance of European powers in global affairs. Technological advancements, particularly in navigation and shipbuilding, allowed European explorers to venture further and map previously unknown territories. This exploration led to the establishment of colonies, trade networks, and the spread of European culture and influence.
The emergence of European dominance, however, came at a steep cost. The exploitation of resources and subjugation of indigenous populations fueled tensions and conflicts, leading to the eventual decline of some empires and the rise of new powers.
Uncharted Territories and Scientific Advancements:
Despite the expanding European influence, large portions of the world remained uncharted or poorly understood. The map of 1750 reflects this uncertainty, with vast areas of Africa, Asia, and the Americas marked as "terra incognita."
This era witnessed a surge in scientific exploration and cartographic innovation. Explorers like James Cook and Alexander von Humboldt embarked on expeditions to map new territories, document flora and fauna, and gather data on geography, climate, and culture. These expeditions helped refine existing maps, expand knowledge of the world, and contribute to the development of modern geography.
The Importance of the 1750 Map:
The map of the world from 1750 holds significant historical and geographical value. It serves as a tangible representation of the world at a critical juncture in history, capturing the political, economic, and cultural dynamics of the era. This map allows us to:
- Understand the global power dynamics of the time: By observing the empires and their territorial holdings, we can gain insights into the geopolitical landscape and the forces shaping global events.
- Trace the evolution of exploration and cartography: The map highlights the areas of the world that were known and unknown, showcasing the progress of exploration and the development of cartographic techniques.
- Examine the impact of colonialism: The map clearly depicts the extent of colonial possessions and the influence of European powers, revealing the impact of colonialism on global trade, resource extraction, and cultural exchange.
- Appreciate the interconnectedness of the world: The map demonstrates how trade routes and the exchange of goods and ideas connected different parts of the world, illustrating the interconnectedness of global systems.
FAQs about the Map of the World in 1750:
1. What were the major empires in 1750?
The major empires in 1750 included the British Empire, French Empire, Spanish Empire, Russian Empire, Ottoman Empire, Mughal Empire, Qing Dynasty, and the Japanese Shogunate. These empires controlled vast territories and exerted significant influence on the global political and economic landscape.
2. What were the major trade routes in 1750?
The major trade routes in 1750 connected Europe to Asia, Africa, and the Americas. These routes carried goods such as spices, textiles, tea, coffee, sugar, and precious metals. The most important trade routes included the Silk Road, the Spice Route, the Atlantic Slave Trade, and the Transatlantic Trade.
3. What were the major technological advancements in cartography in 1750?
Major technological advancements in cartography in 1750 included the development of more accurate instruments for navigation, such as the sextant and the chronometer. The use of projection techniques also allowed for more accurate representations of the Earth’s surface.
4. What were the limitations of the maps in 1750?
Maps in 1750 were limited by the availability of information and the accuracy of instruments. Large parts of the world, particularly in Africa and the interior of the Americas, remained uncharted or poorly understood. The maps also reflected the biases of the cartographers, often depicting European cultures as superior to others.
5. How did the map of the world change between 1750 and 1850?
The map of the world underwent significant changes between 1750 and 1850. The exploration of new territories, particularly in Africa and the Pacific Ocean, led to a more accurate representation of the globe. The decline of some empires and the rise of new powers also resulted in shifts in political boundaries.
Tips for Understanding the Map of the World in 1750:
- Focus on the major empires and their territorial holdings.
- Identify the major trade routes and their significance.
- Pay attention to the areas marked as "terra incognita" and what they reveal about the limitations of knowledge at the time.
- Compare the map of 1750 to maps from other periods to understand the evolution of cartography and global knowledge.
- Consider the historical context of the map and the biases that may have influenced its creation.
Conclusion:
The map of the world in 1750 provides a snapshot of a world on the cusp of transformation. It reveals the dominance of empires, the power of trade, the limitations of knowledge, and the ongoing exploration of the unknown. By examining this historical map, we can gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped the modern world and appreciate the remarkable progress made in our understanding of the globe. The 1750 map serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of history and the importance of understanding the past to navigate the complexities of the present.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World Transformed: Navigating the Globe in 1750. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!