A Tapestry of Tongues: Unveiling the Asian Language Map
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Tongues: Unveiling the Asian Language Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Tongues: Unveiling the Asian Language Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Tongues: Unveiling the Asian Language Map

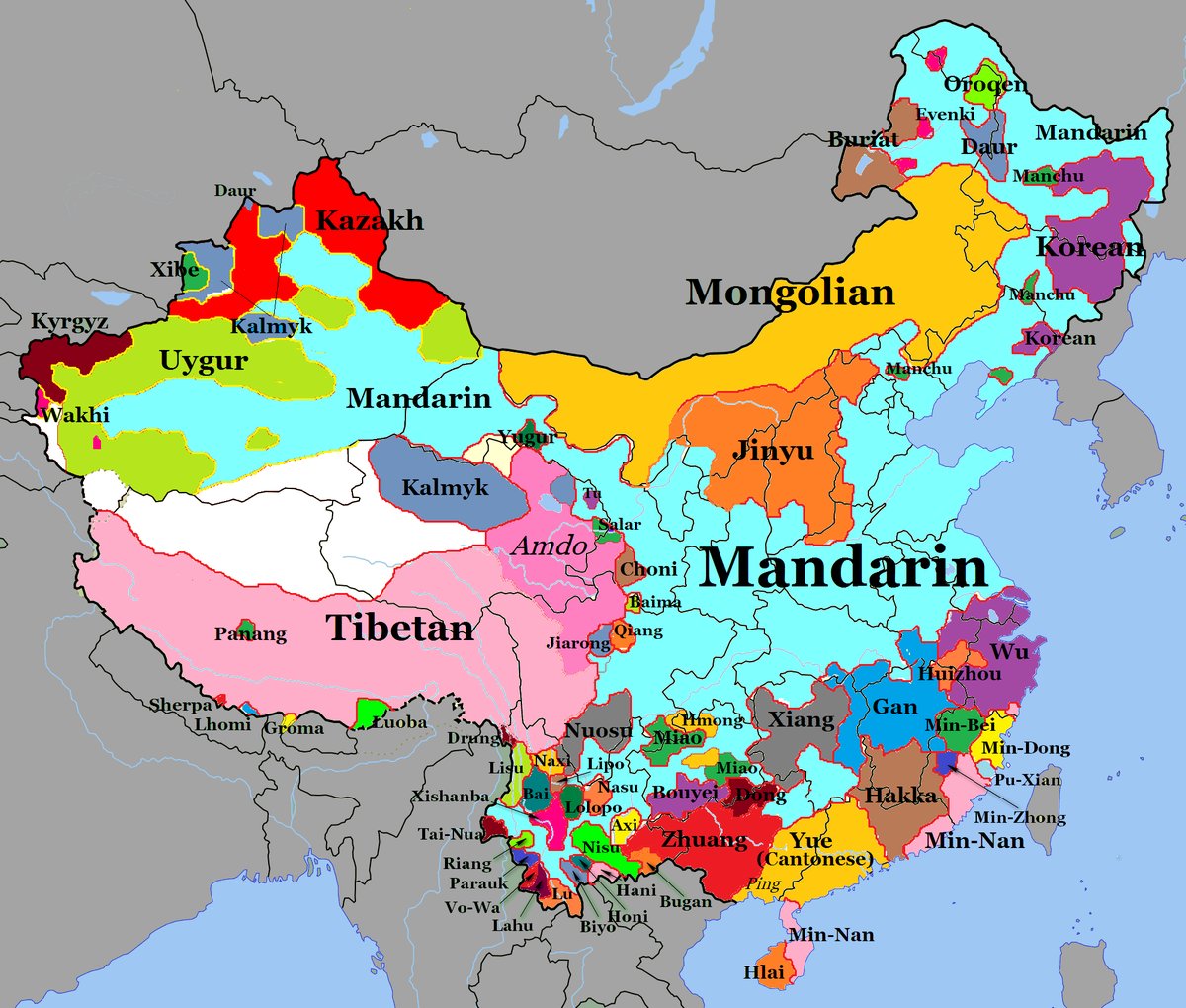
The Asian continent, a vast expanse of diverse cultures and landscapes, is also home to a rich tapestry of languages. This linguistic diversity, reflected in the intricate patterns of the Asian language map, is a testament to the continent’s rich history and the enduring influence of its many civilizations. Understanding this map offers valuable insights into the interconnectedness of Asian cultures, the complexities of language evolution, and the challenges and opportunities presented by linguistic diversity.
Tracing the Threads of Linguistic History
The Asian language map is not static; it is a dynamic representation of a complex and constantly evolving linguistic landscape. The languages spoken across Asia belong to various language families, each reflecting a distinct historical origin and evolution. The major language families represented on the map include:
- Sino-Tibetan: This family, encompassing languages like Chinese, Tibetan, and Burmese, is the largest in the world, with over 1.4 billion speakers. It is characterized by tonal features and a complex writing system.
- Indo-European: This family, with its roots in the Indo-European language spoken in ancient Europe, extends across Asia, encompassing languages like Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, and Persian.
- Austroasiatic: This family, encompassing languages like Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon, is found primarily in Southeast Asia and is characterized by its diverse phonological systems and complex grammatical structures.
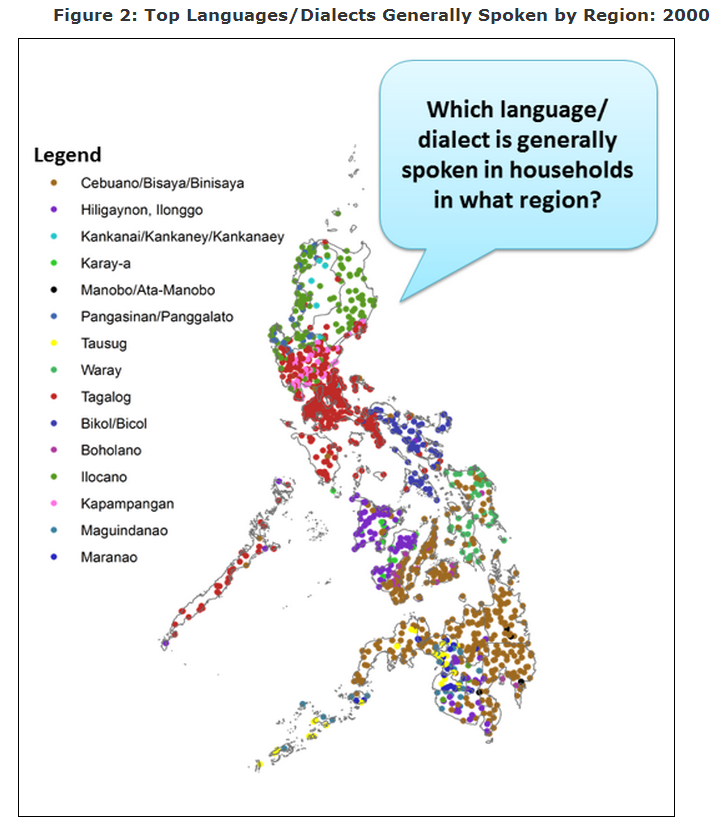
- Austronesian: This family, originating in Taiwan, includes languages like Malay, Indonesian, and Filipino. It is characterized by its extensive use of prefixes and suffixes.
- Turkic: This family, encompassing languages like Turkish, Azerbaijani, and Uzbek, is found in Central Asia and is characterized by its agglutinative morphology, where words are formed by adding suffixes.
- Japonic: This family, encompassing languages like Japanese and Korean, is found in East Asia and is characterized by its agglutinative morphology and complex writing systems.
Navigating the Complexities of Language Distribution
The Asian language map reveals a fascinating pattern of language distribution, reflecting the historical migrations, cultural interactions, and political boundaries that have shaped the continent’s linguistic landscape. For example, the spread of Indo-European languages across South Asia is a testament to the influence of the Indo-Aryan migrations, while the dominance of Mandarin Chinese in East Asia reflects the historical and cultural influence of China.
The map also highlights the presence of language families that are geographically isolated, such as the Dravidian languages of South India, which are believed to have originated independently of the Indo-European languages. This isolation has allowed these languages to develop unique features and maintain their distinct identities.
The Importance of Linguistic Diversity
The Asian language map is not merely a geographical representation; it is a symbol of the rich cultural heritage and the vibrant linguistic diversity of the continent. This diversity is a source of strength, fostering creativity, innovation, and a deeper understanding of the world.
- Cultural Preservation: Languages are the carriers of cultural identity, preserving traditions, values, and knowledge systems. The Asian language map reflects the diverse cultural tapestry of the continent, highlighting the importance of language preservation in safeguarding cultural heritage.
- Cognitive Benefits: Studies have shown that bilingualism and multilingualism can enhance cognitive abilities, improving memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. The diverse linguistic landscape of Asia provides a unique opportunity for developing cognitive skills and fostering intellectual growth.
- Economic Advantages: In a globalized world, multilingualism is a valuable asset. The Asian language map highlights the importance of language learning and communication in fostering economic growth and promoting international cooperation.
- Intercultural Understanding: Language is a bridge that connects people across cultures. Understanding the languages spoken across Asia is essential for building bridges of communication and fostering intercultural understanding.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the richness of its linguistic diversity, Asia faces challenges in preserving and promoting its languages. The spread of global languages like English and the increasing use of technology can threaten the vitality of smaller languages. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration.
- Language Revitalization: Efforts to revitalize endangered languages are crucial for preserving cultural heritage and promoting linguistic diversity. These efforts often involve community-based initiatives, language education programs, and the development of language resources.
- Technological Innovation: Technology can play a crucial role in language preservation and promotion. Online language learning platforms, digital dictionaries, and language translation tools can make it easier for people to learn and use minority languages.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is essential for promoting linguistic diversity and supporting language revitalization efforts. Sharing resources, expertise, and best practices can help to address the challenges faced by endangered languages.
FAQs
Q: What is the most spoken language in Asia?
A: Mandarin Chinese is the most spoken language in Asia, with over 1 billion speakers.
Q: What are the major language families in Asia?
A: The major language families in Asia include Sino-Tibetan, Indo-European, Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Turkic, and Japonic.
Q: Why is it important to understand the Asian language map?
A: Understanding the Asian language map is crucial for appreciating the linguistic diversity of the continent, its cultural heritage, and the challenges and opportunities presented by language preservation and promotion.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by languages in Asia?
A: Languages in Asia face challenges such as the spread of global languages, the influence of technology, and the decline of speakers due to migration and urbanization.
Q: How can we promote linguistic diversity in Asia?
A: We can promote linguistic diversity in Asia by supporting language revitalization efforts, developing language resources, promoting bilingualism and multilingualism, and fostering intercultural understanding.
Tips
- Learn a language from Asia: Immerse yourself in the rich linguistic diversity of the continent by learning a new language.
- Explore Asian literature and media: Engage with Asian culture through literature, films, and music, which offer a window into the richness of Asian languages.
- Support language revitalization efforts: Contribute to organizations and initiatives dedicated to preserving and promoting endangered languages.
- Promote multilingualism: Encourage the use of multiple languages in education, business, and everyday life.
Conclusion
The Asian language map is a testament to the continent’s rich linguistic heritage and the enduring influence of its diverse cultures. Understanding this map is essential for appreciating the complexities of language evolution, the importance of linguistic diversity, and the challenges and opportunities presented by language preservation and promotion. By embracing the richness of Asian languages, we can foster intercultural understanding, promote cognitive development, and safeguard the cultural heritage of the continent for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Tongues: Unveiling the Asian Language Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!