A Journey Through Time: Examining the Shifting Landscape of Russia, 1900-Present
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Examining the Shifting Landscape of Russia, 1900-Present
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Examining the Shifting Landscape of Russia, 1900-Present. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Examining the Shifting Landscape of Russia, 1900-Present
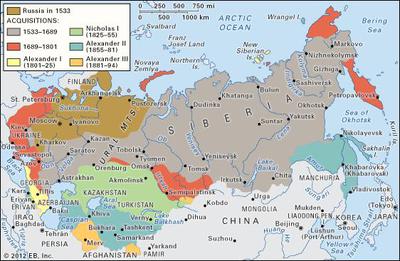
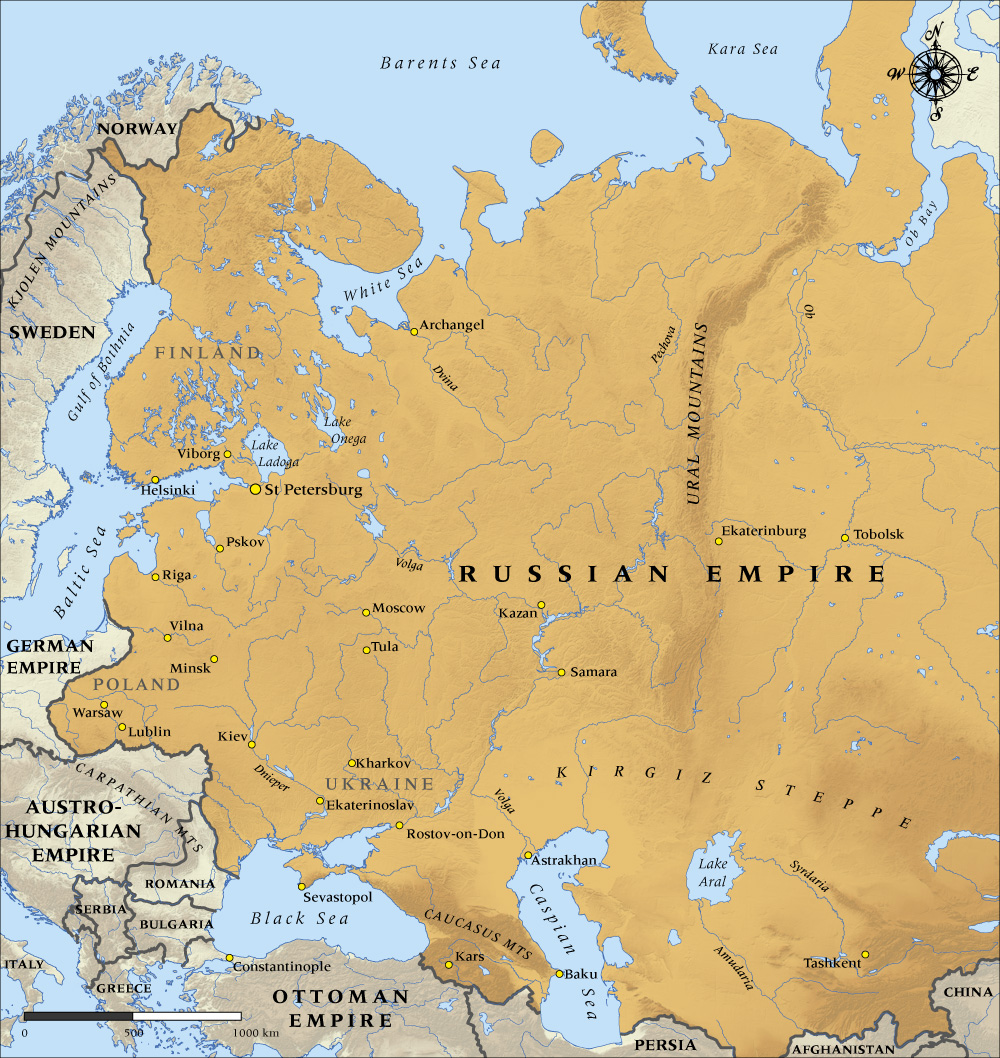
The map of Russia in 1900 paints a picture of a vast empire, stretching across eleven time zones and encompassing a diverse tapestry of peoples, cultures, and landscapes. From the Baltic Sea to the Pacific Ocean, the Russian Empire encompassed a territory larger than the entire continent of Europe. Understanding this historical map is crucial to comprehending the complexities of Russia’s past and its present-day geopolitical landscape.
The Tsar’s Dominion: A Multi-Ethnic Empire
The Russian Empire in 1900 was a mosaic of ethnicities, religions, and languages. While the core of the empire was predominantly Russian, its vast expanse encompassed numerous other groups, including Ukrainians, Belarusians, Poles, Finns, Latvians, Lithuanians, Georgians, Armenians, Azerbaijanis, and many more. This diversity was a source of both strength and tension, contributing to the empire’s cultural richness but also fueling internal conflicts and separatist movements.
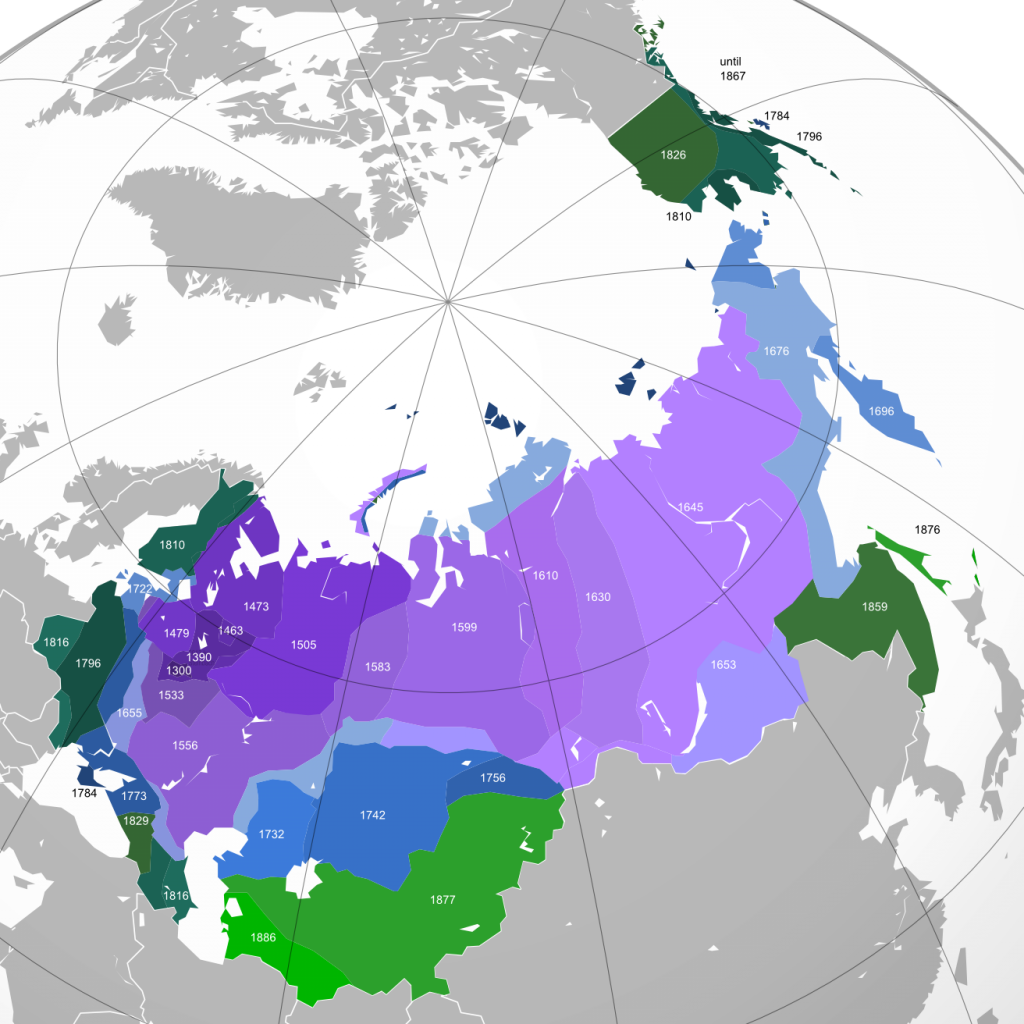
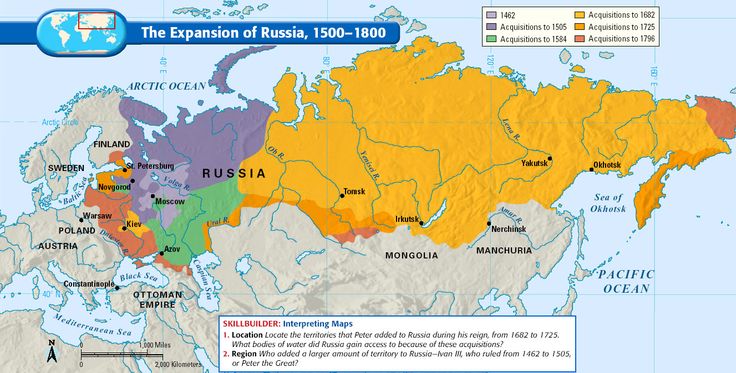
A Legacy of Expansion: The Expansion of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire’s territorial growth was a long and multifaceted process, driven by a combination of military conquest, diplomacy, and economic ambitions. From the 16th century onwards, Russia steadily expanded its borders eastward, pushing across Siberia and the Far East. This expansion was fueled by the desire for resources, access to trade routes, and the pursuit of imperial prestige.
A Map of Change: The Fall of the Empire and the Rise of the Soviet Union
The year 1917 marked a turning point in Russian history. The Bolshevik Revolution, led by Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Tsarist regime and established the Soviet Union, a new socialist state. The map of Russia underwent a radical transformation, with the former empire dissolving into a federation of republics. While the Soviet Union encompassed a territory roughly equivalent to the former Russian Empire, its internal structure and political system differed significantly.
The Soviet Era: A Period of Transformation and Conflict
The Soviet Union’s map was marked by significant changes throughout its existence. The period between 1922 and 1991 witnessed the incorporation of new territories, including the Baltic states, Moldova, and parts of Poland and Finland. This expansion was often accompanied by violence and forced resettlement of populations, reflecting the Soviet regime’s centralized control and its ambition to create a homogenous socialist state.
The Collapse of the Soviet Union and the Re-Emergence of Russia
The disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the creation of 15 independent states, including the Russian Federation. This event marked a dramatic shift in the geopolitical landscape, with Russia emerging as a successor state to the Soviet Union, inheriting its vast territory, nuclear arsenal, and legacy of complex relationships with neighboring countries.
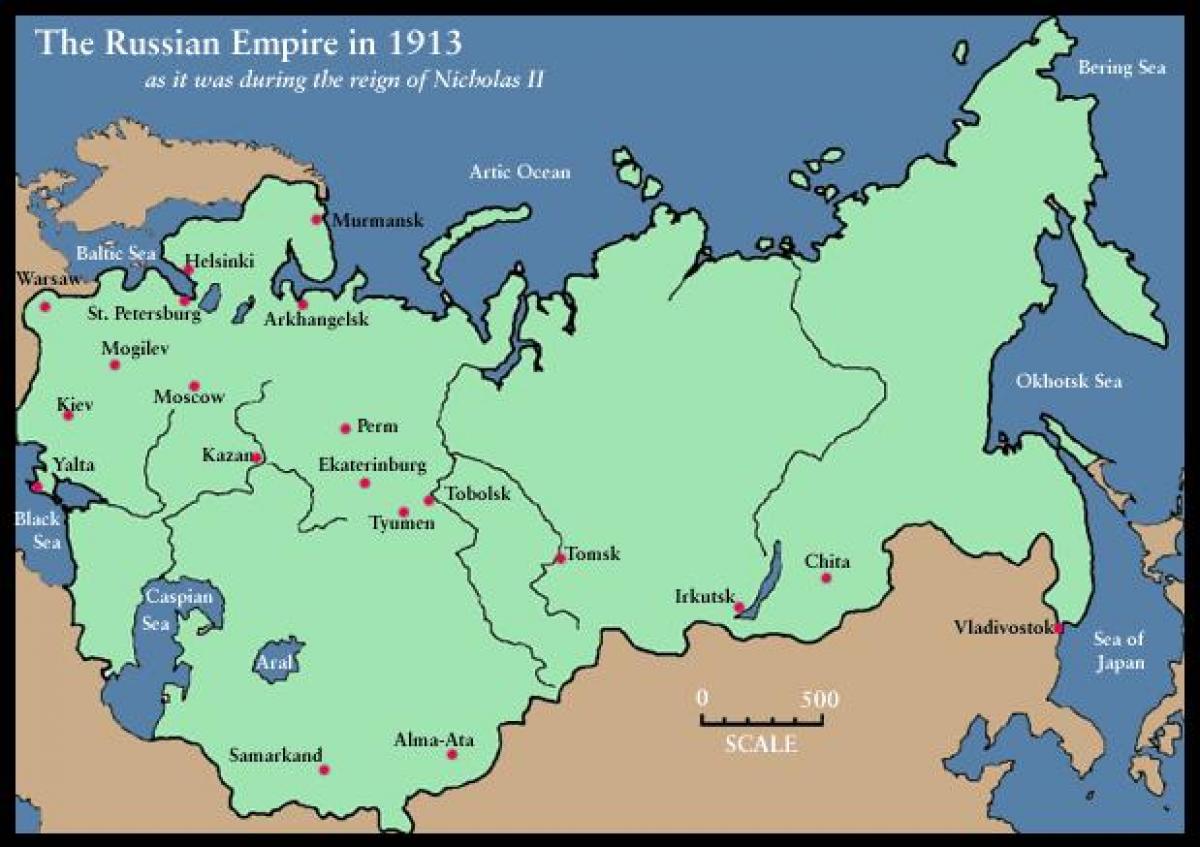
The Modern Map of Russia: Challenges and Opportunities
The current map of Russia reflects the country’s ongoing struggle to define its place in the world. While the Russian Federation is a vast and powerful nation, its internal and external challenges are significant. The country faces economic difficulties, social unrest, and a strained relationship with the West. However, Russia also possesses vast natural resources, a highly educated population, and a long tradition of innovation.
Understanding the Importance of the Map of Russia
The map of Russia, throughout its various iterations, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s history, its present-day challenges, and its potential for the future. By studying the geographical and political changes that have shaped Russia’s borders, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics that have driven its development.
FAQs: Exploring the Map of Russia’s Past
1. What were the major events that led to the expansion of the Russian Empire?
The expansion of the Russian Empire was a multi-faceted process, influenced by several key events:
- The conquest of Siberia: Starting in the 16th century, Russian explorers and Cossacks pushed eastward, conquering vast territories and establishing settlements across Siberia.
- The Crimean War (1853-1856): This conflict with the Ottoman Empire resulted in Russia’s loss of control over the Black Sea region, but also highlighted the need for further modernization and military reform.
- The Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905): Russia’s defeat in this war against Japan exposed weaknesses in its military and industrial capabilities, contributing to internal unrest and the eventual revolution.
2. How did the Soviet Union’s map differ from the Tsarist Empire’s map?
While the Soviet Union inherited much of the territory of the former Russian Empire, there were key differences:
- Internal Structure: The Soviet Union was a federation of republics, each with its own government and legislature, reflecting a more decentralized structure than the Tsarist Empire.
- Political System: The Soviet Union was a socialist state, governed by the Communist Party, with a centralized command economy. This contrasted with the Tsarist autocracy, which was based on a monarchy and a more decentralized economic system.
- Territorial Changes: The Soviet Union incorporated new territories, including the Baltic states, Moldova, and parts of Poland and Finland, through annexations and territorial adjustments.
3. What are some of the key challenges facing Russia in the 21st century?
Russia faces a complex set of challenges in the 21st century:
- Economic Stagnation: Despite its vast natural resources, Russia’s economy has been plagued by corruption, inefficient bureaucracy, and dependence on oil and gas exports.
- Demographic Decline: Russia’s population is declining due to low birth rates and high mortality rates, leading to concerns about future economic growth and military manpower.
- Political Instability: Russia’s political system remains highly centralized, with limited space for dissent and opposition. This has led to concerns about corruption, human rights abuses, and the lack of democratic accountability.
Tips: Navigating the Complexities of the Russian Map
- Focus on Key Events: When studying the map of Russia, focus on major events that shaped its borders and internal structure.
- Explore Historical Maps: Consult historical maps from different periods to understand the evolution of Russia’s territory and its changing political landscape.
- Engage with Different Perspectives: Consider the perspectives of different ethnic groups and regions within Russia to appreciate the diversity and complexity of its history.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Change and Resilience
The map of Russia has undergone significant transformations over the past century, reflecting a complex history of expansion, revolution, and geopolitical shifts. From the Tsarist Empire to the Soviet Union and the modern Russian Federation, the country’s borders have been shaped by a combination of military conquest, political upheavals, and economic ambitions. Understanding the historical map of Russia is essential for comprehending the country’s present-day challenges and its potential for the future.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Examining the Shifting Landscape of Russia, 1900-Present. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!