A Comprehensive Guide to the Natural Resource Map of the United States: Unlocking the Nation’s Wealth
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Natural Resource Map of the United States: Unlocking the Nation’s Wealth
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Natural Resource Map of the United States: Unlocking the Nation’s Wealth. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Natural Resource Map of the United States: Unlocking the Nation’s Wealth
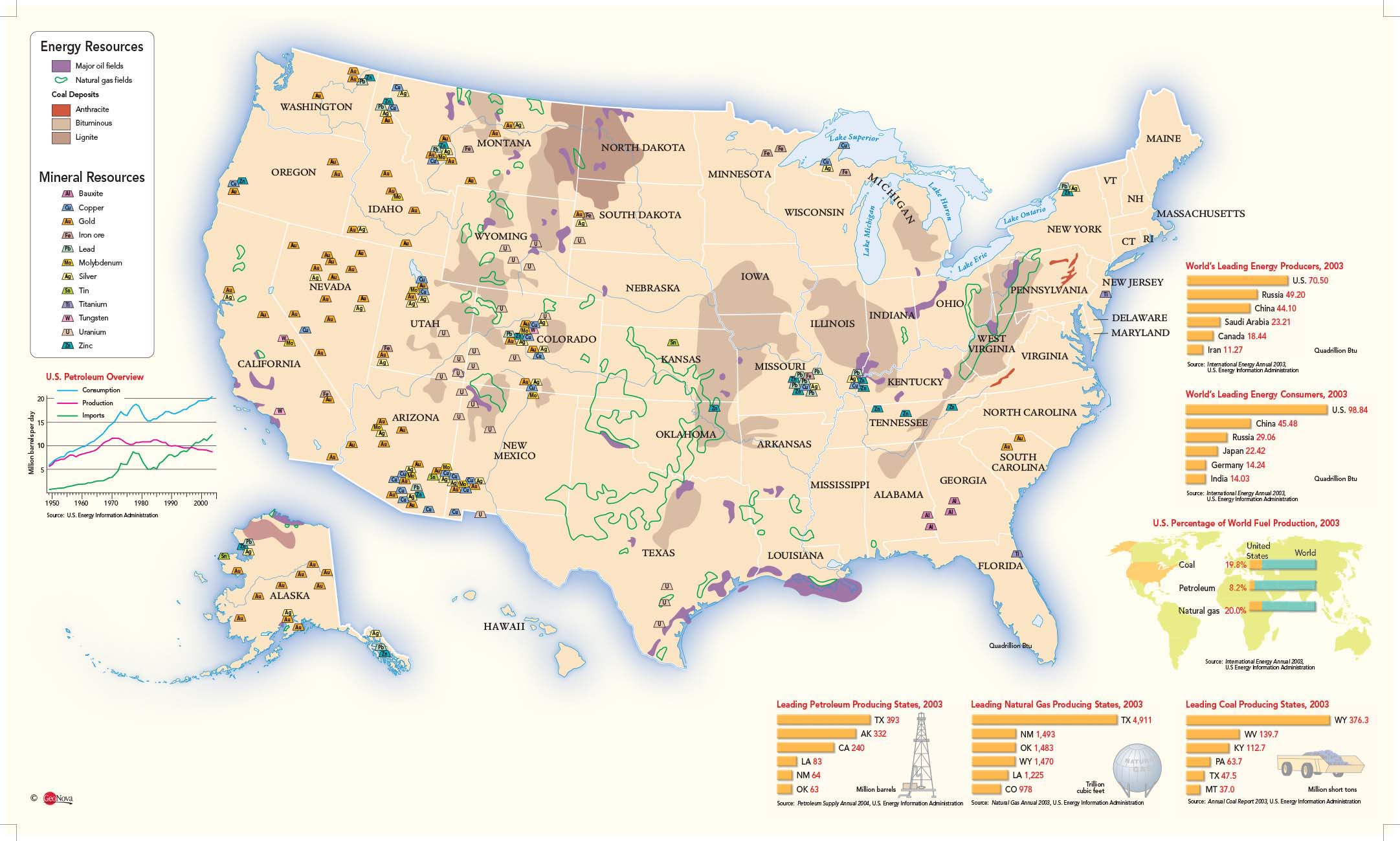
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, possesses a rich tapestry of natural resources that have played a pivotal role in its economic prosperity and global influence. Understanding the distribution and abundance of these resources is crucial for informed decision-making, sustainable development, and strategic planning. This article delves into the intricate landscape of the United States’ natural resources, exploring their geographical distribution, significance, and the challenges and opportunities they present.
I. A Mosaic of Natural Resources: Uncovering the Geographic Distribution
The United States is blessed with a diverse range of natural resources, each occupying specific regions and contributing to the nation’s economic and environmental fabric.
A. Energy Resources: Fueling the Nation’s Growth
- Fossil Fuels: The United States is a leading producer of fossil fuels, with significant deposits of coal, oil, and natural gas. Coal reserves are concentrated in the Appalachian region, the Midwest, and the western states. Oil and natural gas production are primarily located in Texas, North Dakota, and the Gulf of Mexico.
- Renewable Energy: The United States is increasingly embracing renewable energy sources, with significant potential for solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower. The Southwest boasts abundant solar energy potential, while the Great Plains and the Midwest are prime locations for wind energy. Geothermal energy is concentrated in the West, and hydropower resources are abundant in the Pacific Northwest and the Appalachian Mountains.
B. Mineral Resources: Building Blocks of Industry
- Metallic Minerals: The United States is a major producer of metallic minerals, including iron ore, copper, gold, and aluminum. Iron ore deposits are concentrated in the Great Lakes region and the Appalachian Mountains, while copper is mined in Arizona, Utah, and Montana. Gold is found in Nevada, Alaska, and California, and aluminum production is concentrated in the Southeast.
- Non-Metallic Minerals: The United States also possesses abundant non-metallic minerals, such as limestone, granite, and phosphate rock. Limestone is used in construction and agriculture, granite is a key building material, and phosphate rock is essential for fertilizer production.
C. Forest Resources: A Vital Ecosystem and Economic Engine
- Timber: The United States is home to vast forests that provide timber, pulpwood, and other wood products. The Pacific Northwest, the Southeast, and the Appalachian Mountains are major timber-producing regions.
- Wildlife Habitat: Forests provide essential habitat for a wide array of wildlife, including birds, mammals, and insects. They also play a vital role in regulating water cycles, mitigating climate change, and protecting soil quality.
D. Water Resources: The Lifeblood of the Nation
- Surface Water: The United States has an extensive network of rivers, lakes, and reservoirs that provide water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation. The Mississippi River, the largest river system in North America, is a major source of water for the Midwest.
- Groundwater: Groundwater is a vital resource, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. The Ogallala Aquifer, located in the Great Plains, is the largest aquifer in the United States and supplies water for agriculture and industry.
E. Agricultural Resources: Feeding the Nation and the World
- Croplands: The United States is a leading agricultural producer, with vast croplands dedicated to growing grains, fruits, vegetables, and livestock. The Midwest, the Great Plains, and the Southeast are major agricultural regions.
- Pasturelands: Pasturelands provide grazing for livestock, supporting the nation’s meat, dairy, and wool industries. The Great Plains, the Southwest, and the Southeast are major pastureland regions.
II. The Importance of the Natural Resource Map: A Framework for Sustainability and Economic Growth
The natural resource map of the United States serves as a vital tool for understanding the nation’s resource endowment and its potential for sustainable development.
A. Strategic Planning and Resource Management:
- Resource Allocation: The map helps policymakers and resource managers allocate resources effectively, ensuring that they are utilized sustainably and efficiently.
- Infrastructure Development: The map informs infrastructure development decisions, such as the construction of pipelines, power plants, and transportation networks.
- Environmental Protection: The map aids in identifying areas of environmental sensitivity and developing strategies for resource conservation and pollution mitigation.
B. Economic Development and Job Creation:
- Resource Extraction and Processing: The map guides investment decisions in resource extraction and processing industries, creating jobs and contributing to economic growth.
- Manufacturing and Industry: The map informs the location of manufacturing facilities and industrial parks, leveraging the availability of resources and transportation infrastructure.
- Tourism and Recreation: The map helps identify areas with natural beauty and recreational potential, attracting tourists and supporting tourism-related businesses.
C. National Security and Resilience:
- Energy Independence: The map aids in developing strategies for energy independence, reducing reliance on foreign sources of energy.
- Disaster Preparedness: The map helps identify areas vulnerable to natural disasters and develop preparedness plans to mitigate their impacts.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The map informs climate change adaptation strategies, such as water conservation, renewable energy development, and land-use planning.
III. Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Complexities of Resource Management
The natural resource map of the United States presents both challenges and opportunities for the nation’s future.
A. Environmental Sustainability:
- Resource Depletion: The extraction and use of natural resources can lead to depletion, requiring careful management to ensure their long-term availability.
- Pollution and Degradation: Resource extraction and processing activities can generate pollution and degrade ecosystems, necessitating environmental regulations and mitigation strategies.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, affecting water availability, and increasing the frequency and intensity of natural disasters, requiring adaptation measures.
B. Economic Development and Social Equity:
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: The development of natural resources can create jobs and contribute to economic growth, but it must be done in a way that benefits all communities.
- Environmental Justice: The distribution of environmental burdens and benefits must be equitable, ensuring that marginalized communities are not disproportionately affected by resource extraction or pollution.
C. Technological Innovation and Policy Reform:
- Resource Efficiency: Technological innovations are needed to improve resource efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impacts.
- Policy Reform: Policy reforms are necessary to incentivize sustainable practices, promote innovation, and ensure responsible resource management.
IV. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Natural Resource Map of the United States:
1. How is the Natural Resource Map of the United States Created?
The natural resource map is created through a combination of geological surveys, remote sensing, and data analysis. Geological surveys involve field studies, rock and soil sampling, and geophysical surveys to identify and characterize resource deposits. Remote sensing techniques, such as satellite imagery and aerial photography, provide a broad overview of the landscape and resource distribution. Data analysis involves processing and interpreting the collected data to create maps and reports that illustrate the location, abundance, and quality of natural resources.
2. How Often is the Natural Resource Map Updated?
The natural resource map is constantly being updated as new data becomes available. Geological surveys and remote sensing technologies are continuously improving, providing more accurate and detailed information. The frequency of updates depends on the specific resource and the purpose of the map. For example, maps of critical minerals might be updated more frequently than maps of timber resources.
3. How Can I Access the Natural Resource Map of the United States?
The natural resource map is available through various government agencies and online resources. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) is a primary source of geological data, including maps of mineral resources, water resources, and land cover. The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) provides maps of public lands, including information on mineral resources, timber resources, and grazing lands. Other agencies, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), also contribute to the natural resource map.
4. What are the Benefits of Using the Natural Resource Map?
The natural resource map provides a comprehensive and detailed overview of the nation’s resource endowment, enabling informed decision-making in various sectors. It facilitates strategic planning for resource management, economic development, environmental protection, and national security. By understanding the distribution and abundance of natural resources, policymakers, resource managers, and businesses can make informed decisions that promote sustainability, economic growth, and environmental protection.
5. What are the Challenges Associated with Using the Natural Resource Map?
The natural resource map is a valuable tool, but it is not without its limitations. Data collection and analysis can be challenging, especially in remote or inaccessible areas. The map may not always reflect the most up-to-date information, as resource availability and distribution can change over time. The map also does not always capture the complex interactions between different resources and the potential for environmental impacts.
V. Tips for Using the Natural Resource Map Effectively:
- Understand the Scale and Purpose of the Map: Different maps are designed for different purposes and at different scales. Ensure that you are using the appropriate map for your needs.
- Consider the Data Sources and Accuracy: The accuracy of the map depends on the data sources and the methods used to collect and analyze the data. Be aware of the limitations of the data and the potential for errors.
- Interpret the Map in Context: The natural resource map should be interpreted in the context of other relevant factors, such as environmental regulations, market conditions, and social impacts.
- Use the Map as a Starting Point: The natural resource map is a valuable tool, but it is not a substitute for careful research and analysis. Use the map to identify areas of interest and to inform further investigation.
VI. Conclusion:
The natural resource map of the United States is a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s wealth and its potential for sustainable development. It provides a framework for strategic planning, resource management, economic growth, and environmental protection. However, it is essential to recognize the challenges associated with resource management, such as environmental sustainability, economic development, and social equity. By embracing technological innovation, promoting policy reform, and fostering collaborative partnerships, the United States can harness its natural resources to create a more prosperous and sustainable future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Natural Resource Map of the United States: Unlocking the Nation’s Wealth. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!